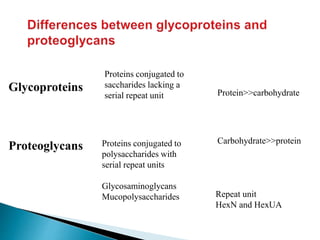
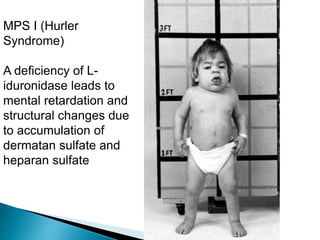
Glycoproteins and proteoglycans are important biomolecules that function in the extracellular matrix. Glycoproteins have short carbohydrate chains without repeats attached to proteins, serving roles like structure, lubrication, and cell signaling. Proteoglycans contain long repeating disaccharide units that bind large amounts of water, functioning mainly as structural components. Both are synthesized in the Golgi and degraded in lysosomes, with defects causing diseases like mucopolysaccharidoses due to glycosaminoglycan accumulation.