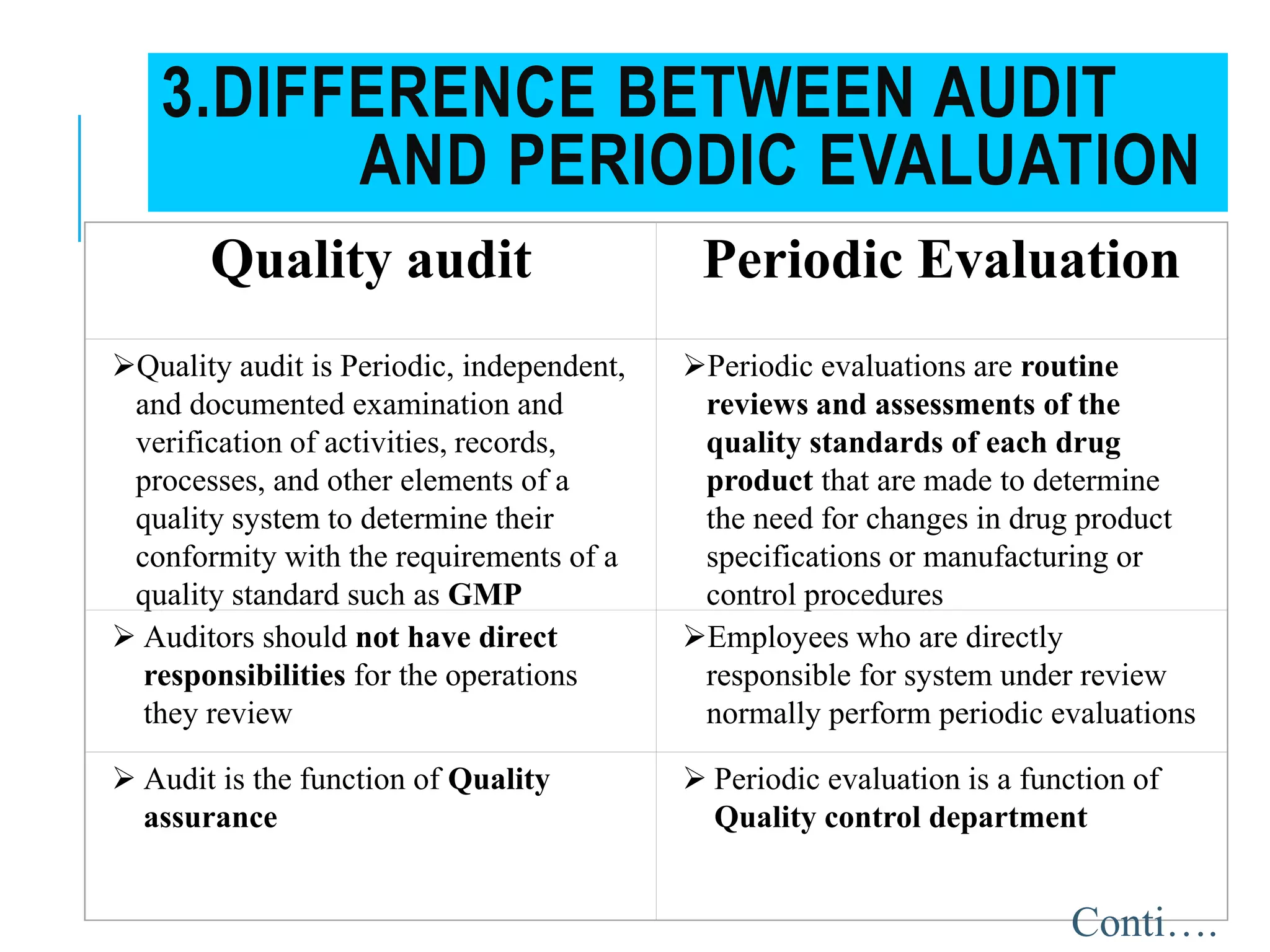
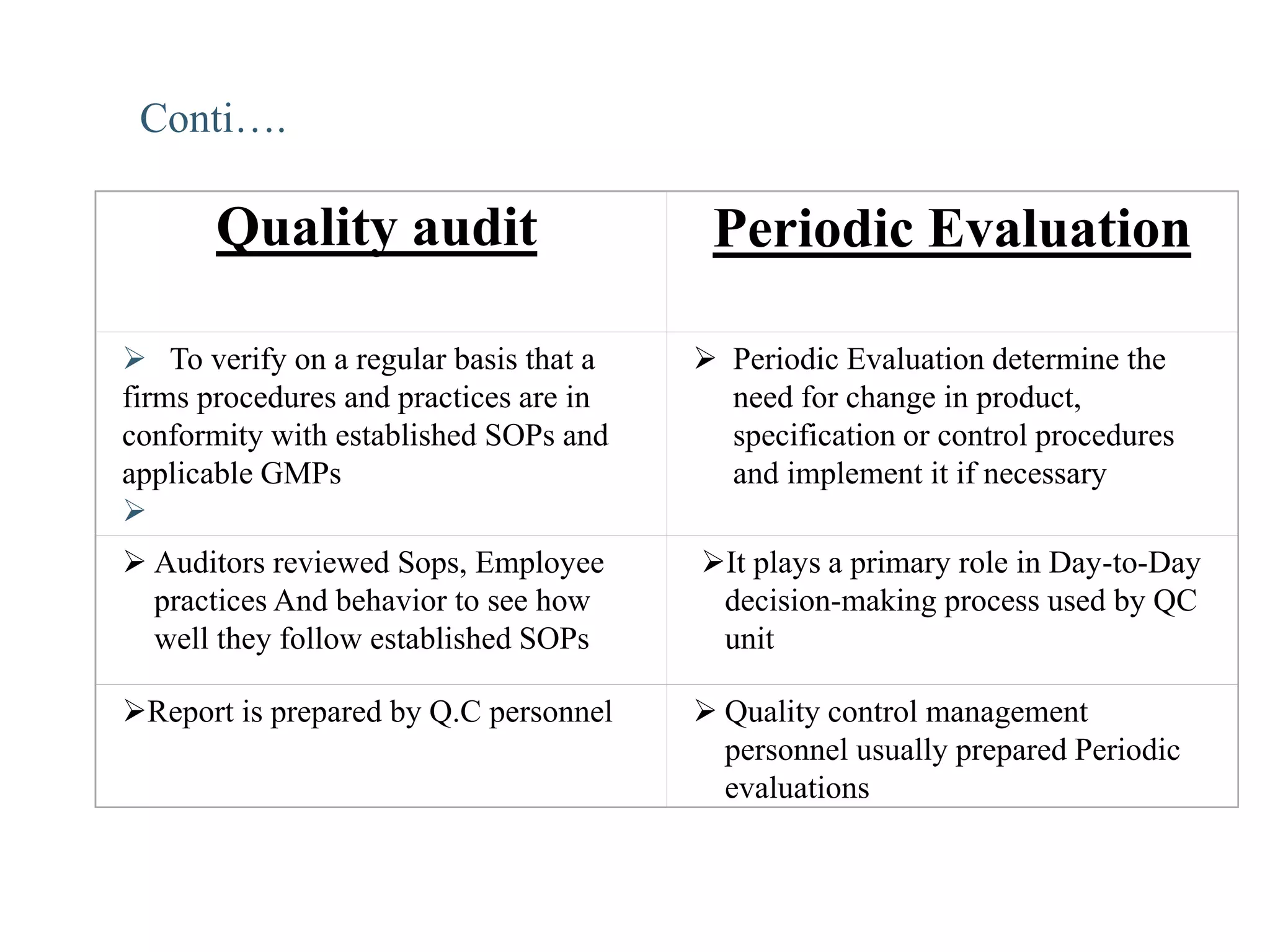
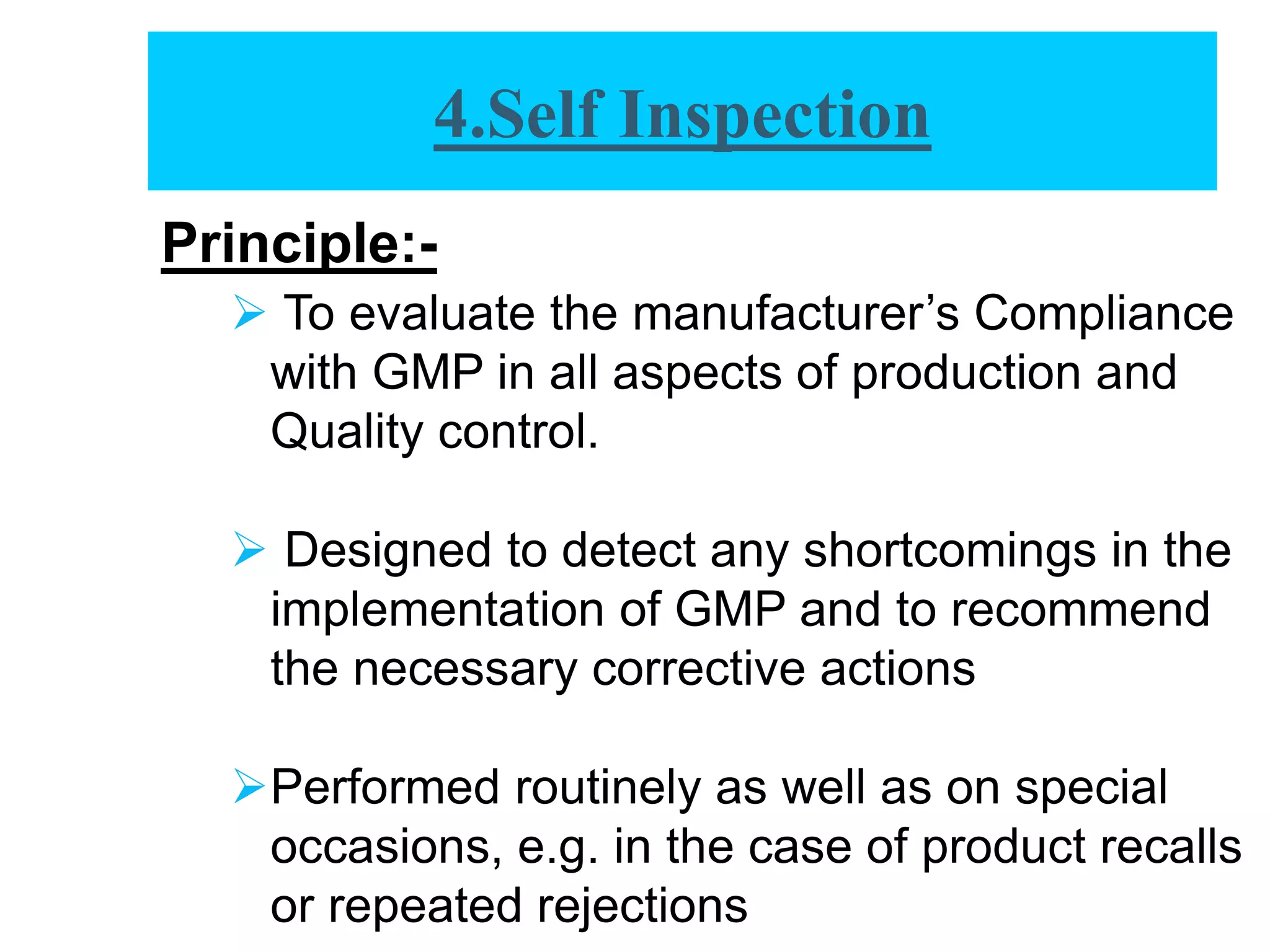
