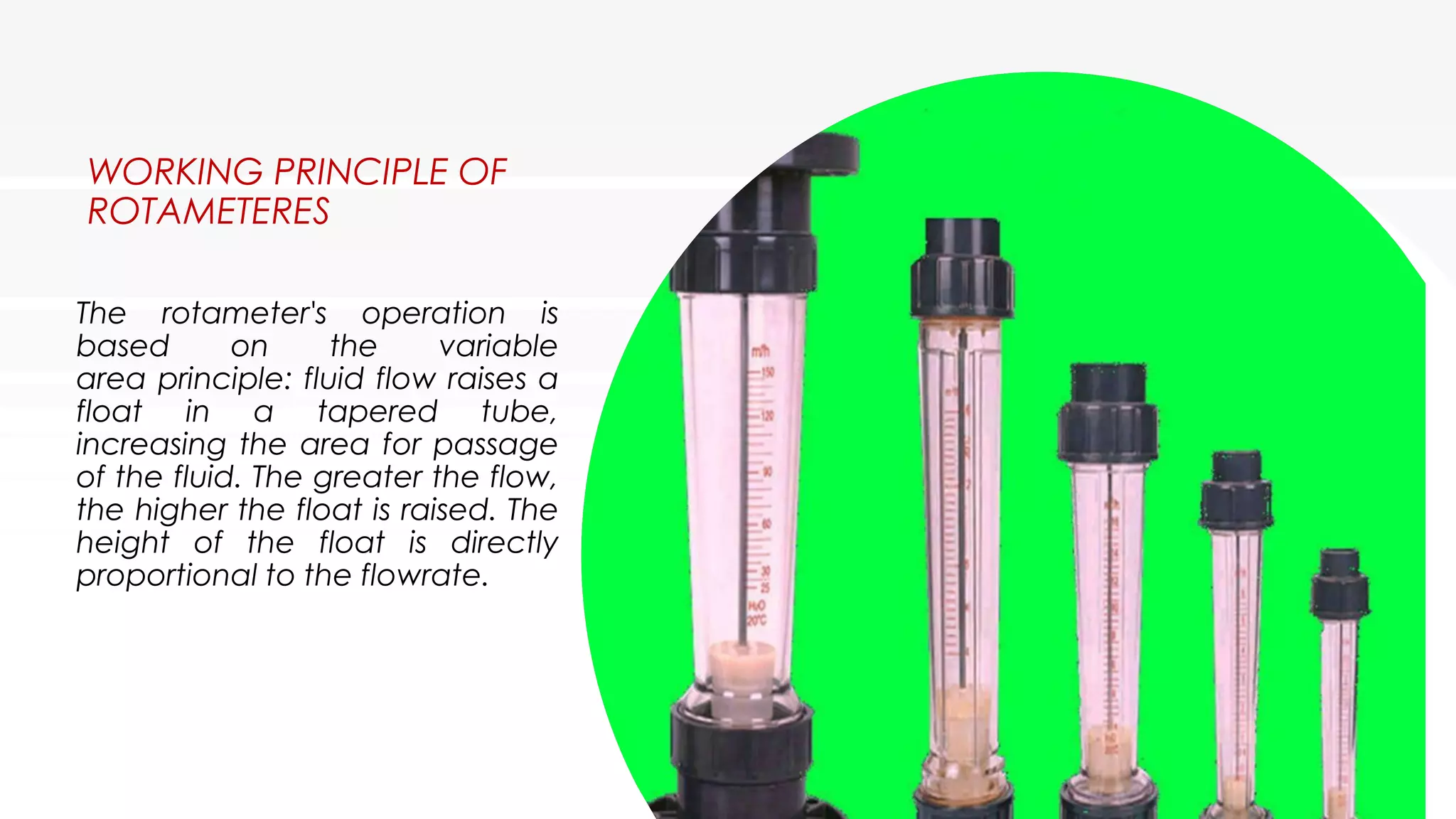
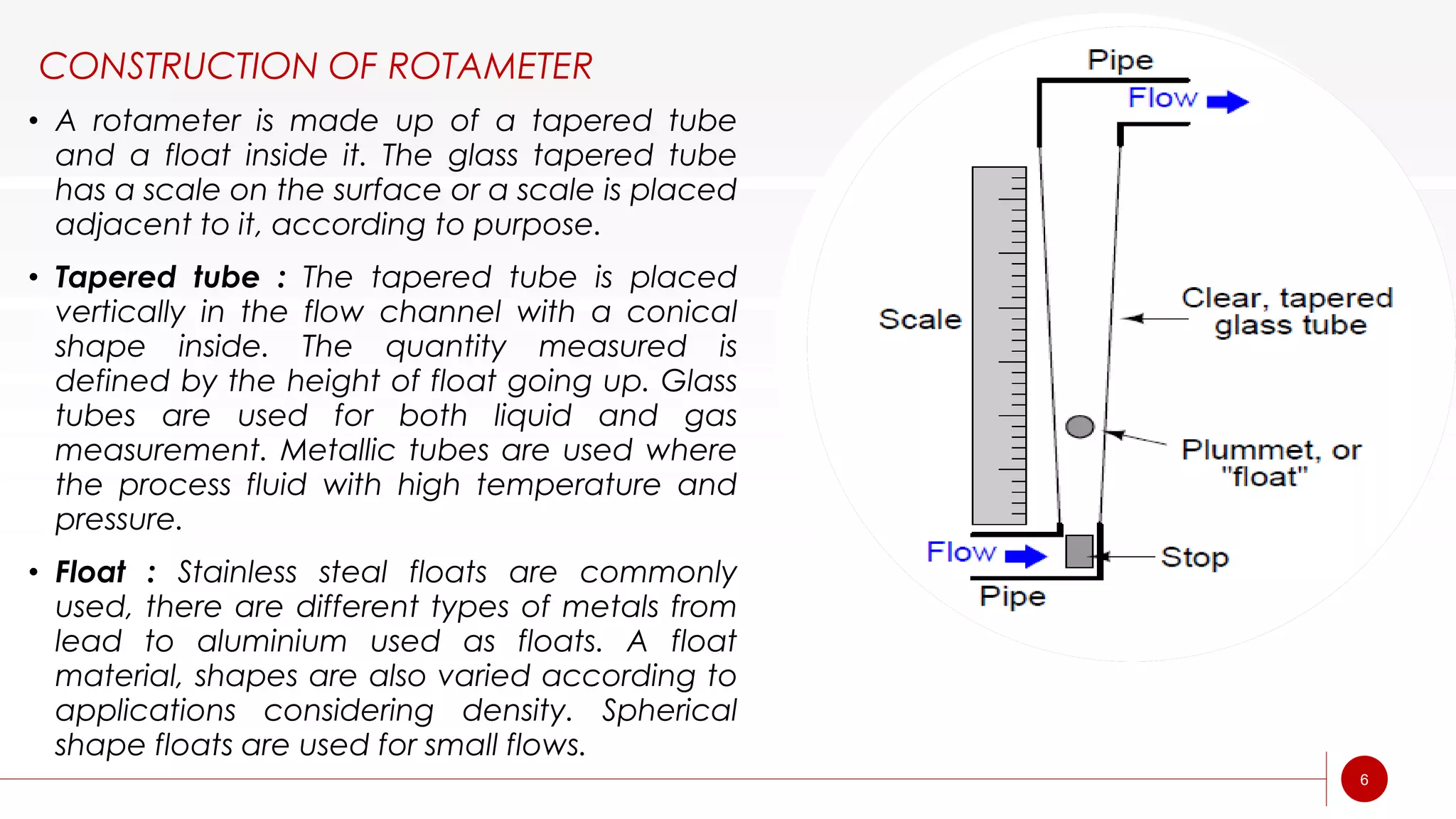
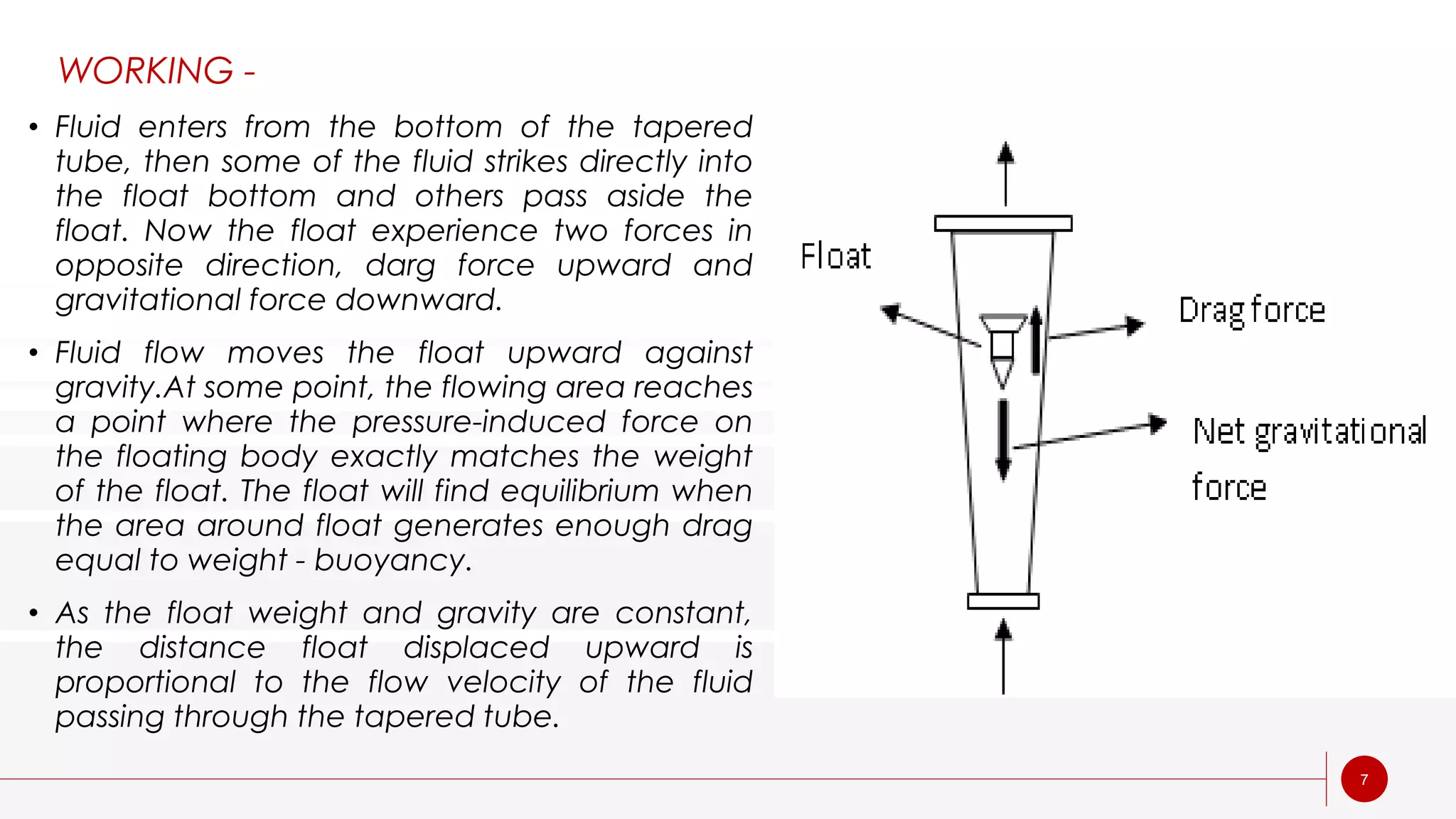
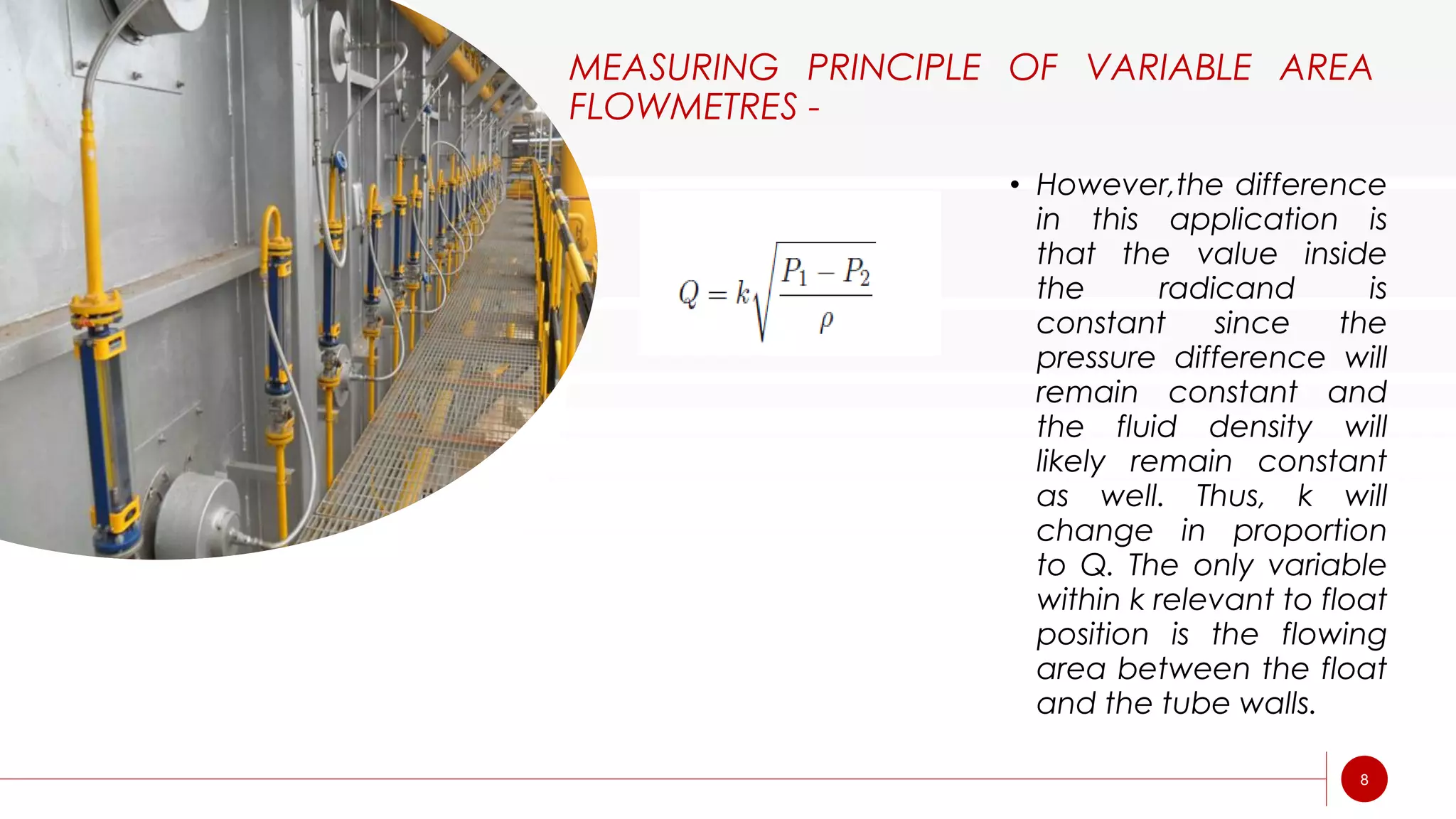
