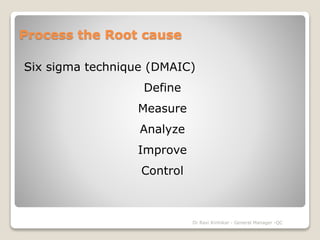
This document discusses guidelines for handling Out of Specification (OOS) test results in the pharmaceutical industry. It provides an overview of the history of OOS guidelines, including FDA audits in the 1980s-90s that identified issues like "testing until pass", which led the FDA to publish formal OOS guidelines in 2006. The document outlines the OOS investigation process, which should first thoroughly check for laboratory errors and assign a cause, then may proceed to extended investigations including retesting or plant investigations if no error is found. Tools like 5M analysis and the five whys technique can be used to identify and analyze the root cause.