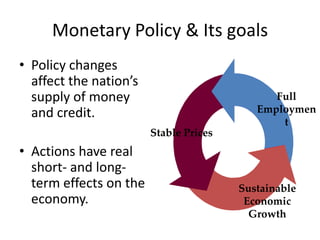
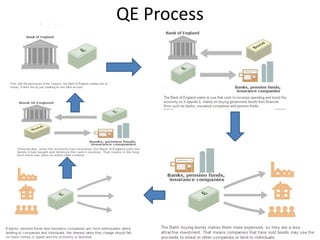
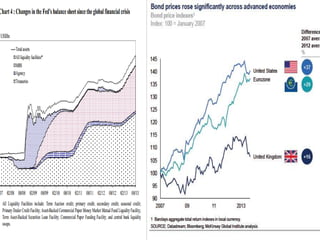
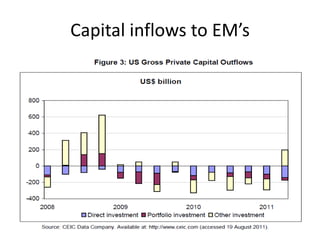
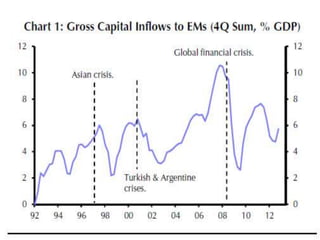
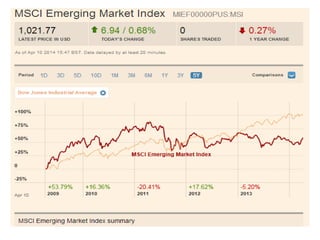
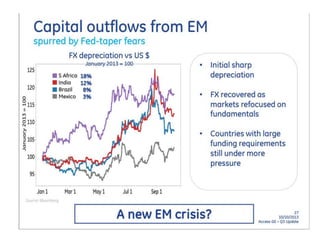
- Central banks took unprecedented actions like quantitative easing to stabilize financial markets and inject liquidity during the 2007-2008 global financial crisis.
- Quantitative easing involves central banks buying bonds and other assets to increase liquidity in the markets.
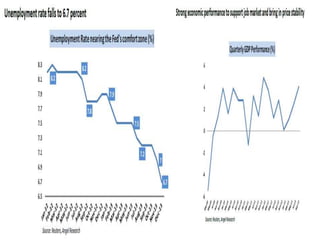
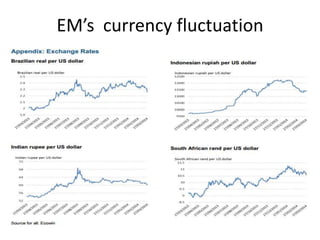
- As economies improved, the US Federal Reserve began tapering or slowly reducing its quantitative easing program in 2013 to wind down the stimulus, which impacted emerging markets through capital outflows, currency declines, and increased borrowing costs.