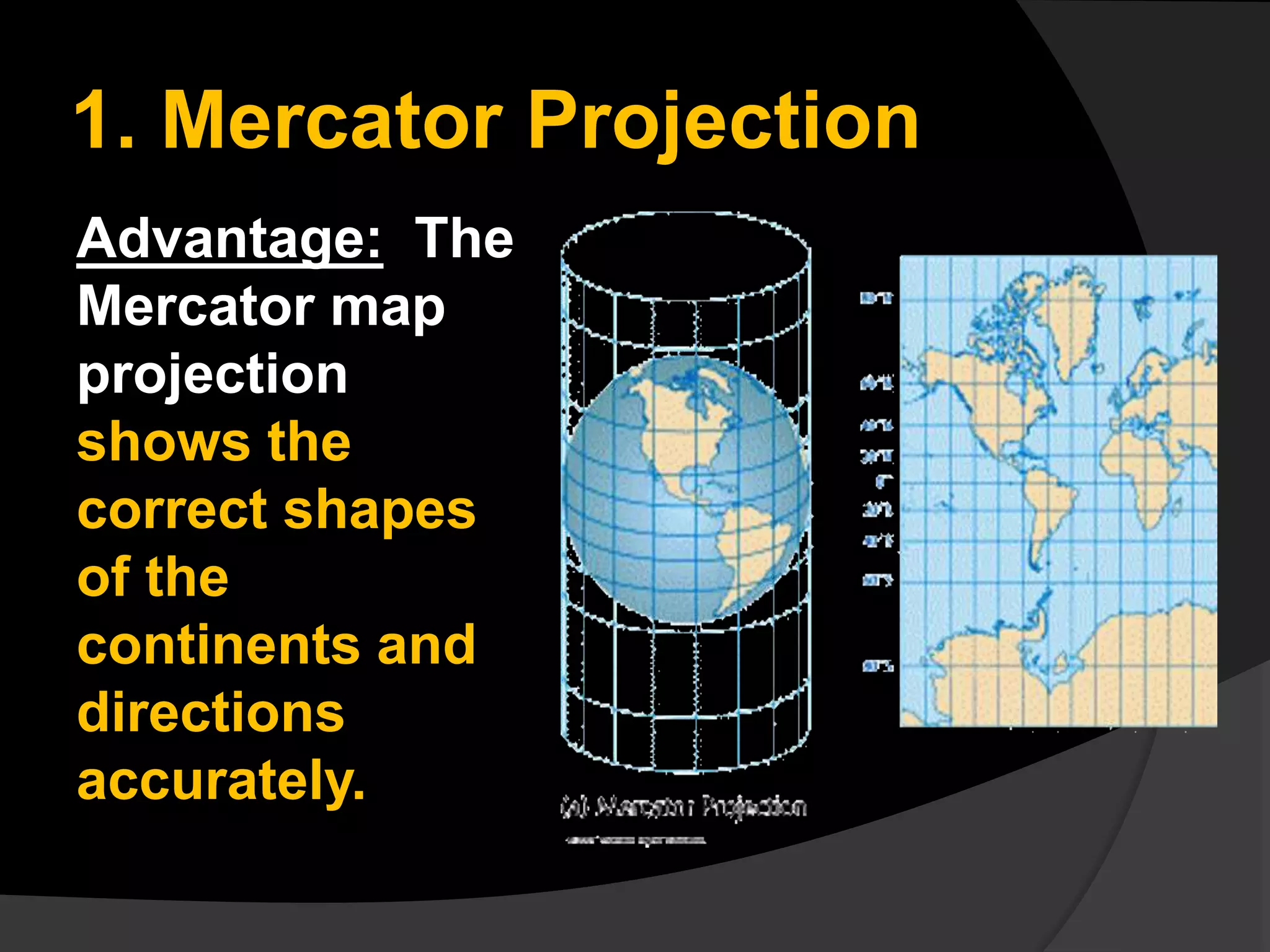
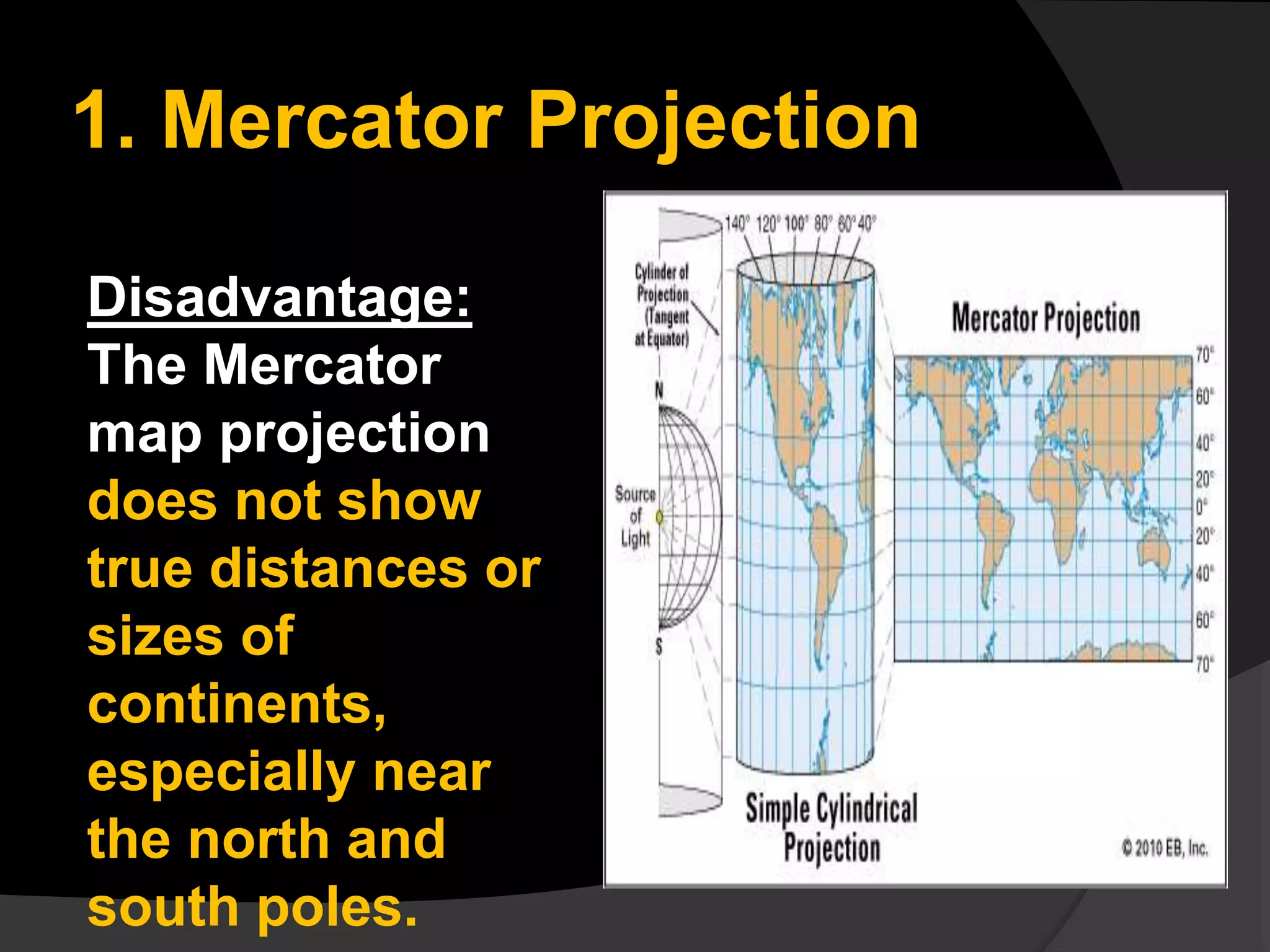
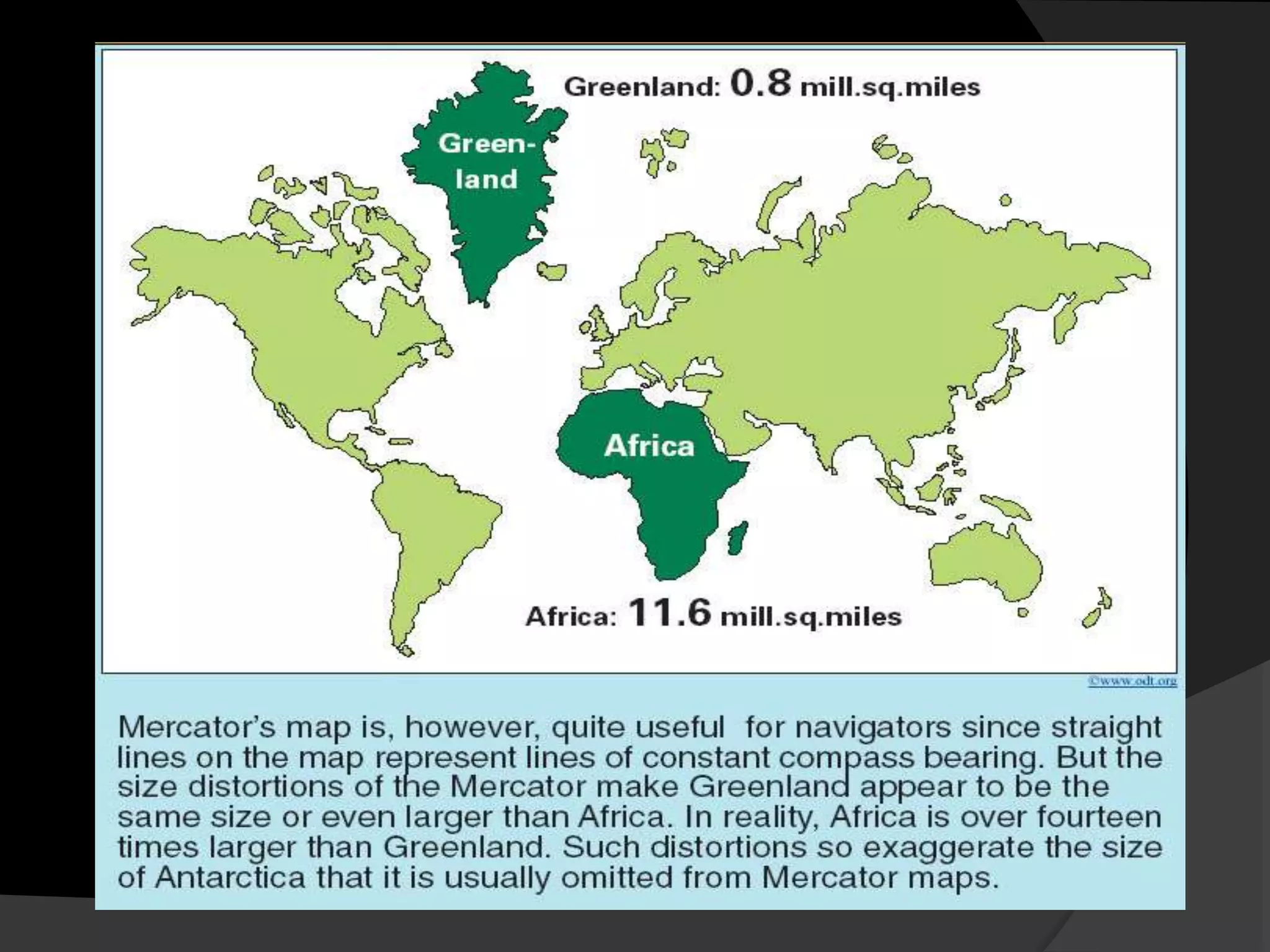
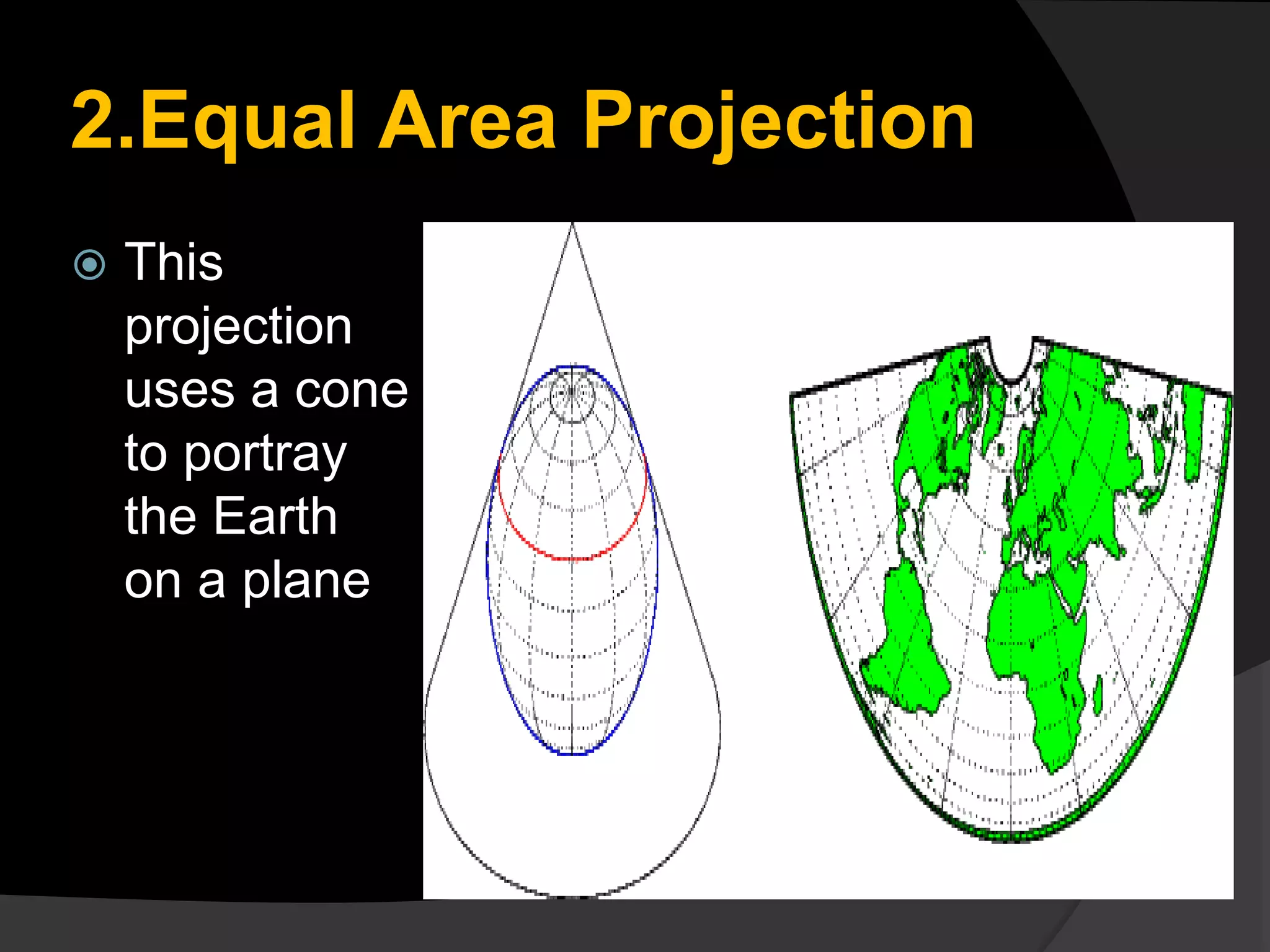
The document discusses three common types of map projections: Mercator, equal area, and gnomonic. It describes the Mercator projection as a cylindrical projection that accurately shows directions but distorts sizes, especially at the poles. The equal area projection represents areas correctly on the map using a conic projection. While it shows correct landmass sizes, it alters shapes. The document provides details on the characteristics and purposes of each projection type.