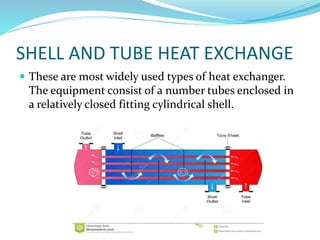
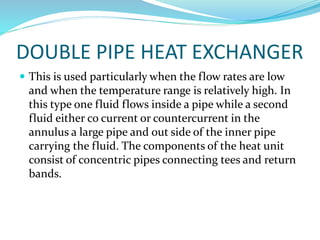
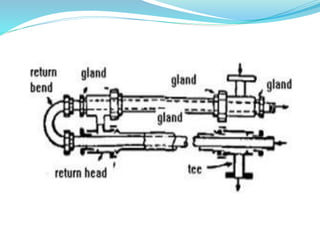
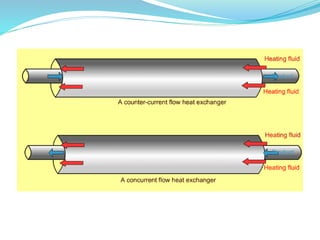
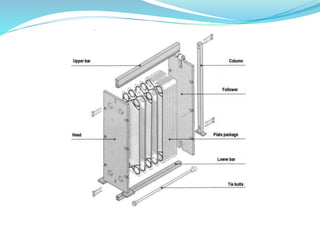
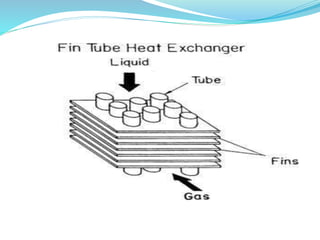
This document discusses heat exchangers, including their types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It describes the main types of heat exchangers as shell and tube, double pipe, plate type, and finned tube. Shell and tube heat exchangers are the most widely used due to their lower cost compared to plate type and ability to handle higher pressures than double pipe. Plate type heat exchangers offer higher efficiency but higher initial cost. Heat exchangers are commonly used in chemical, petrochemical, food, and other industrial processes to transfer heat between fluids.