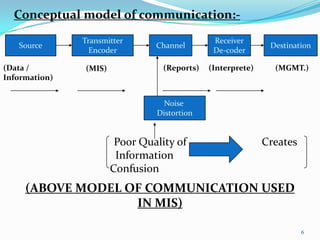
1) Data is raw facts that become useful information when processed. Information reduces uncertainty and aids decision making.
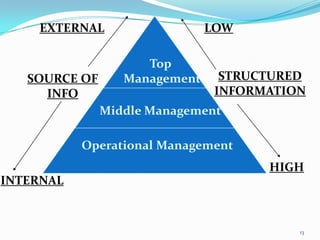
2) There are various types of data and information like internal/external, strategic/tactical/operational. Quality information is timely, accurate, relevant, and impartial with no bias.
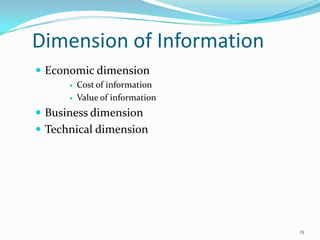
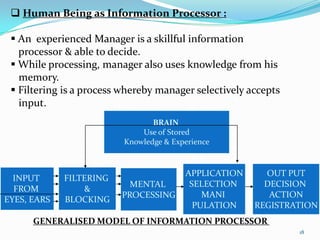
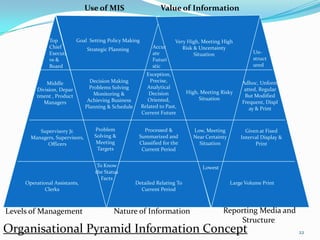
3) MIS aims to provide high quality information to managers by processing data from various sources using principles of classification, summarization, and recognizing human decision making capabilities.