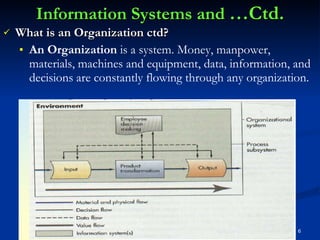
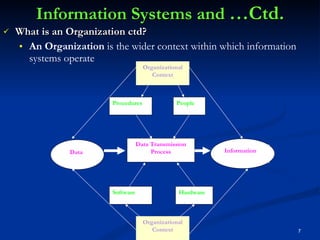
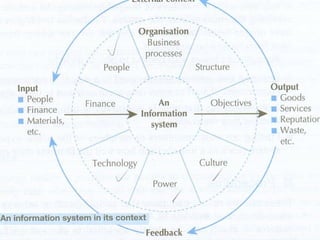
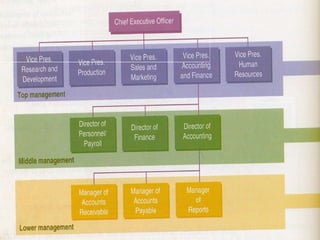
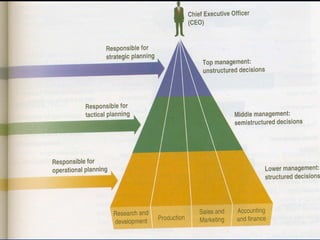
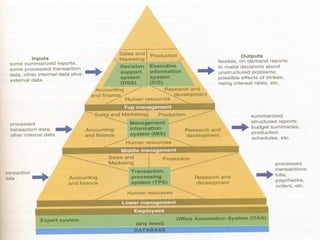
There are different types of information systems in organizations that provide information to managers at different levels to help with decision making. Transaction processing systems provide detailed transaction data to lower managers for operational decisions. Management information systems summarize and report data from multiple departments to middle managers for tactical decisions. Decision support systems use analytical models and allow top managers to simulate "what if" scenarios for strategic decision making. Expert systems and office automation systems provide problem solving assistance and reduce manual work for all employee levels.