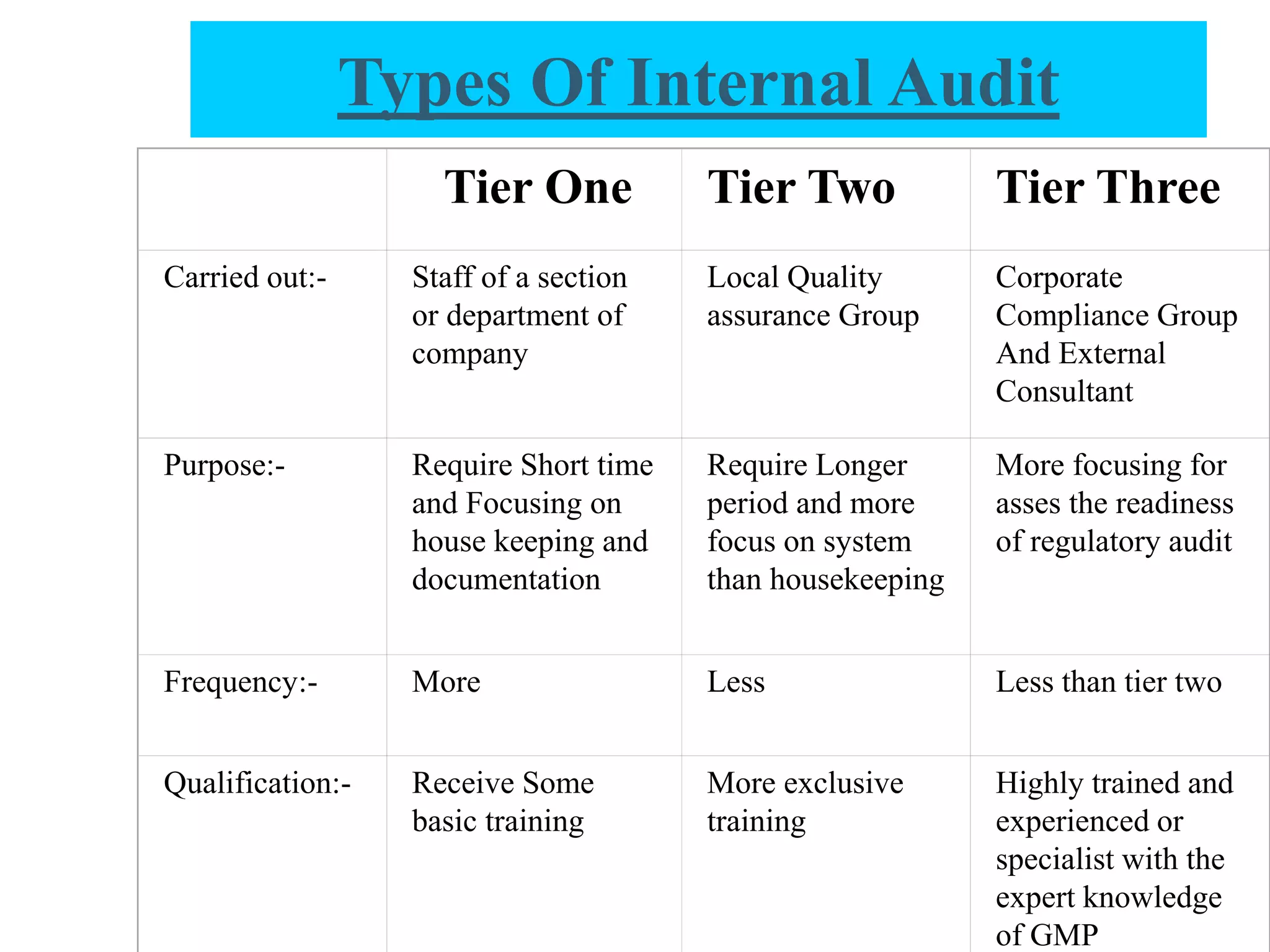
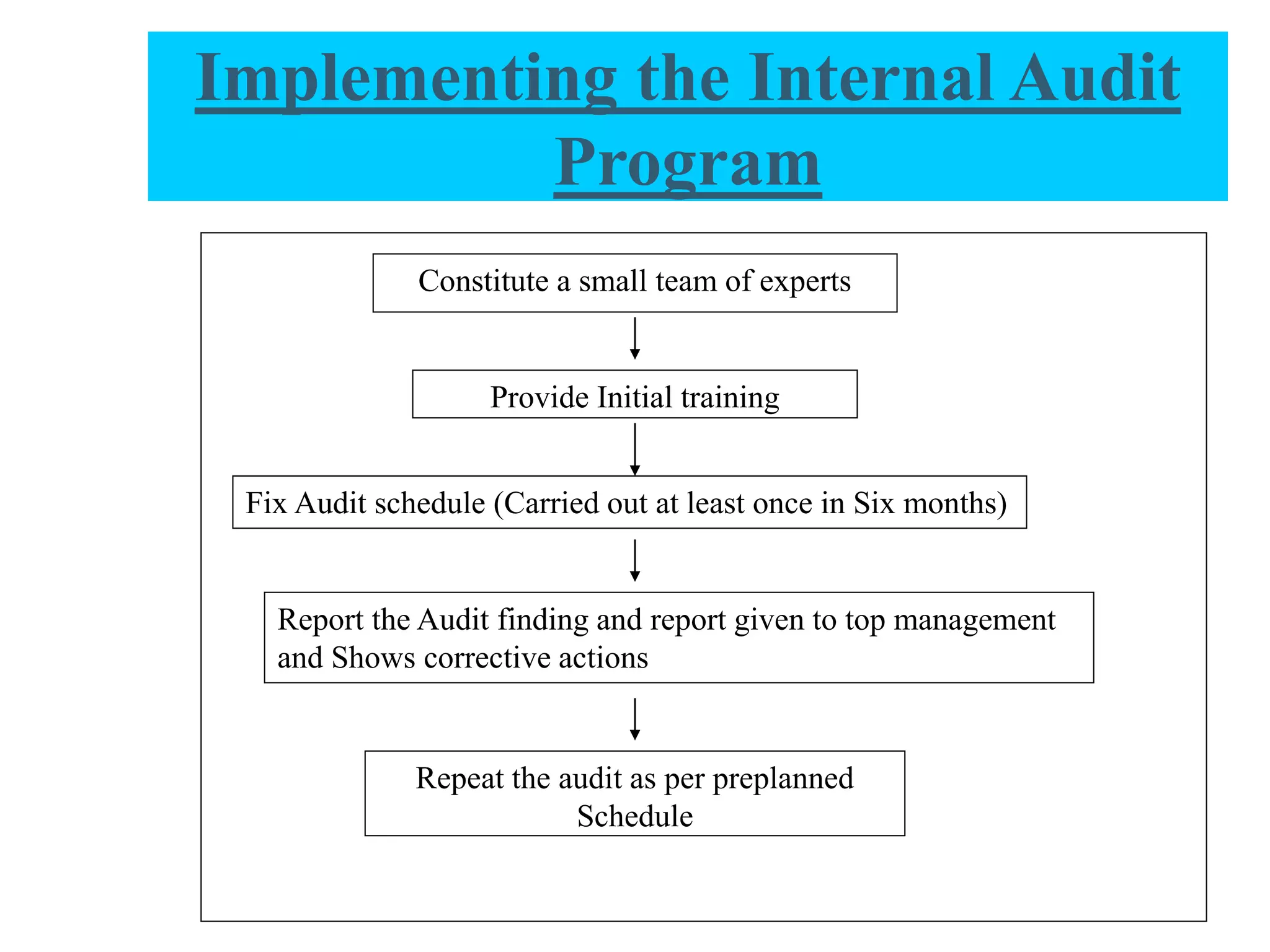
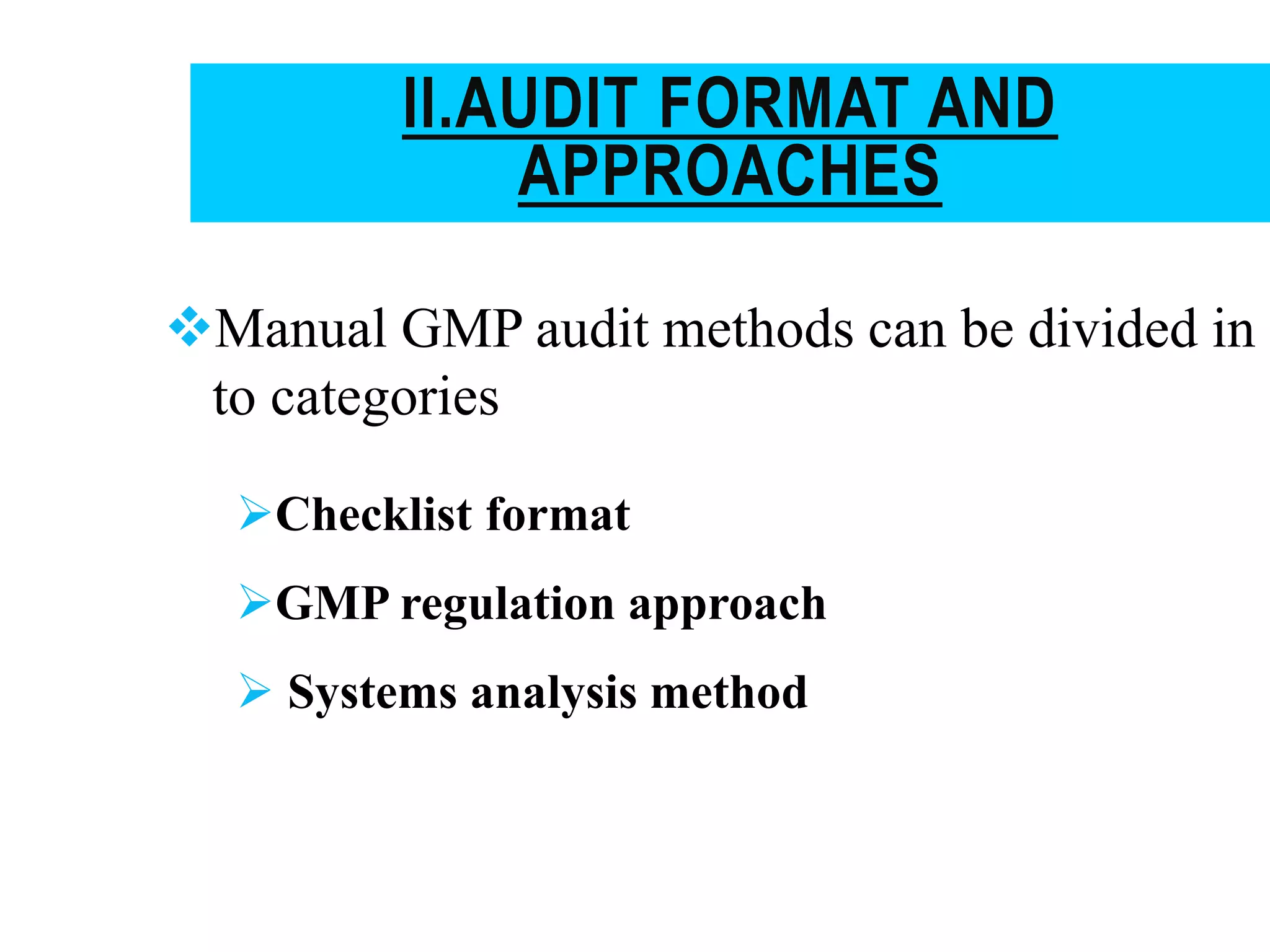
