1) Internal audits are required by cGMP and QMS standards to evaluate compliance and identify improvement opportunities. They help assure compliance, detect potential problems, and increase management awareness.
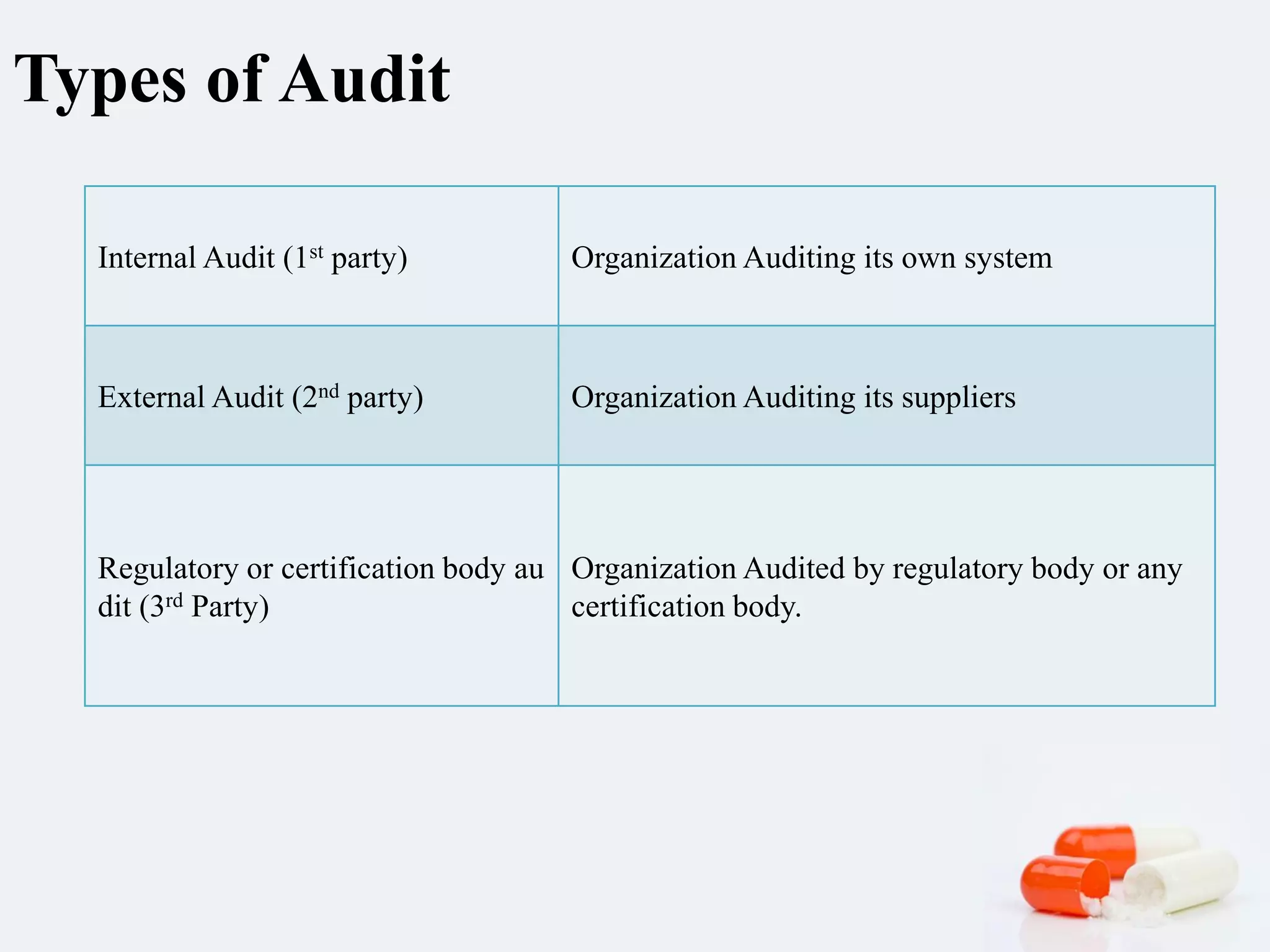
2) There are different types of audits - internal, external by suppliers, and regulatory. Audits check areas like personnel, facilities, equipment, production, documentation, and quality systems.
