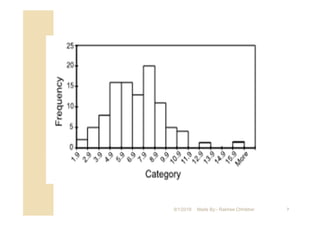
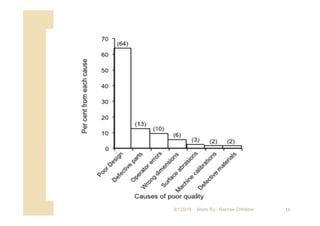
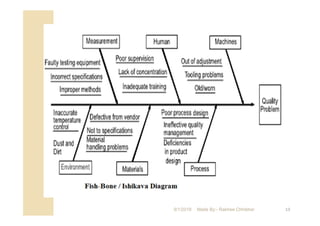
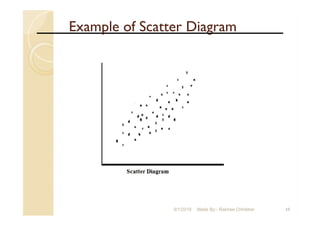
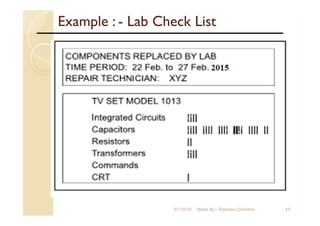
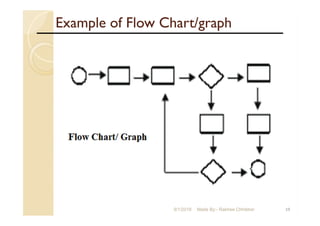
The document focuses on statistical quality control and its importance in quality improvement by reducing process variability. It highlights key tools such as histograms, Pareto charts, cause and effect diagrams, and control charts that assist in analyzing and improving quality. Additionally, it explains how these tools can help identify and prioritize problems to enhance operational effectiveness.