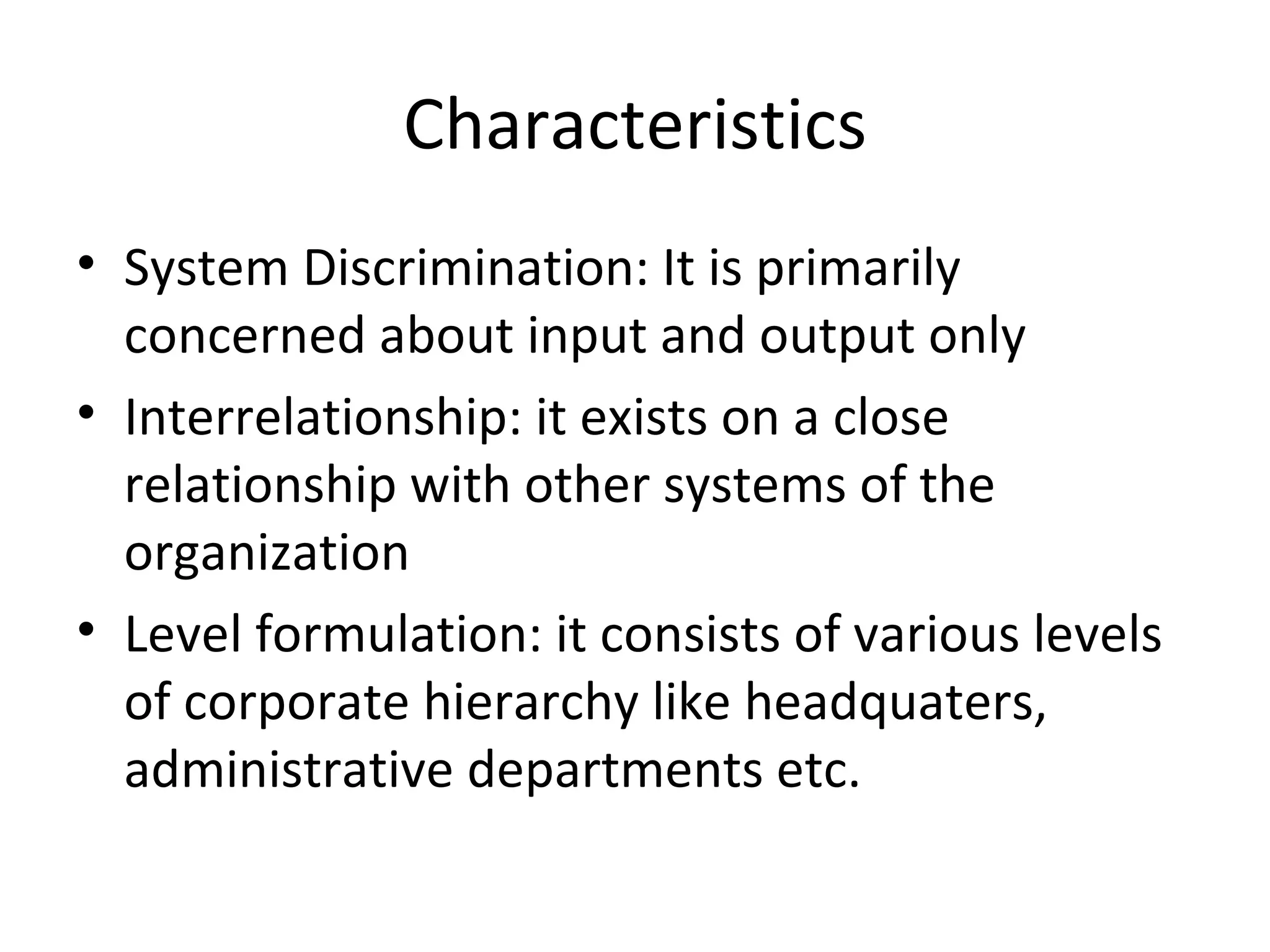
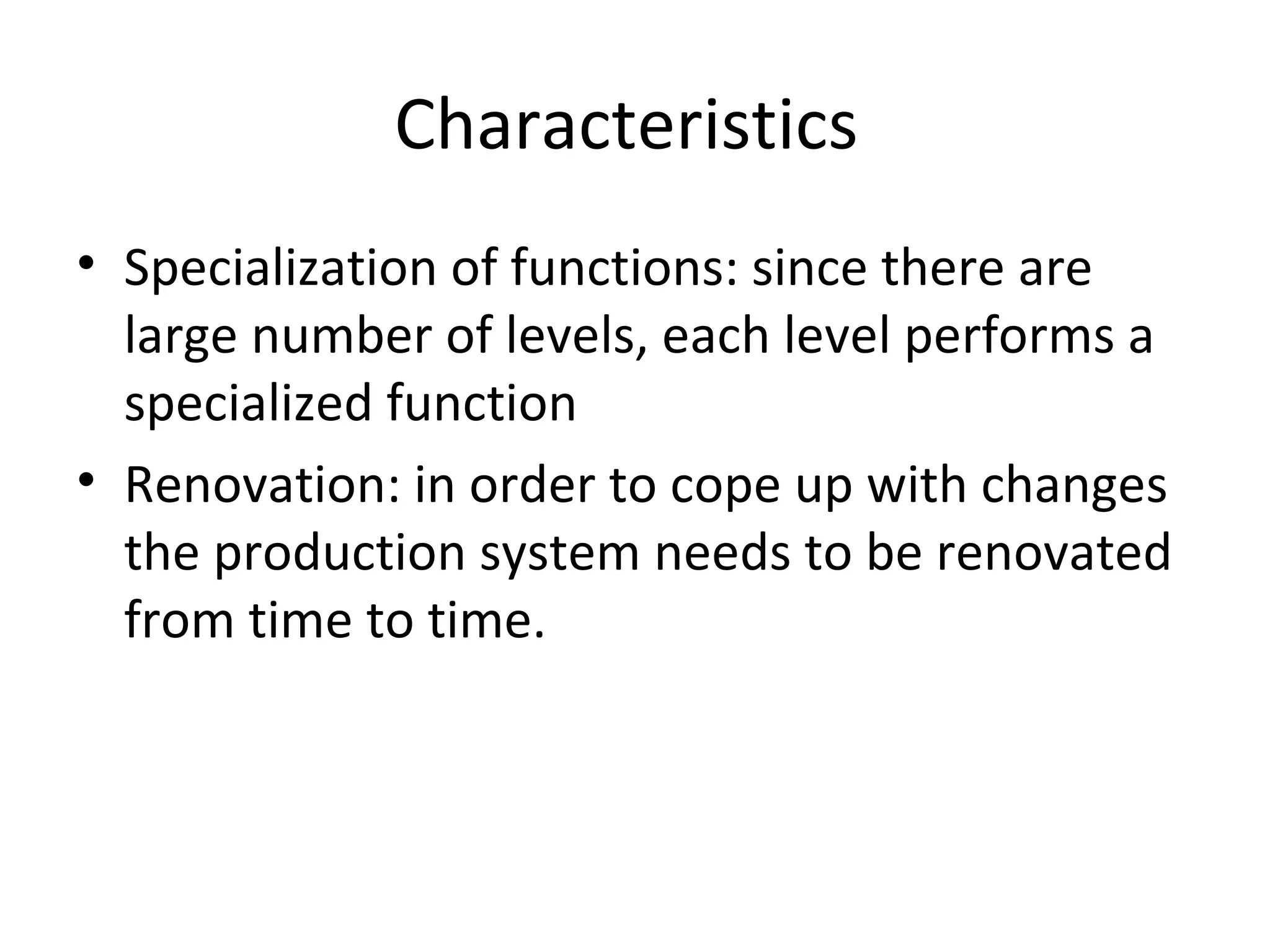
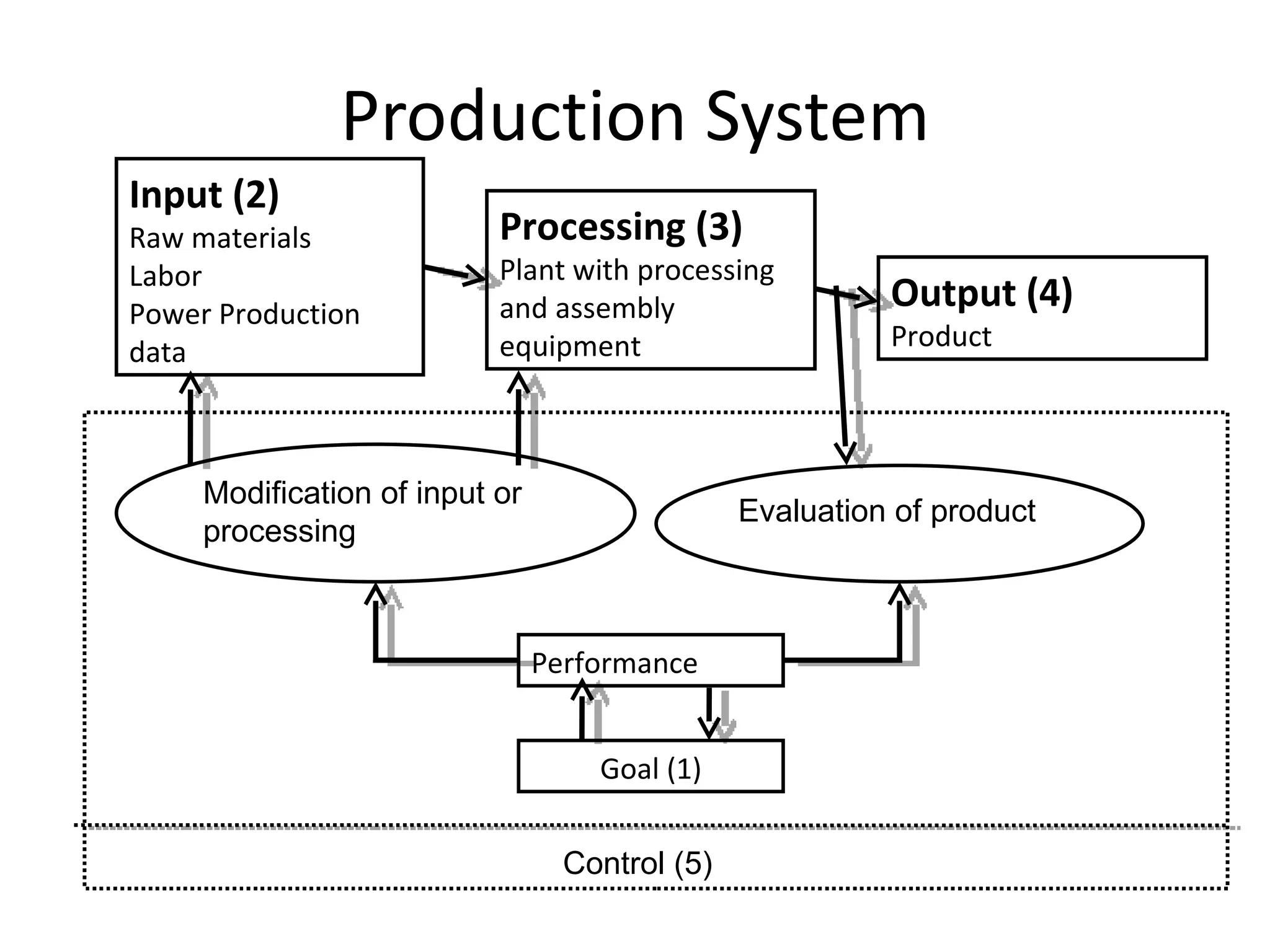
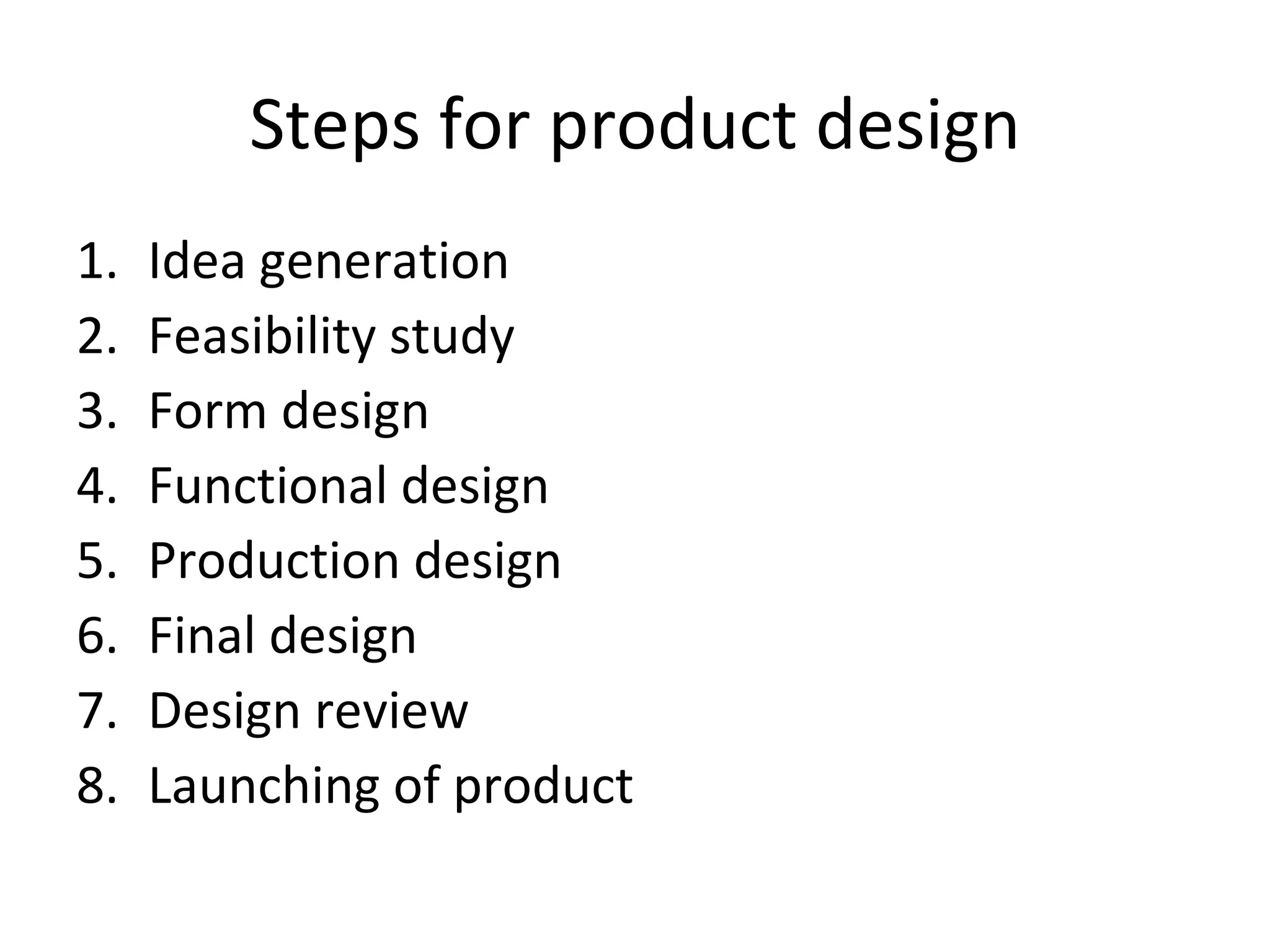
