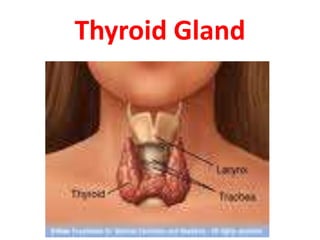
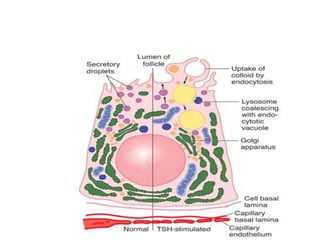
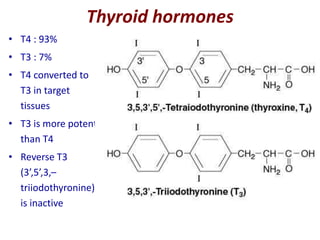
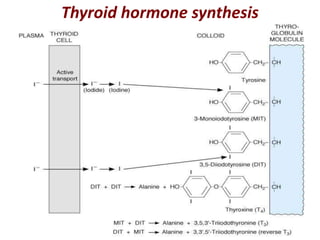
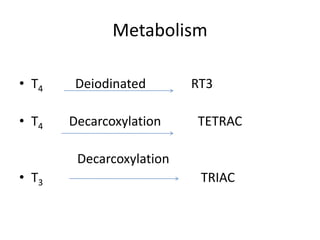
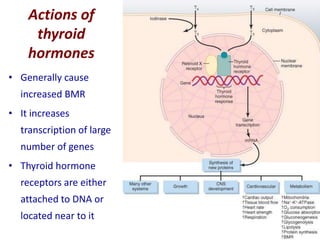
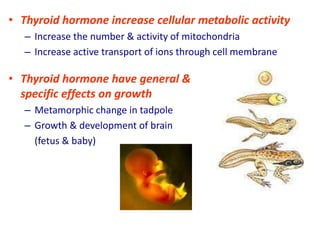
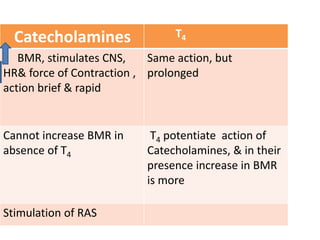
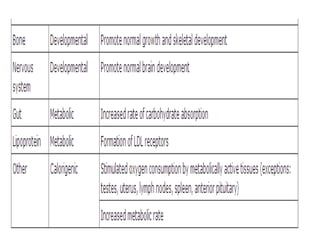
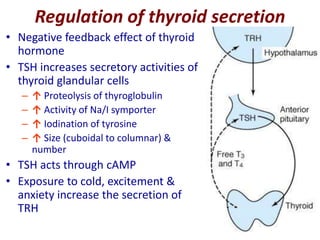
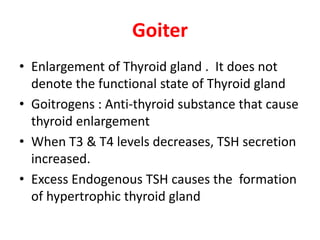
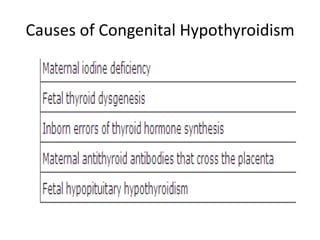
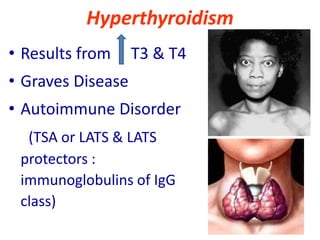
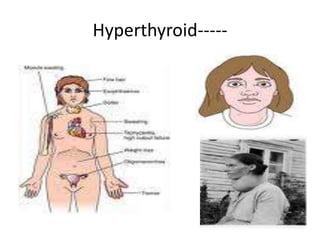
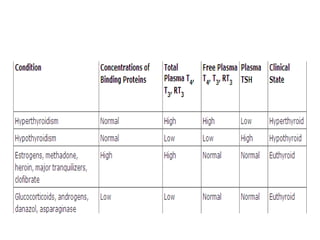
The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland located in the neck. It produces thyroid hormones such as T4 and T3 that regulate metabolism. The thyroid follicles contain colloid made of thyroglobulin, which iodine is attached to in order to produce the hormones. The hormones are then released into circulation and have widespread effects increasing the basal metabolic rate and promoting growth and development. Thyroid hormone production is regulated by TSH from the pituitary gland in a negative feedback loop. Disorders can result from too much or too little thyroid hormone production and affect many body systems.