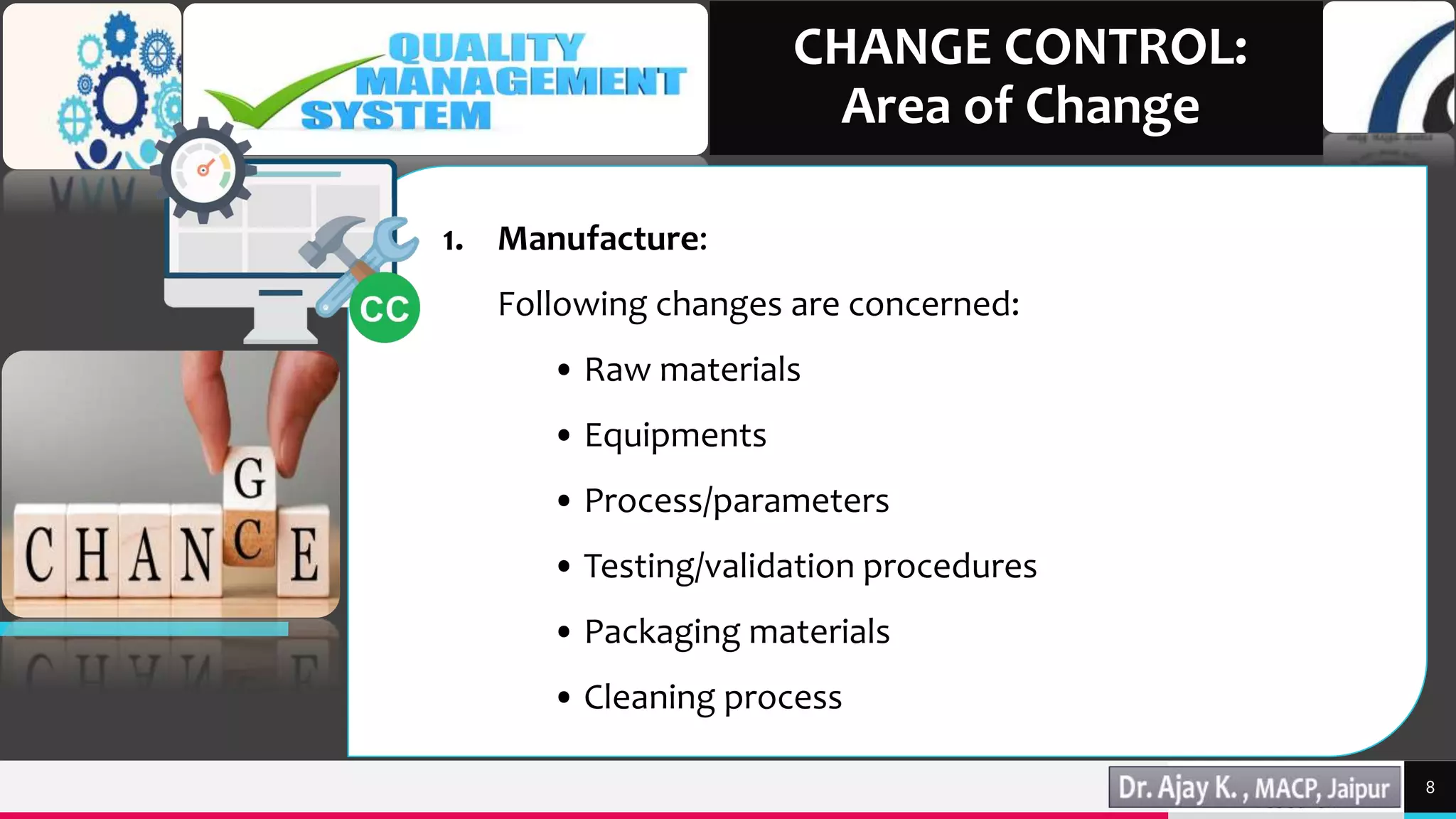
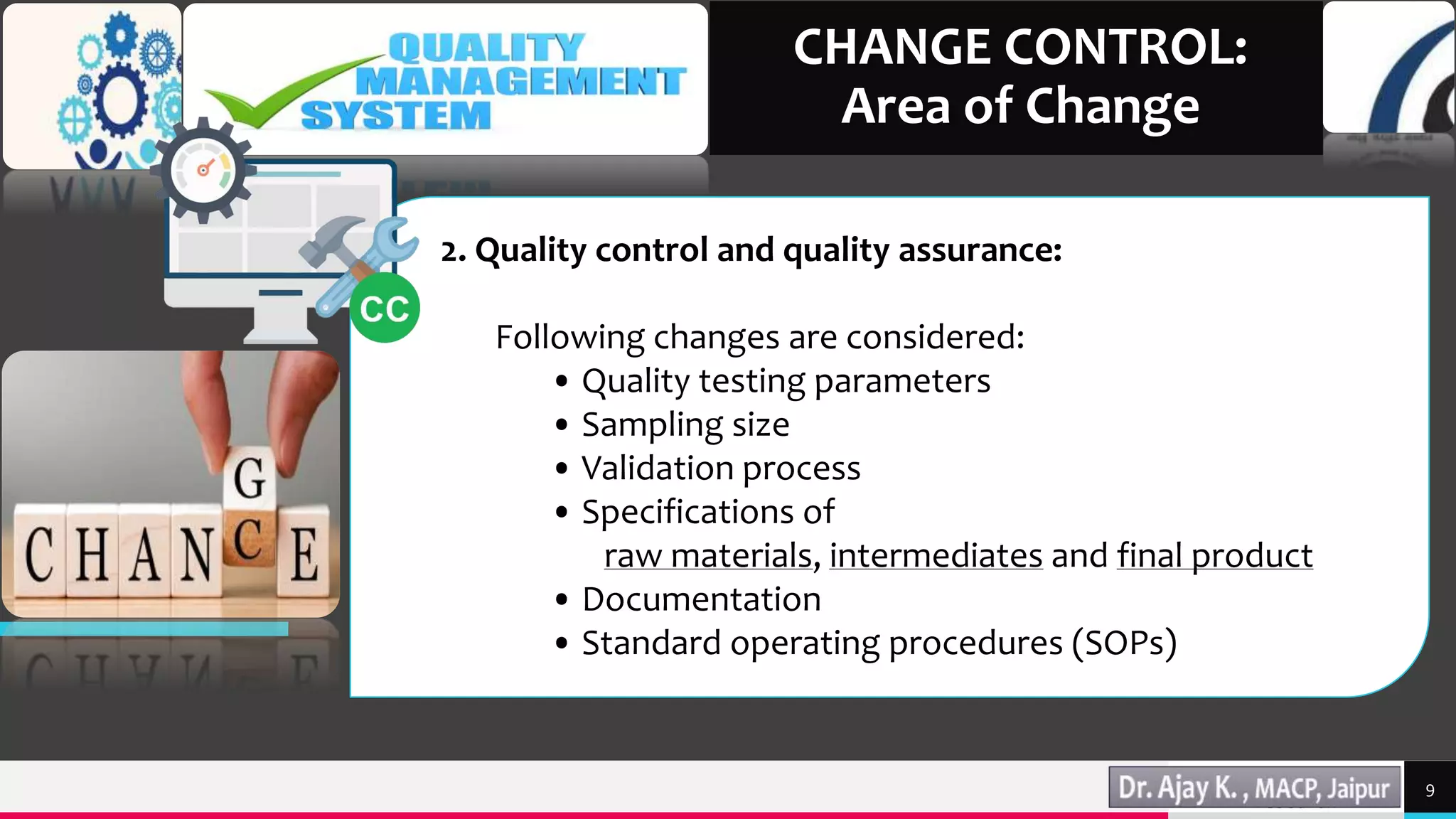
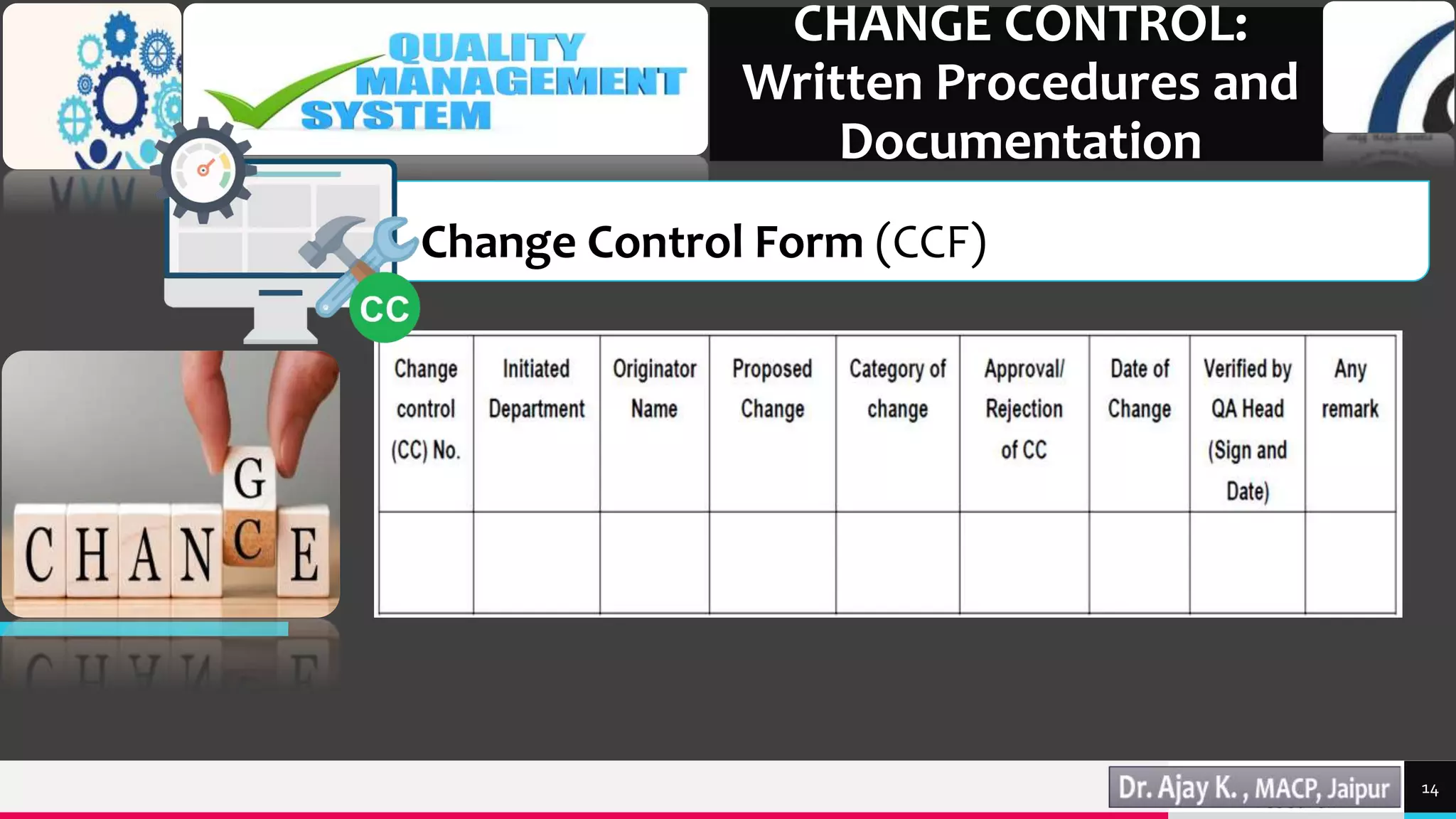
This document discusses change control in the pharmaceutical industry. It begins by defining change control as a formal system to review proposed or actual changes that could affect facilities, systems, equipment, or processes. The functions of change control are then outlined as identifying, reviewing, approving, validating, analyzing, and monitoring changes. The areas of change that would require control are described, including manufacturing, quality control, research and development, engineering, and marketing. Finally, the document states that written procedures and documentation like standard operating procedures and change control forms are necessary parts of the change control system.