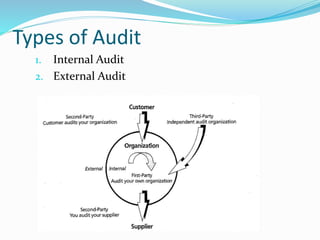
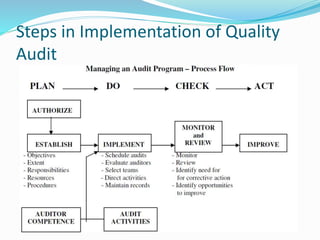
A quality audit is a systematic examination to ensure that quality activities meet planned arrangements and objectives. Conducting quality audits checks product specifications, equipment functionality, adherence to procedures, and compliance with regulations. The process includes various types of audits such as internal, external, process, product, and equipment audits to identify deficiencies and opportunities for improvement.