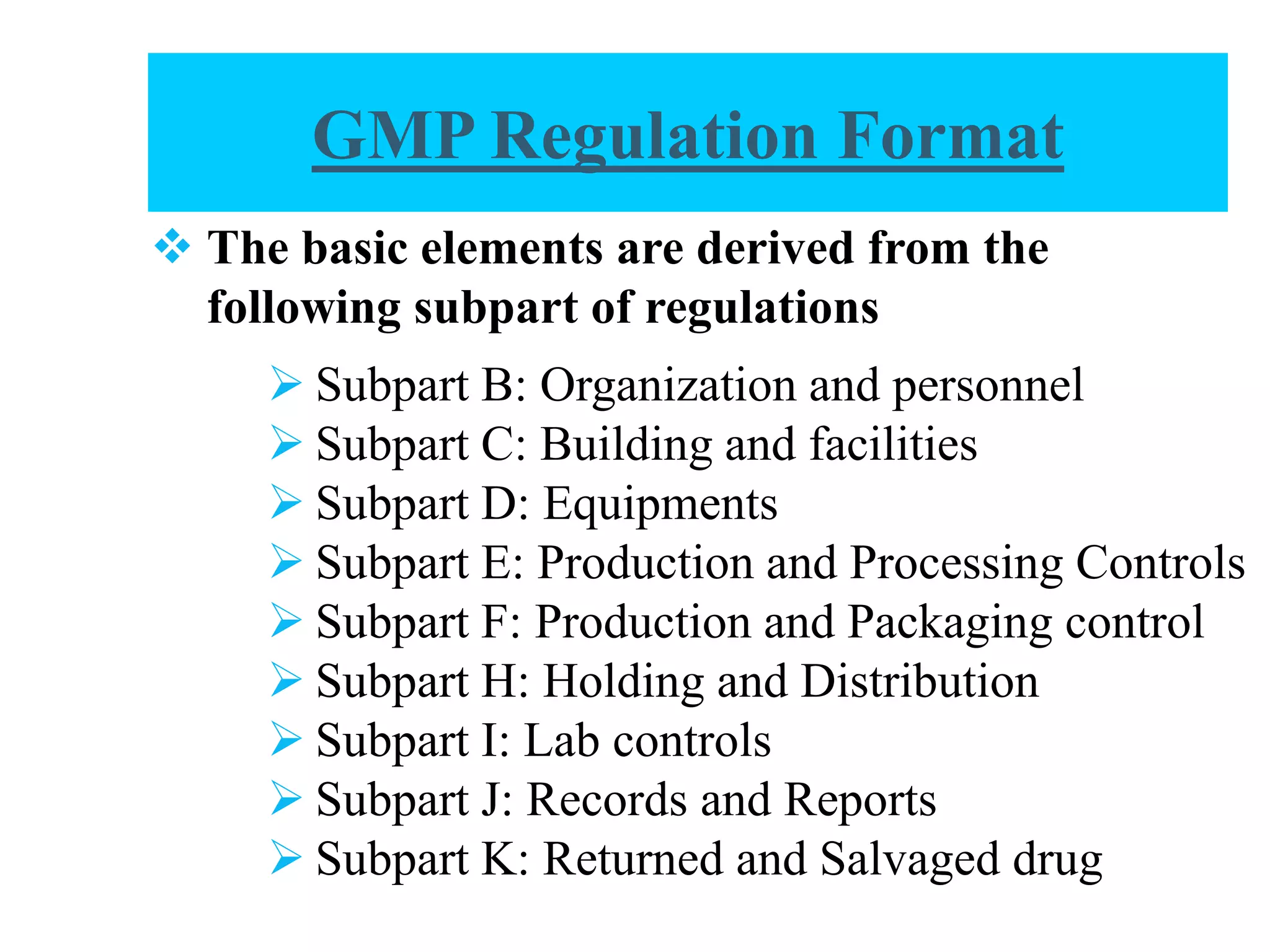
The document provides a comprehensive overview of quality audits, defining them as systematic examinations to ensure compliance with quality standards like GMP. It outlines the objectives, differences from periodic evaluations, types of audits (internal, external, and regulatory), and their purposes in verifying compliance and improving processes. Additionally, it details the roles of different personnel in audits, the importance of auditor qualifications, and the reporting structure for audit findings.