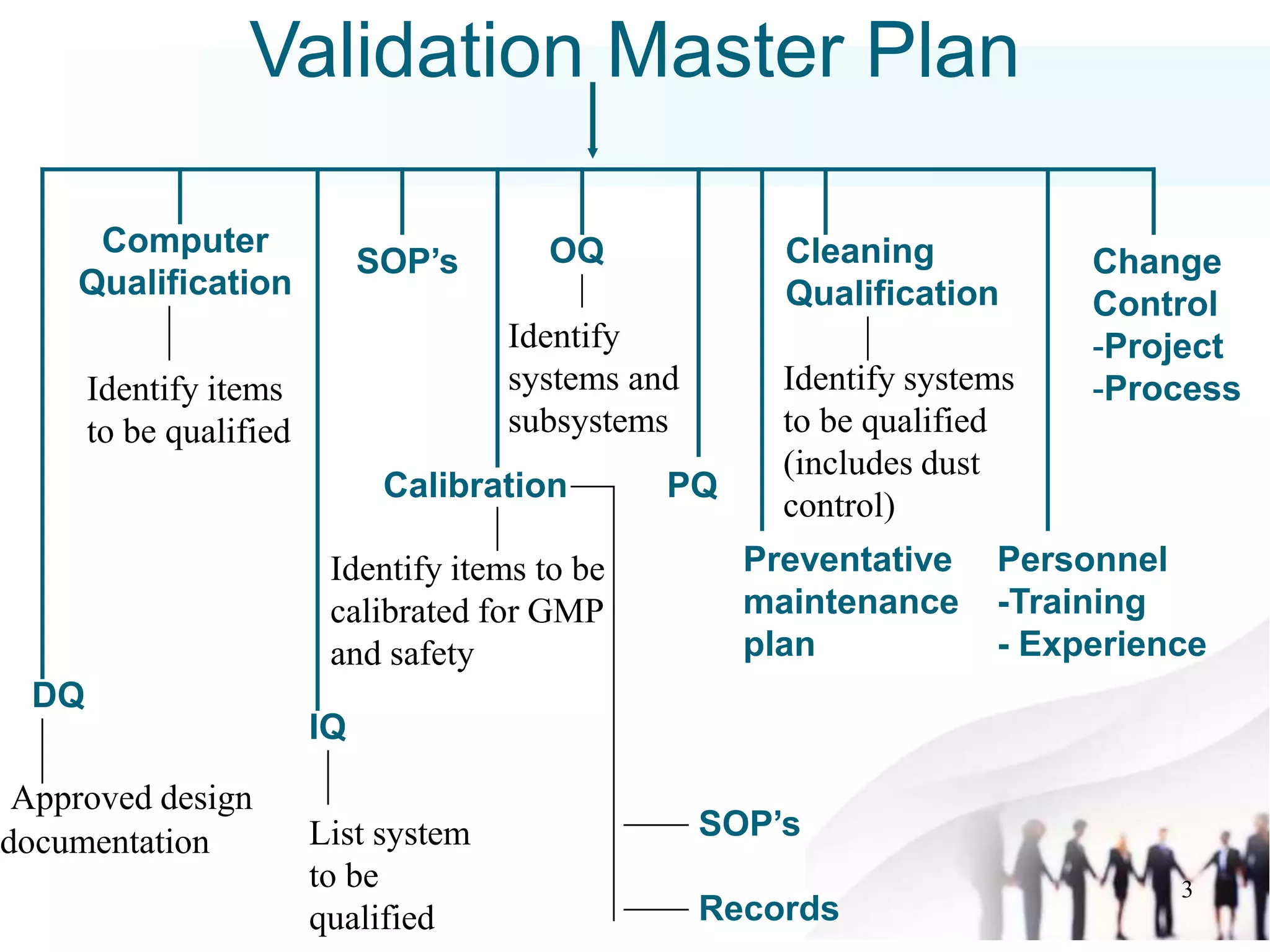
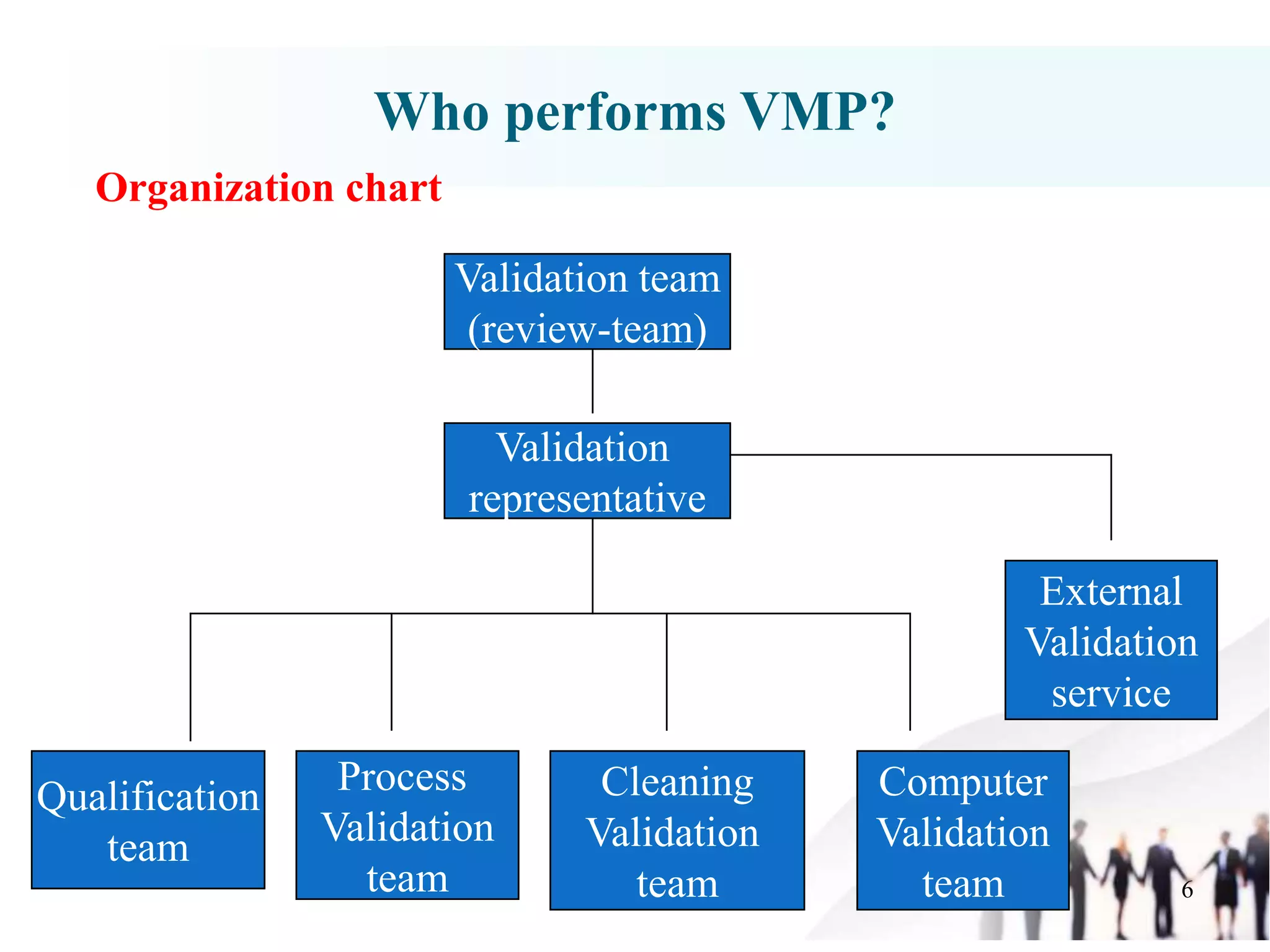
The document outlines a Validation Master Plan (VMP) which is a comprehensive guideline detailing the validation requirements for a facility in the pharmaceutical sector. It describes the contents of the VMP, including methodologies, qualifications, personnel, schedules, and change control procedures essential for ensuring product quality and compliance. While not a regulatory requirement, the VMP serves as an industry standard that aids in maintaining validation objectives and clarity throughout the process.