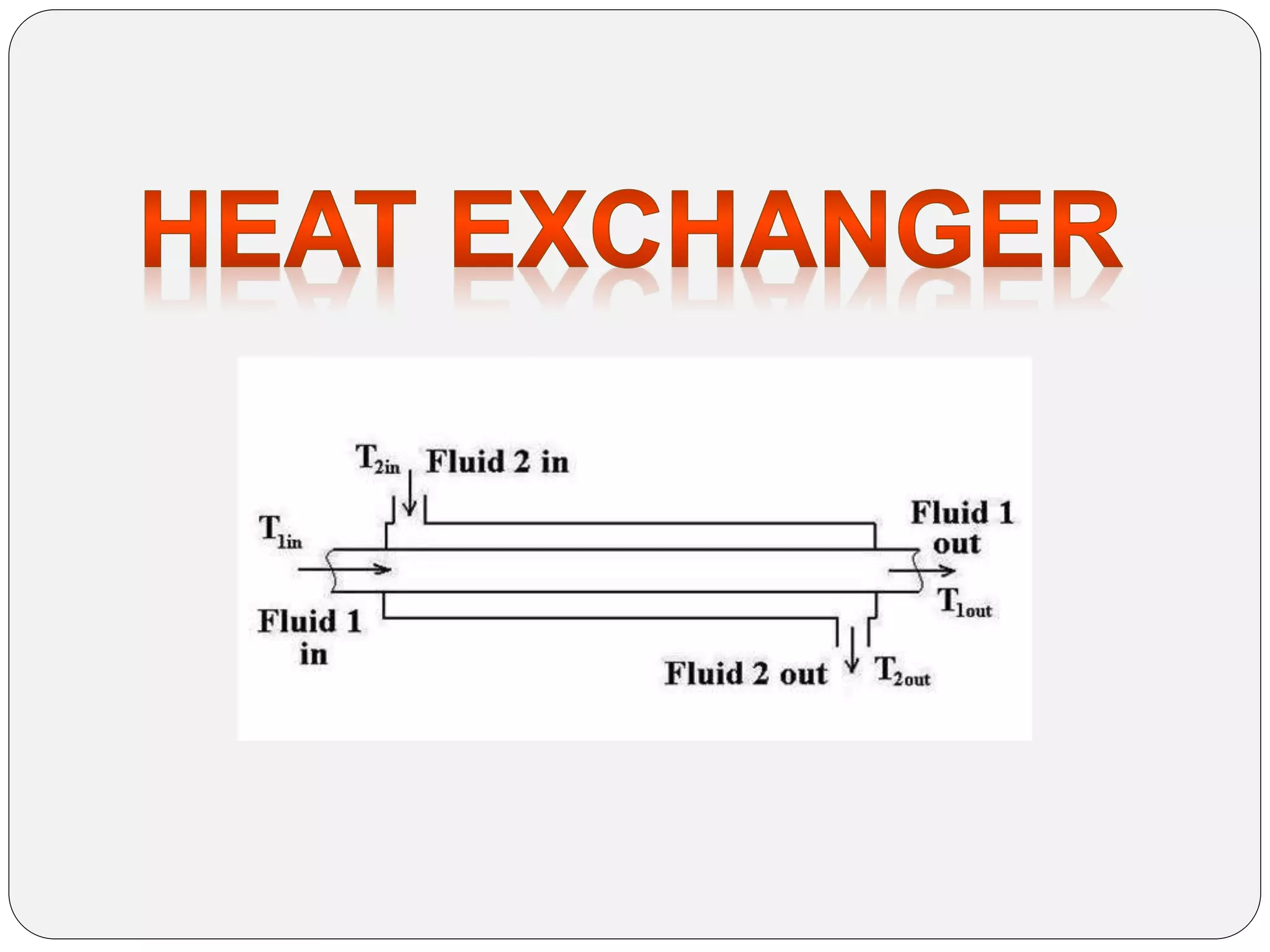
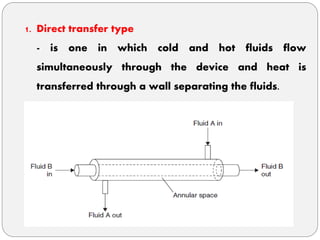
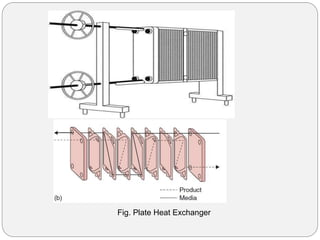
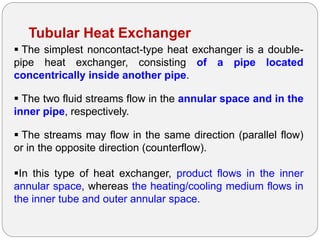
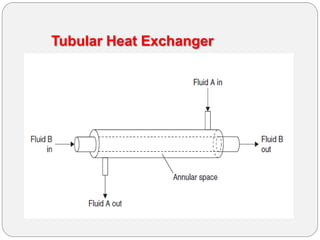
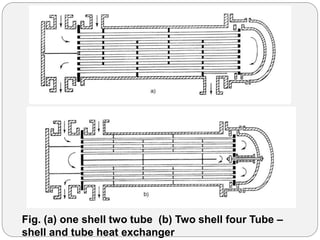
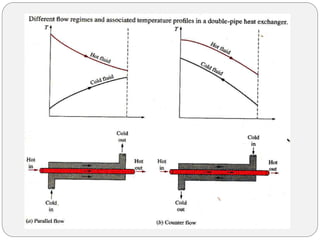
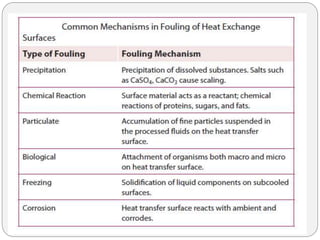
Heat exchangers transfer heat between two or more fluids. There are three main types: direct transfer, storage, and direct contact. Direct transfer type heat exchangers simultaneously flow hot and cold fluids through a separating wall. Storage type heat exchangers alternately flow hot and cold fluids through a porous matrix. Direct contact type heat exchangers do not separate the fluids. Common examples are plate heat exchangers and shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Design considerations include materials, operating parameters, fouling factors, and determining the required heat transfer area.