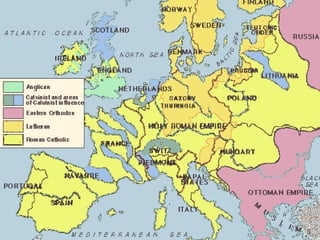
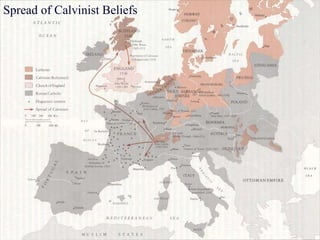
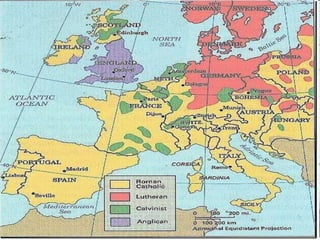
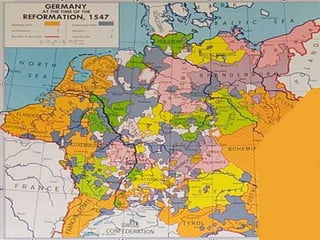
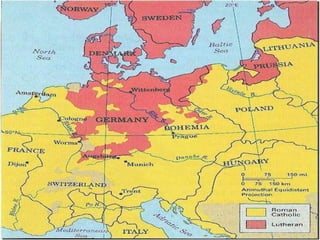
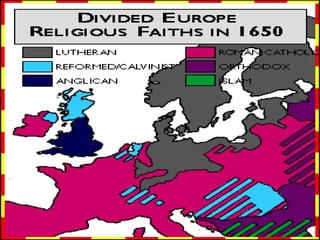
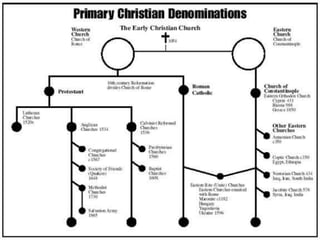
William Shakespeare was an English Renaissance writer. Some of his most famous quotes reflect on themes of wisdom, love, and greatness. The document also provides background on the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century and its effects. Martin Luther's nailing of his 95 Theses challenging Catholic Church practices in 1517 is seen as marking the start of the Protestant Reformation. The Reformation transformed Christianity and had wide-ranging impacts across Europe.