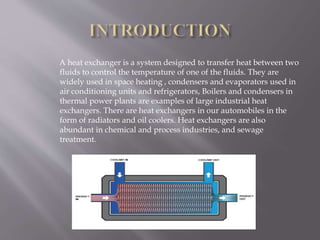
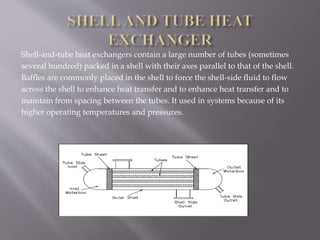
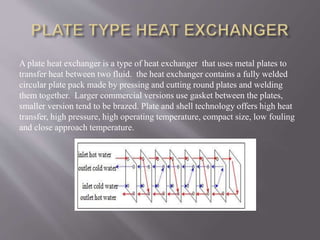
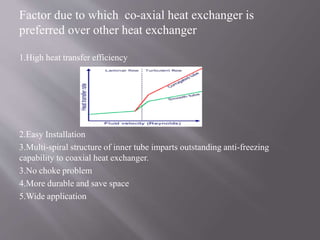
Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat between two fluids to control the temperature of one fluid. There are various types of heat exchangers that differ based on their flow arrangement, surface compactness, construction technique, and whether they use direct or indirect contact between fluids. Common examples include shell and tube heat exchangers, which contain multiple tubes in a shell, and plate heat exchangers, which use metal plates to transfer heat. Coaxial heat exchangers consist of an inner corrugated tube within an outer tube to efficiently transfer heat between fluids flowing separately within the tubes.