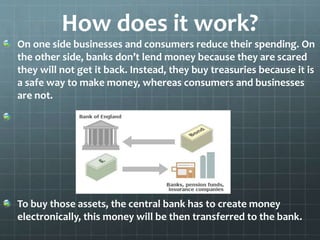
Quantitative easing (QE) is an unconventional monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate the economy through increasing the money supply when standard policies are ineffective. It works by having the central bank buy financial assets like treasury bonds from banks, increasing their prices and lowering interest rates. This aims to encourage borrowing and spending by businesses and households. The document outlines the history of QE programs in the US since 2008 and discusses whether they achieved their goals as well as the potential benefits like economic growth and risks like higher inflation.