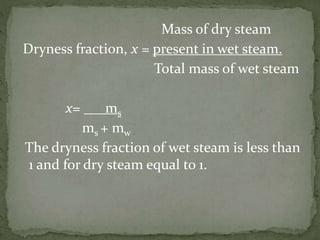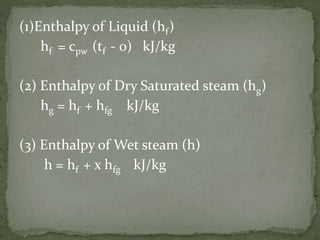There are three main types of steam: wet steam, dry saturated steam, and superheated steam. Wet steam is a mixture of water molecules and steam at the saturation temperature. Dry saturated steam only contains steam at the saturation temperature. Superheated steam is dry saturated steam that has been heated further, raising its temperature above the saturation point. The document also defines terms like dryness fraction, wetness fraction, priming, degree of superheat, and amount of superheat as they relate to describing the properties and conditions of different types of steam.