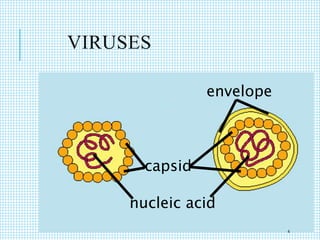
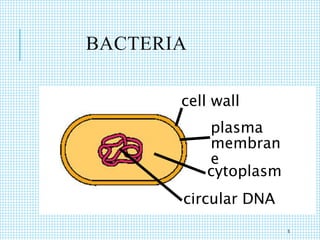
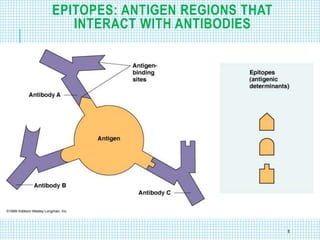
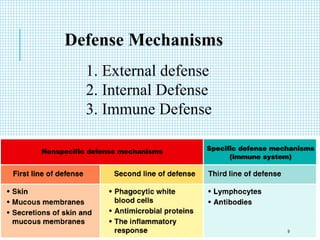
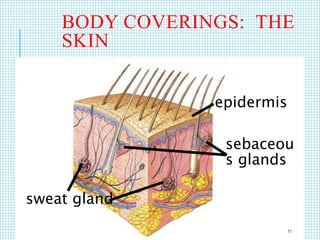
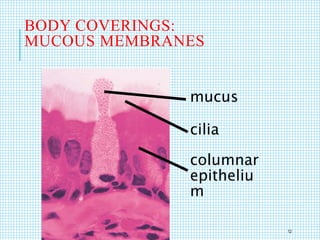
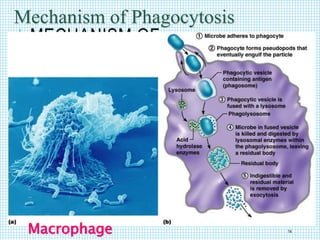
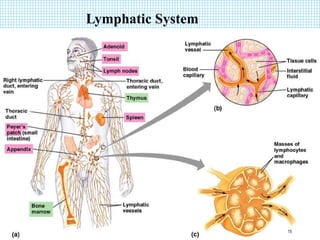
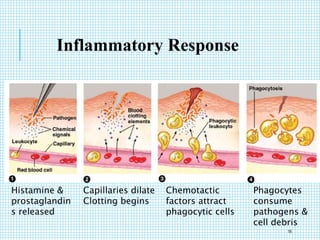
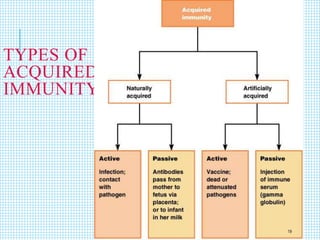
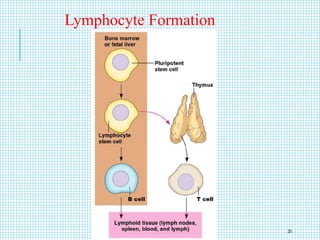
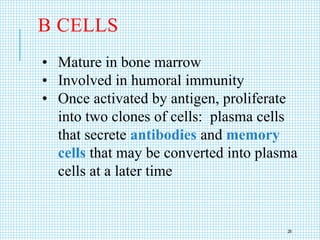
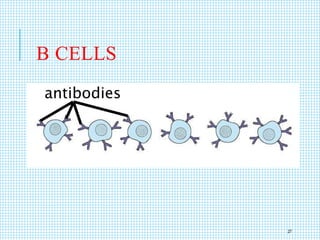
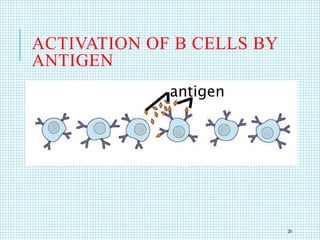
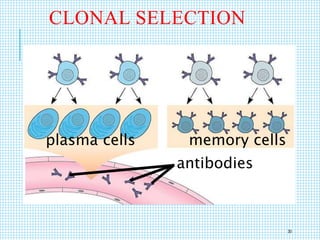
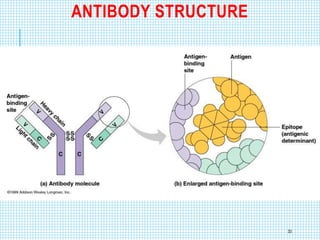
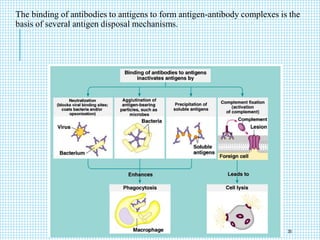
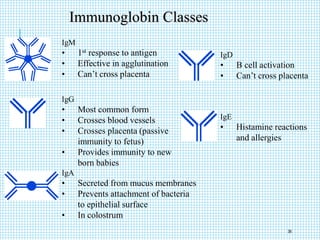
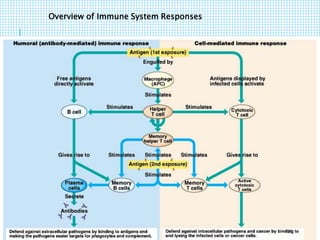
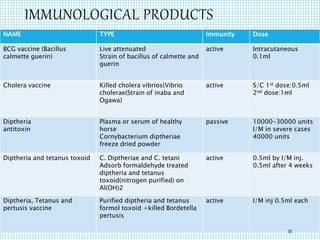
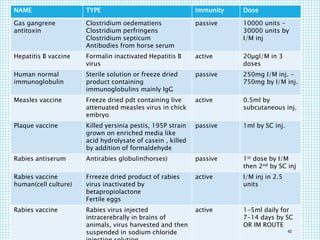
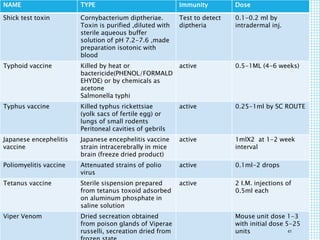
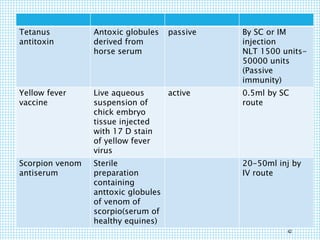
The document discusses the immune system, detailing various types of pathogenic organisms such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and parasites, along with mechanisms of disease caused by these pathogens. It outlines defense mechanisms of the body, types of immunity (active and passive), and the role of antibodies and lymphocytes in immune responses. Additionally, it lists immunological products and their associated details, including vaccines and antitoxins for various diseases.