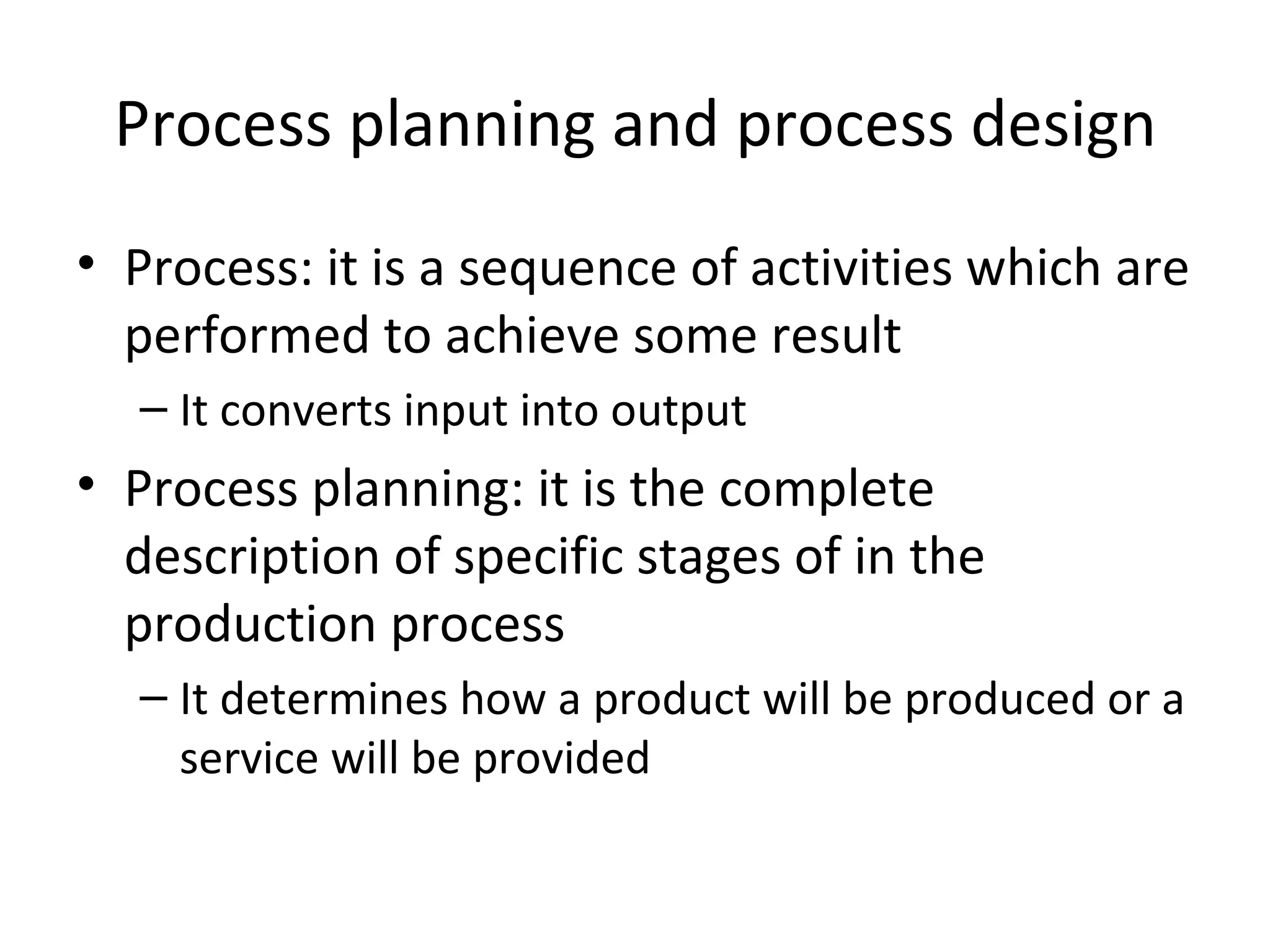
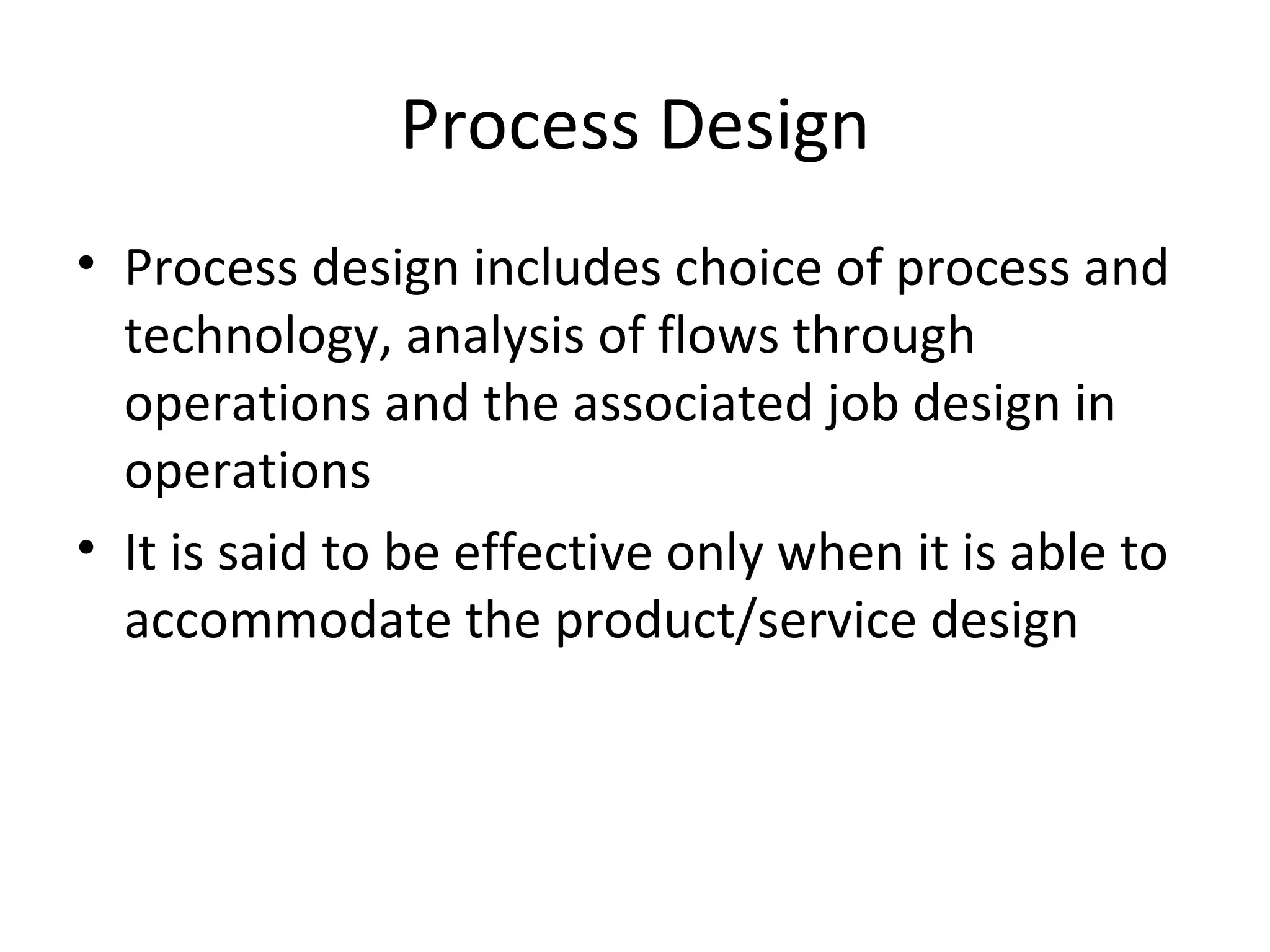
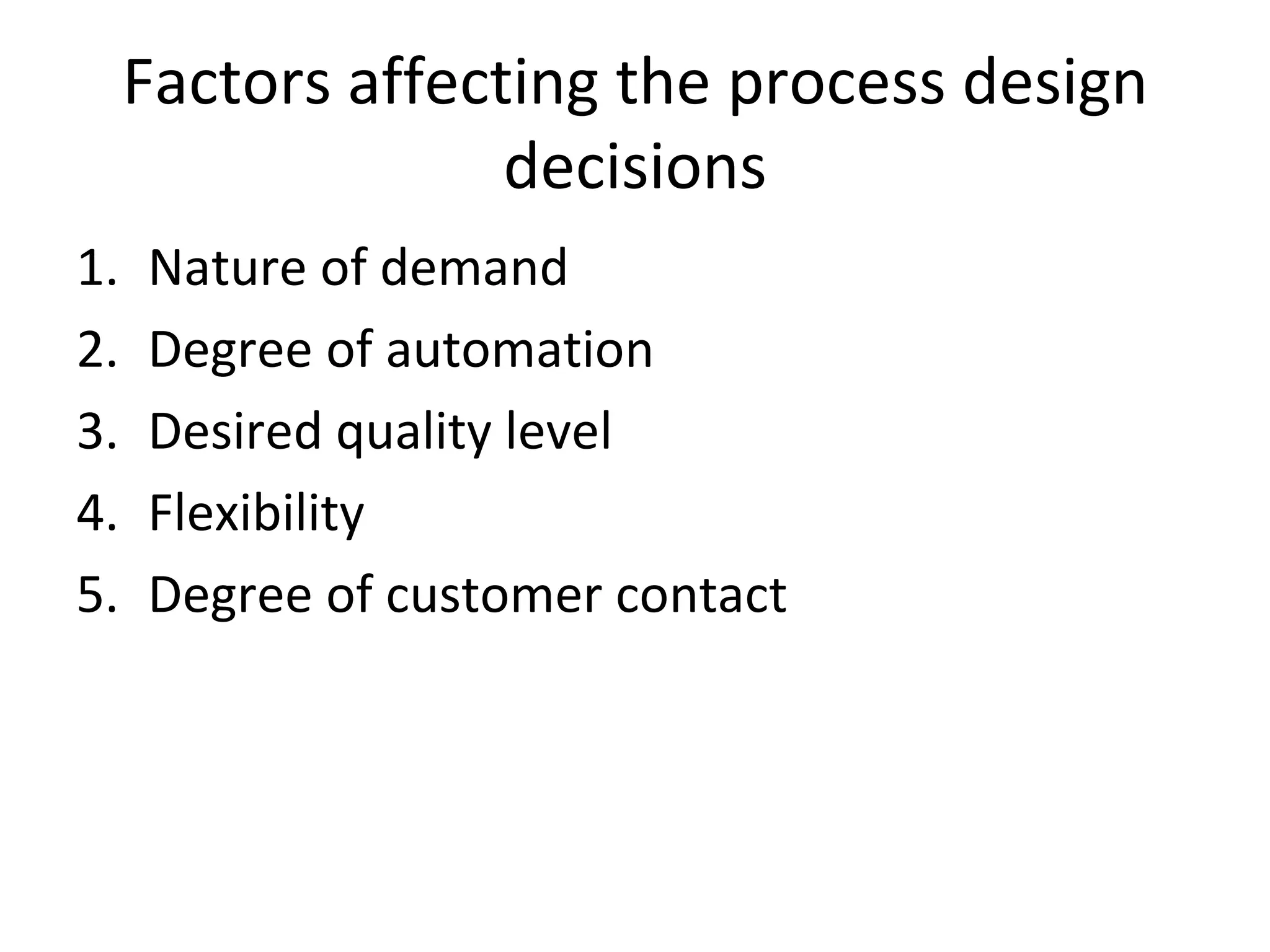
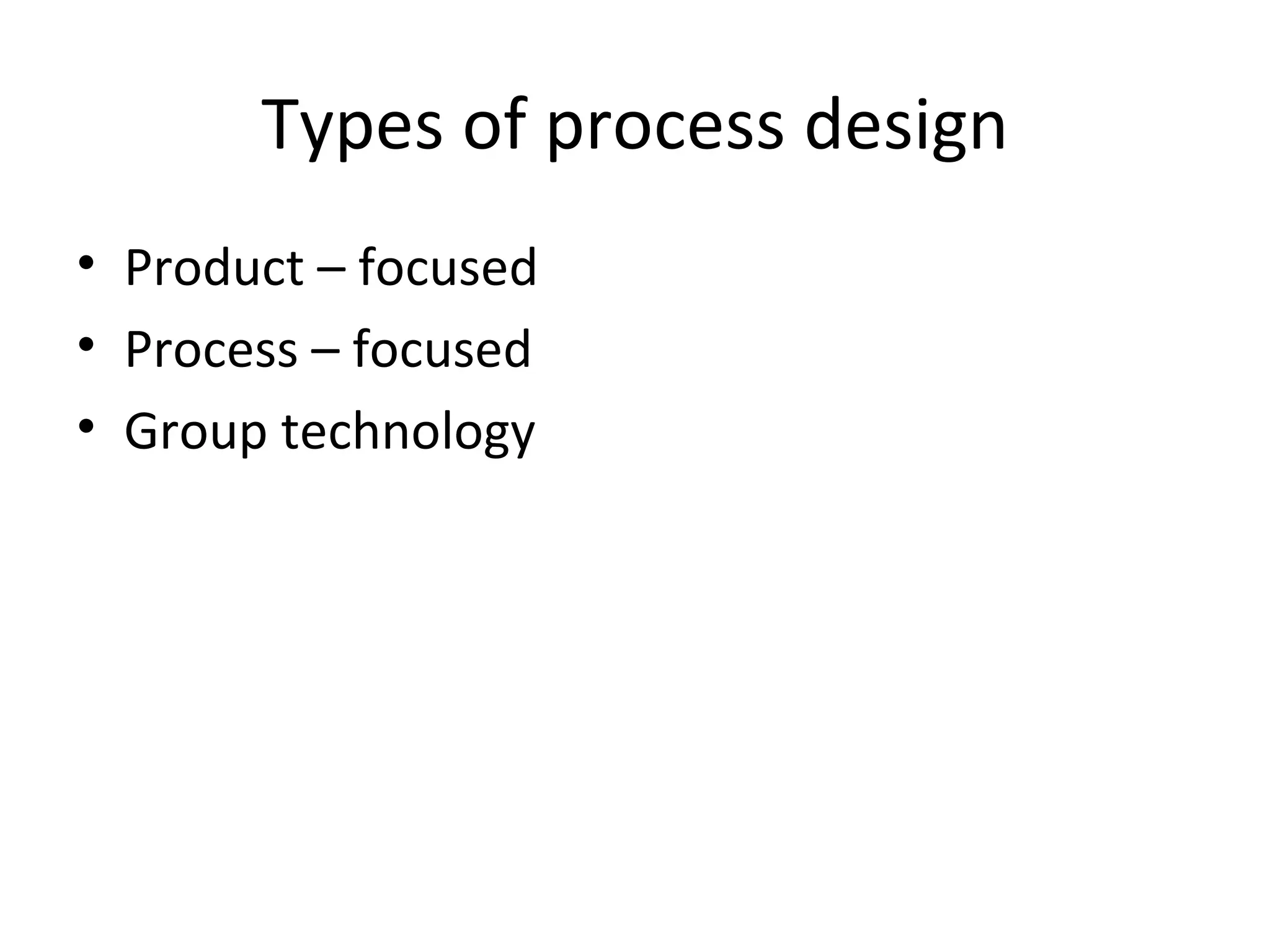