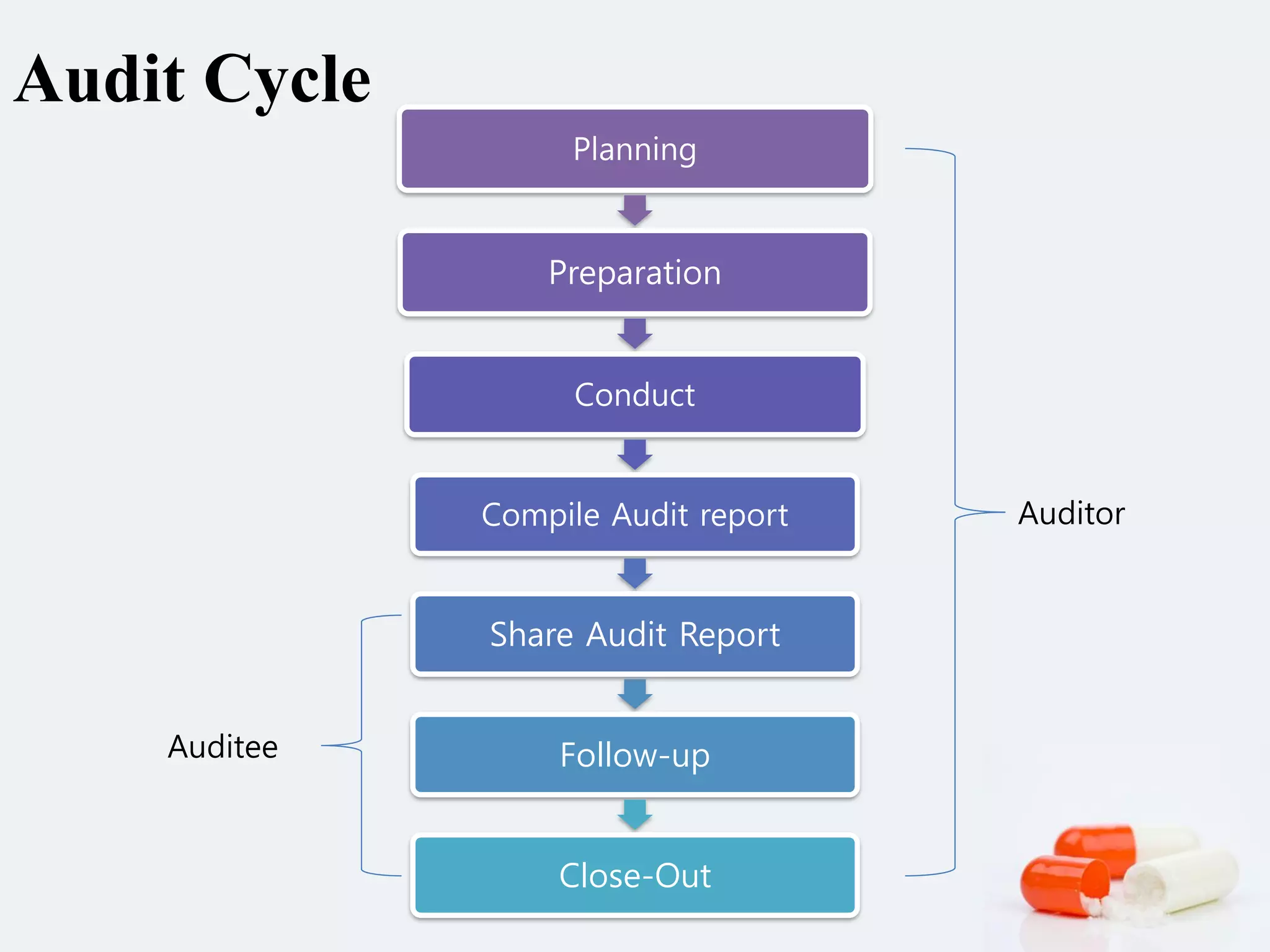
3) Principles of effective auditing include ethical conduct, fair presentation, independence, evidence-based approach. Audit planning includes preparing the audit plan, selecting the team, and arranging logistics. Frequency depends on the compliance risk of the area.