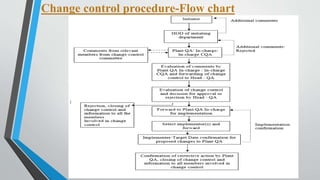
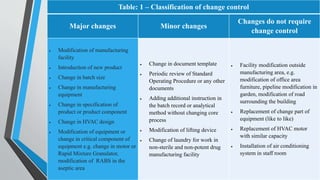
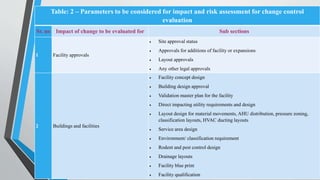
This document provides information on change control procedures for pharmaceutical companies. It defines what constitutes a change, outlines the scope of change control, and describes the change control process. This includes classifying changes as major or minor, evaluating impacts, obtaining approvals, implementing changes, and closing out change controls. Parameters for assessing impact and risk are also listed. The goal is to formally evaluate, document, approve and implement any changes that could affect quality in a validated manner.