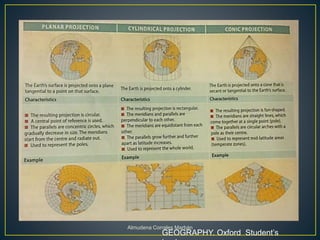
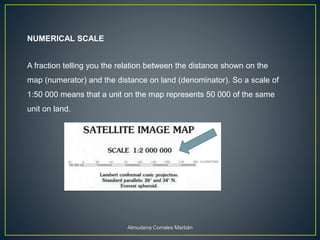
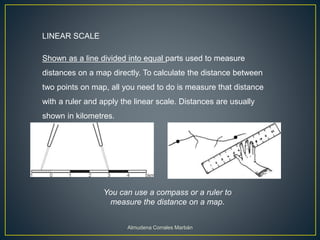
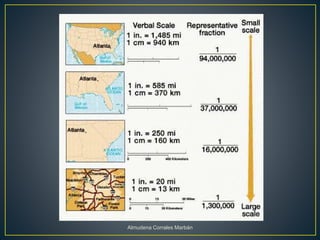
Maps represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface, which requires projections that distort the globe's shape. Projections display the globe using planar, cylindrical, or conic shapes to flatten it. Scale relates distances on a map to actual distances, shown numerically as a ratio or linearly with a divided line. Numerical scale gives the fraction comparing map units to land units, while linear scale directly measures map distances.