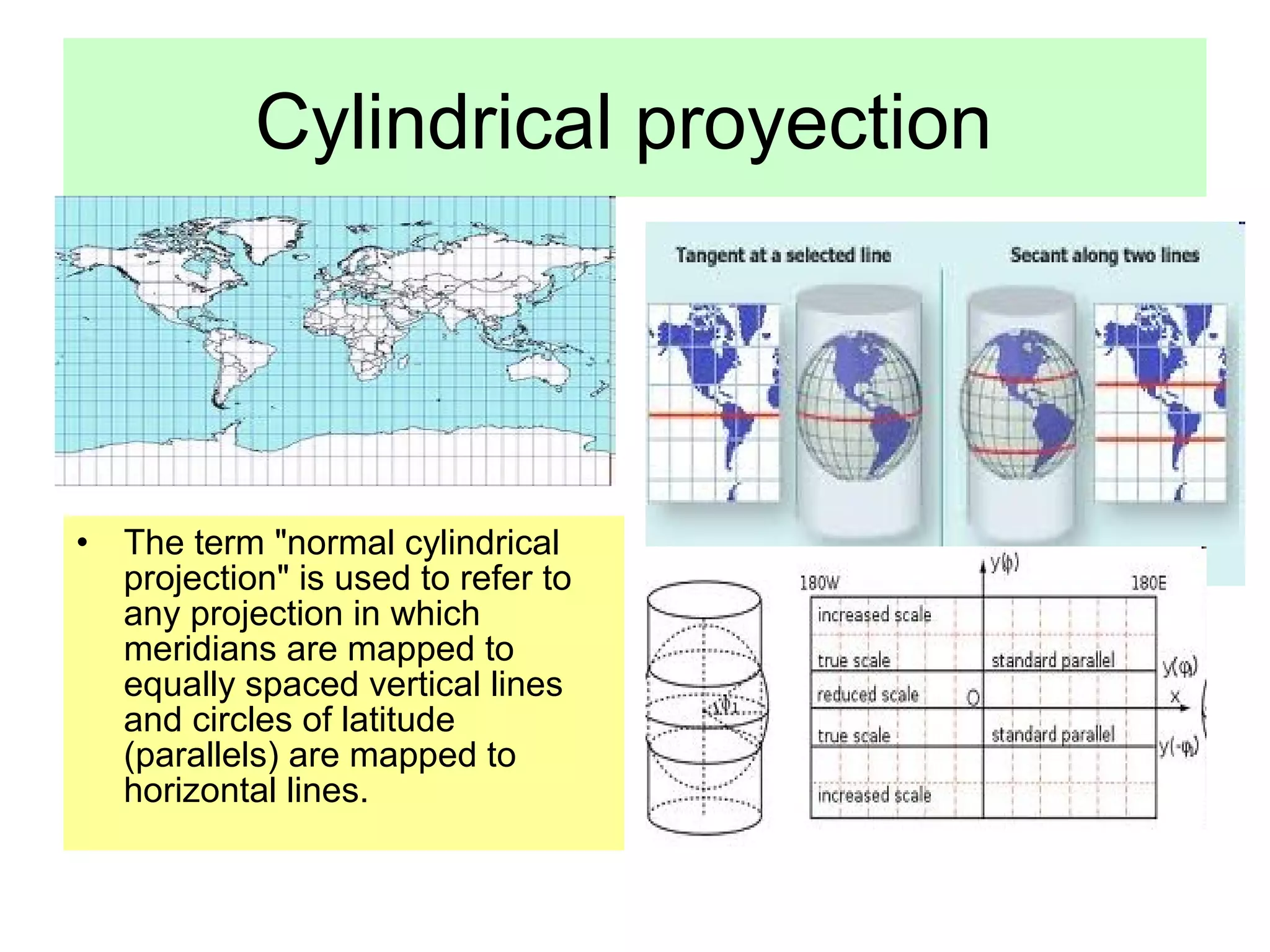
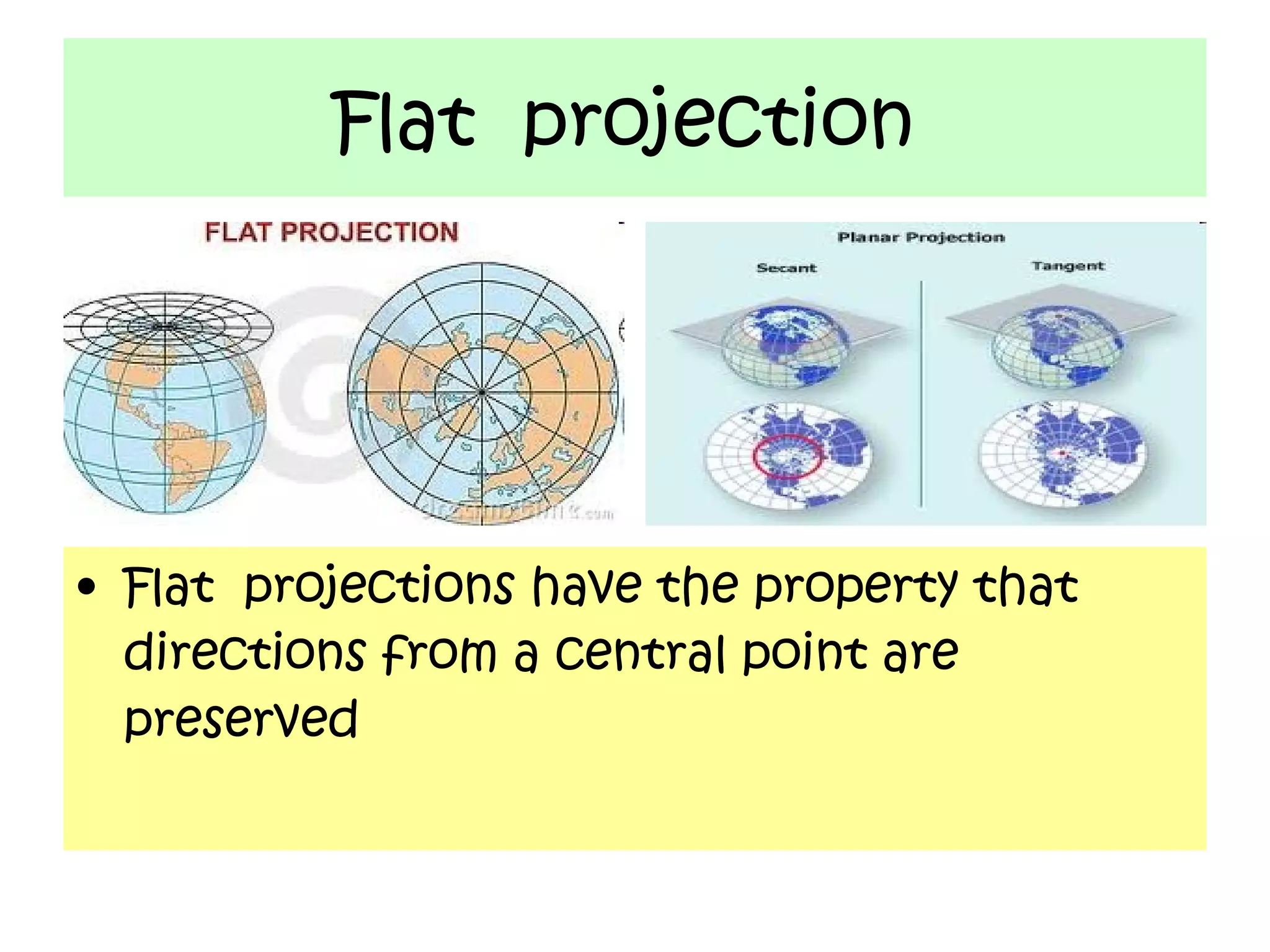
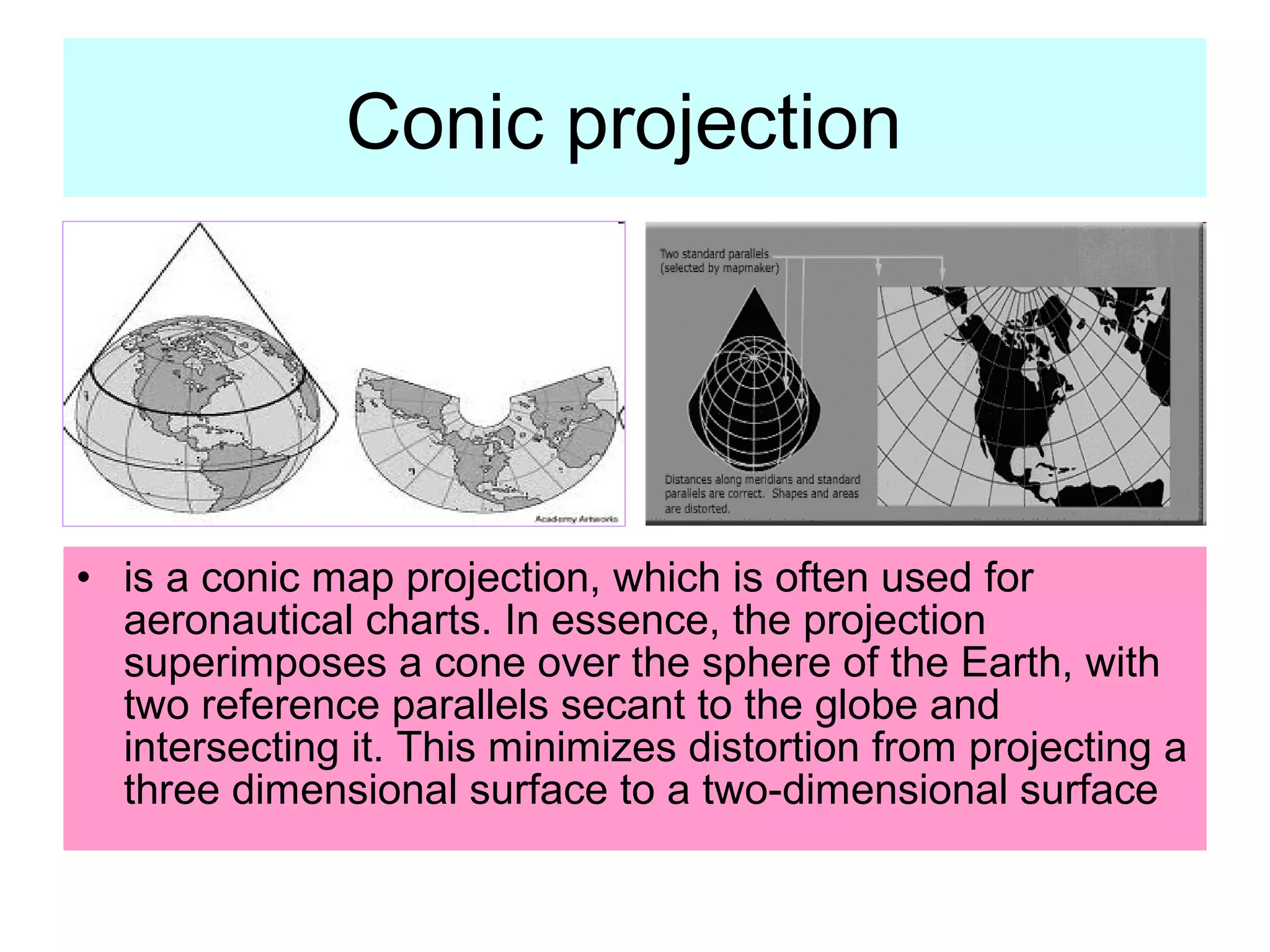
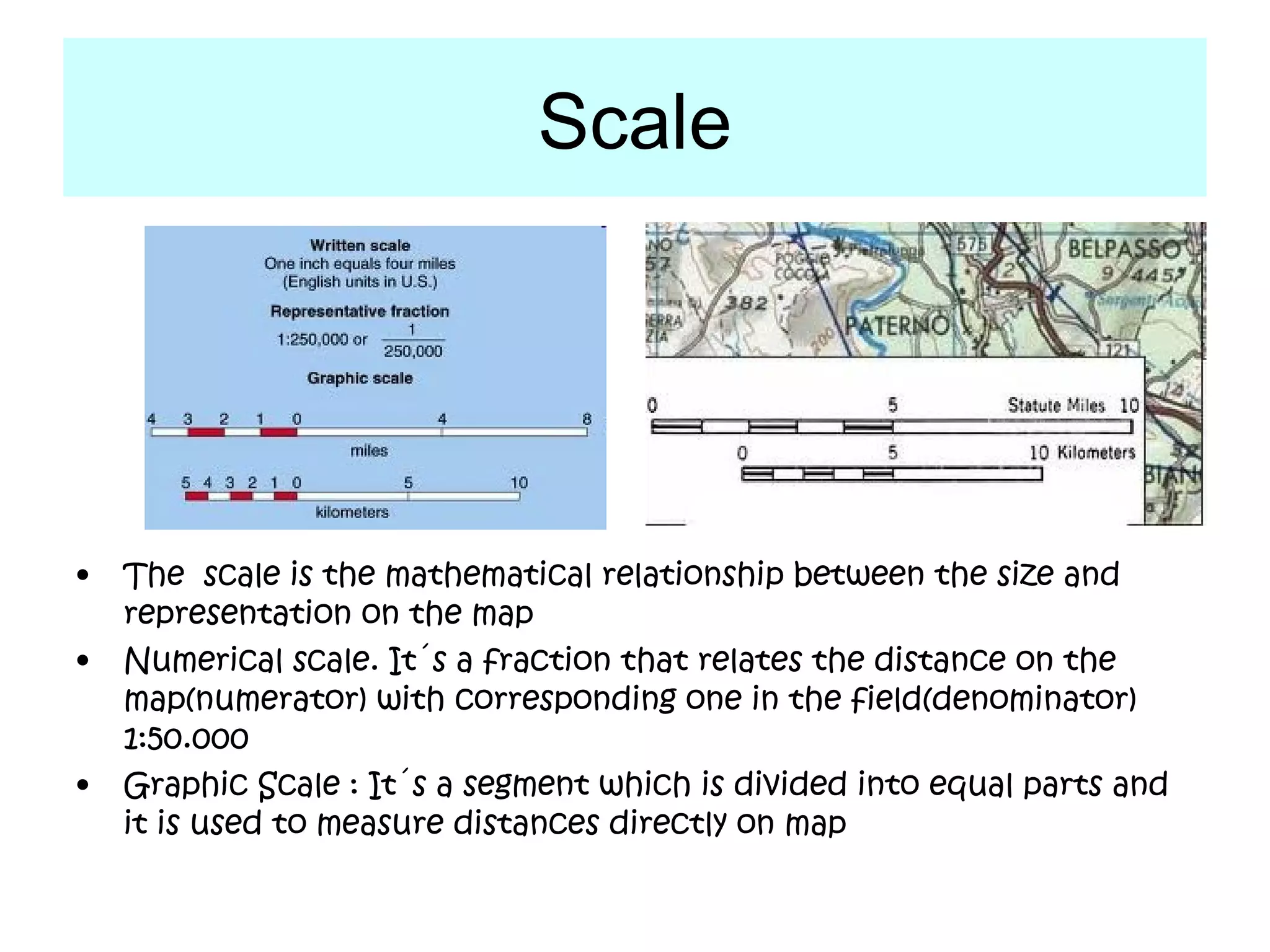
This document discusses different types of map projections used to represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface. It notes that map projections introduce distortions of shapes and distances. It then describes cylindrical, flat, conic, and scale as different projections used by cartographers to minimize distortions. The goal of different projections is to transfer the three-dimensional globe onto a two-dimensional map in a way that best preserves certain properties like directions, shapes, or areas, depending on the specific projection.