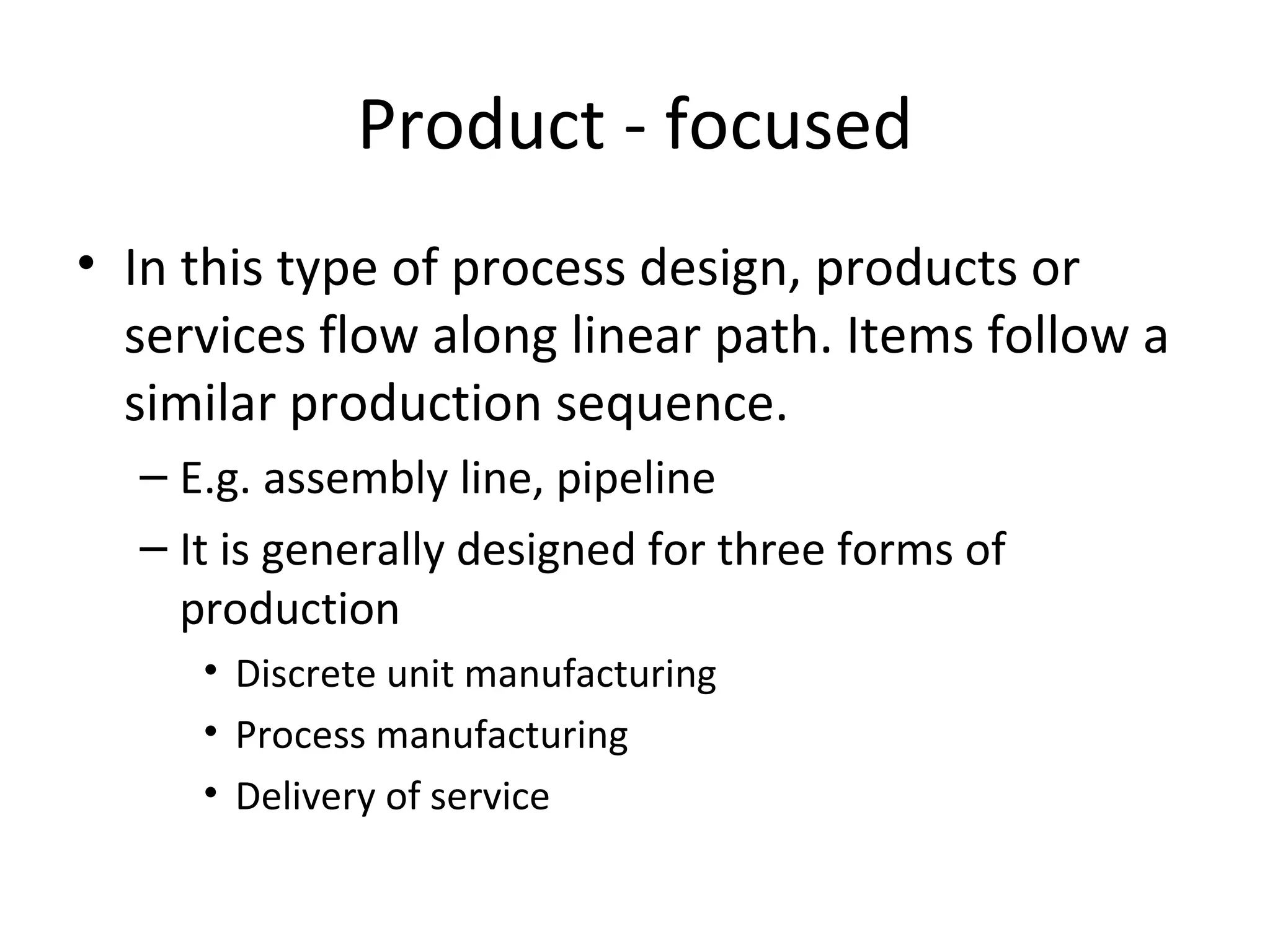
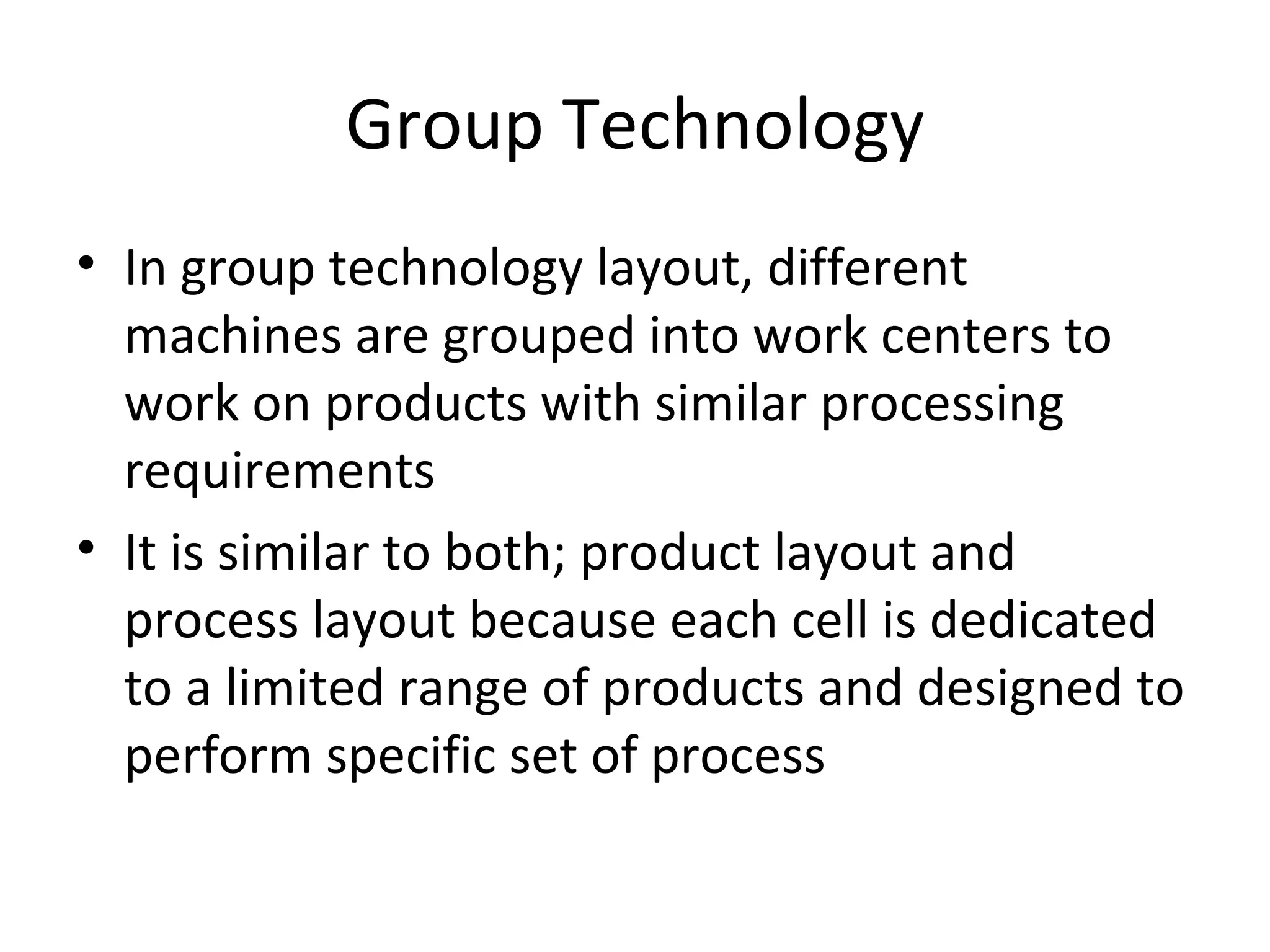
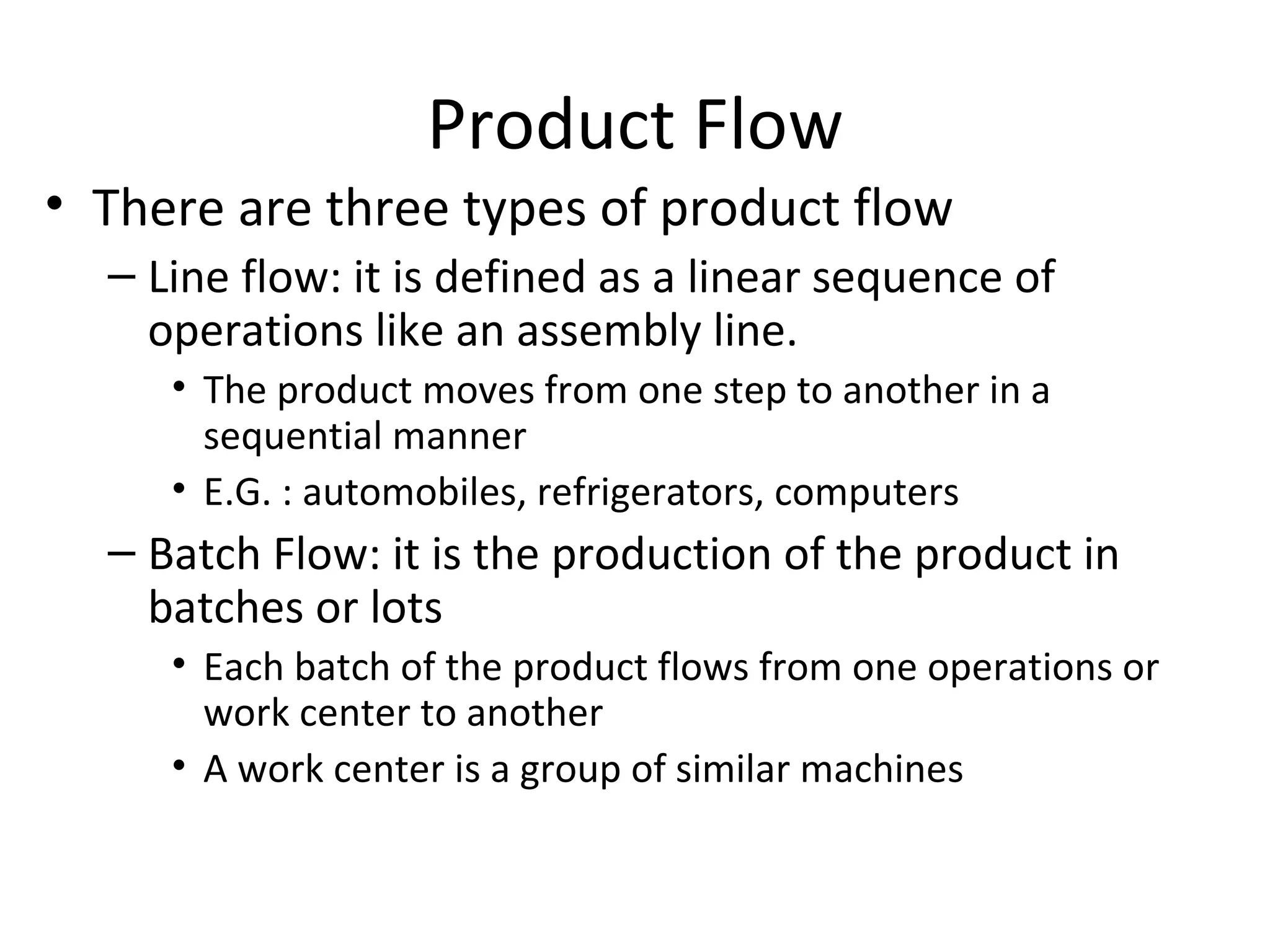
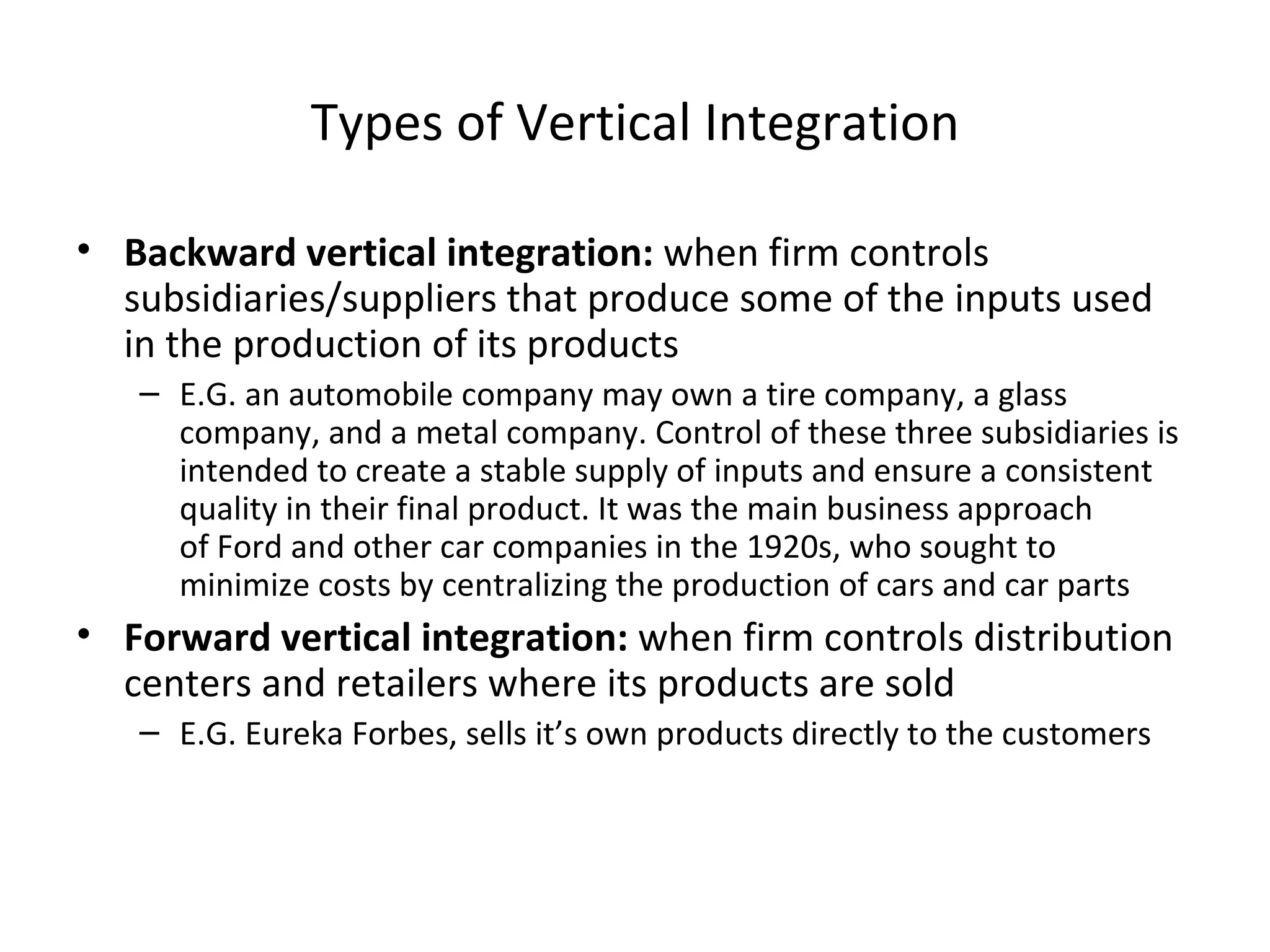
The document discusses various aspects of production systems including their characteristics, inputs, outputs, controls, product design process, and process planning. It describes production systems as manufacturing subsystems that design, produce, distribute, and service products. They have specialized functions at different levels and need renovation over time to adapt to changes. The key aspects covered are input-output relationships, types of control like feedback and forward control, objectives and importance of product design, steps in the design process, factors affecting process design decisions, types of process designs, and major process decisions around process choice, vertical integration, resource flexibility, customer involvement, and capital intensity.