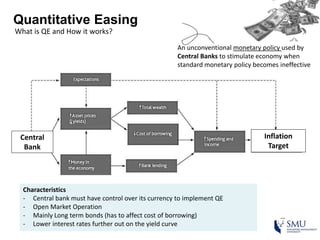
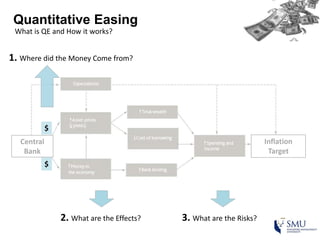
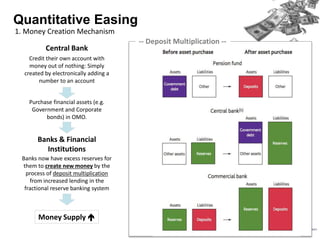
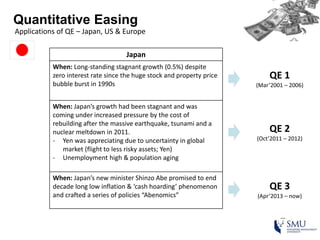
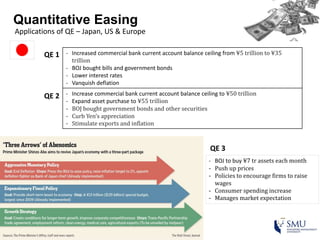
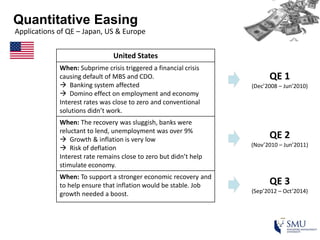
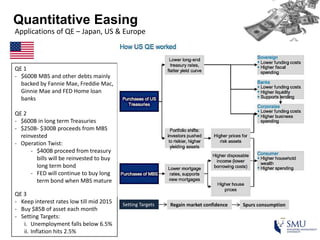
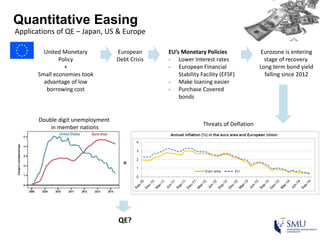
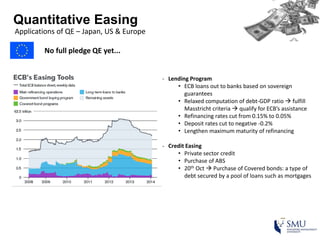
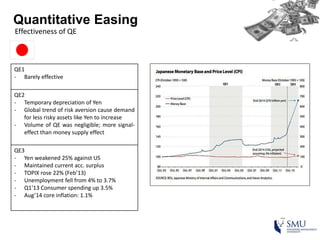
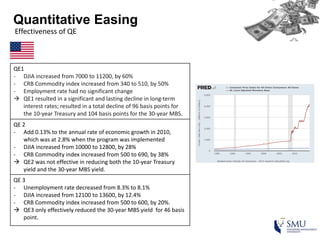
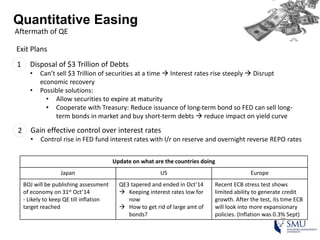
Quantitative easing (QE) is an unconventional monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate the economy. It works by having the central bank purchase financial assets to inject money into the economy. The document then discusses (1) how QE creates money, (2) the economic effects of QE including lower interest rates and higher stock prices, and (3) the risks of QE such as wealth inequality and rising future interest rates. Examples of QE programs in Japan, the US, and Europe are provided. While QE has had some positive effects, its overall effectiveness depends on various economic conditions and factors. Central banks now face challenges in exiting from QE programs as bond holdings are unwound.