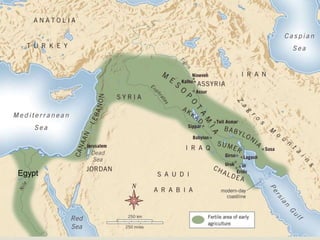
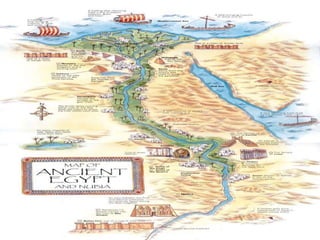
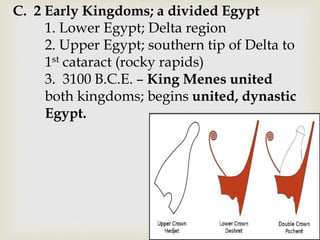
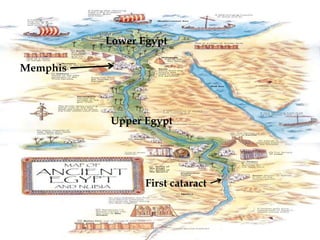
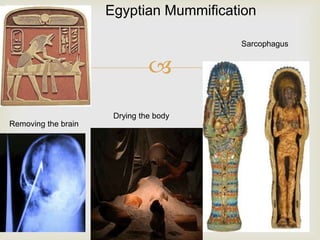
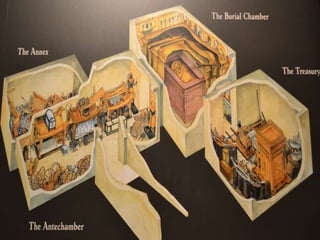
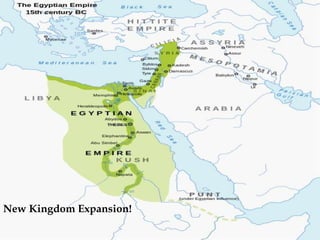
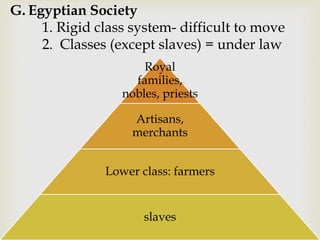
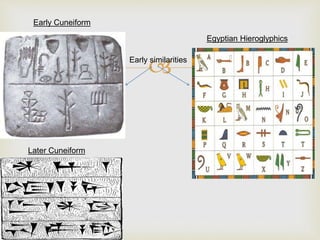
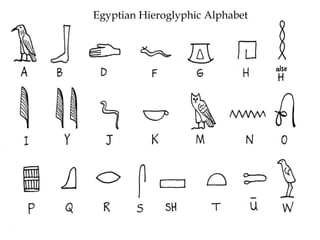
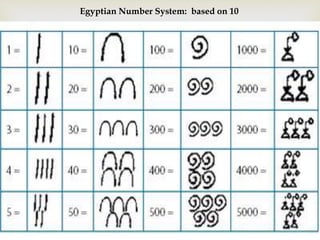
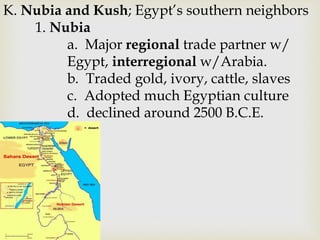
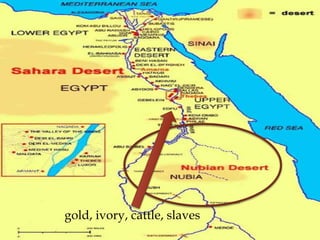
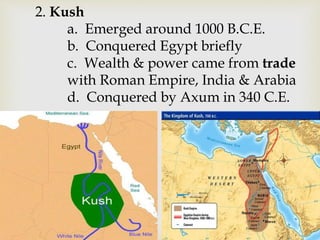
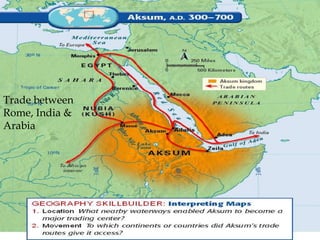
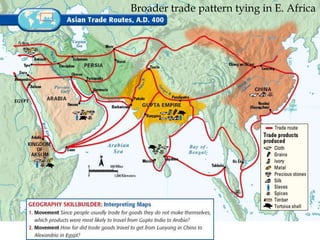
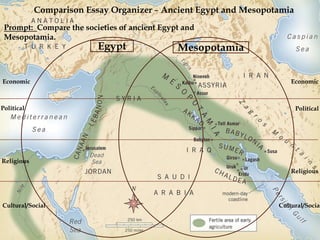
Ancient Egypt developed along the fertile banks of the Nile River from around 5000 BCE. The annual flooding of the Nile provided rich soil for agriculture and allowed Egyptians to develop irrigation canals to increase farmland. By 3000 BCE, towns and cities had emerged along the Nile, with Egypt becoming a core civilization in the Mediterranean region. The Old Kingdom period from 2660-2160 BCE saw the rise of a strong central government and construction of pyramids. The Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom periods saw further cultural and artistic advances as well as military expansion. Egyptian society was organized into a rigid class structure with some rights and roles for women. Egypt had a polytheistic religion and positive views of the afterlife