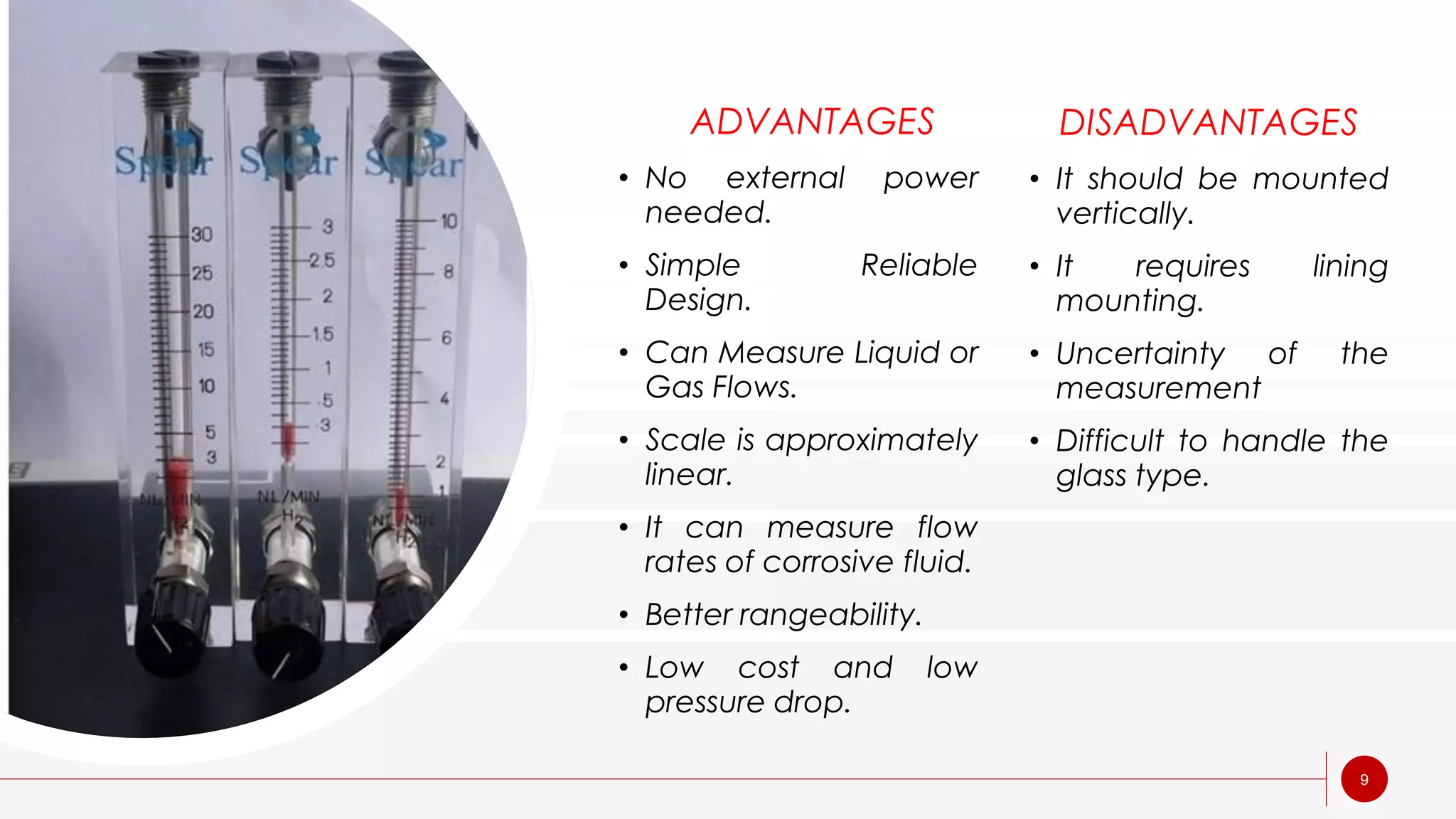
A rotameter is a variable area flow meter that measures fluid flow rate. It consists of a tapered glass or metal tube with a float inside that rises as flow rate increases. As fluid enters the bottom of the tapered tube, the float is pushed upward by drag force from the fluid until it reaches equilibrium where drag equals weight. The height of the float corresponds to flow rate and is read on an adjacent scale. Rotameters are simple, reliable, and provide a linear scale but must be mounted vertically and are susceptible to measurement uncertainty.