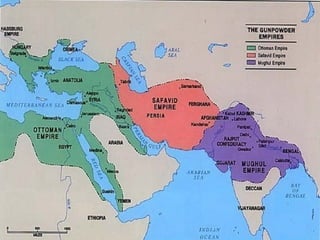
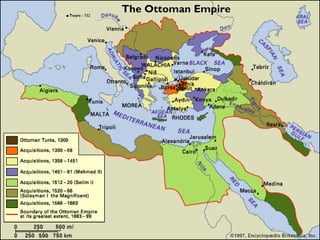
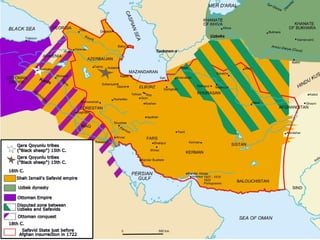
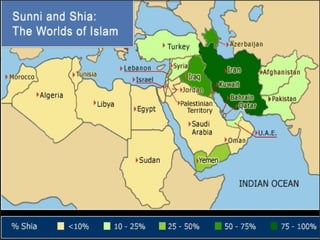
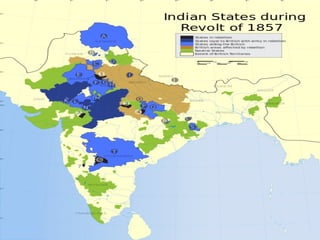
This document provides an overview of the three Islamic "Gunpowder Empires" between 1450-1750: the Ottoman Empire, Safavid Empire, and Mughal Empire. It describes the origins, expansion, characteristics, and trade of each empire. It also identifies several topics of focus for each empire, such as the Ottoman treatment of non-Muslims under the millet system, innovation in Safavid visual arts like miniature paintings, and the intensification of peasant labor and existing elites in Mughal India. The document contains maps and images related to the empires as well.