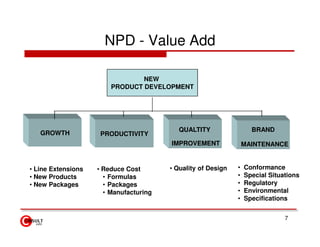
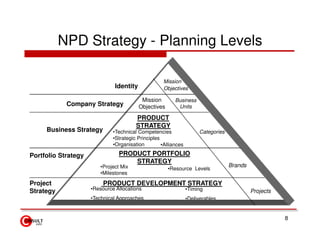
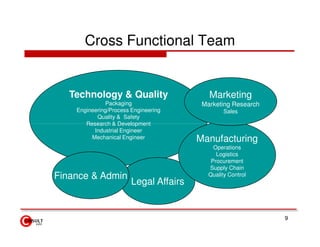
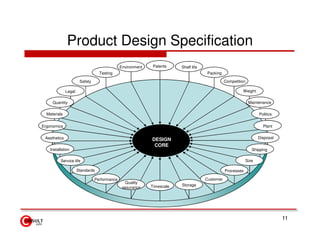
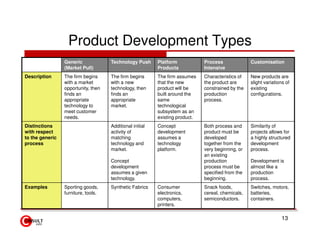
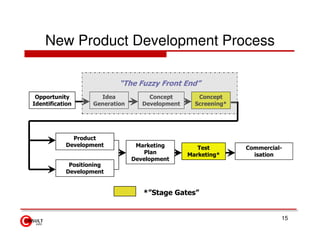
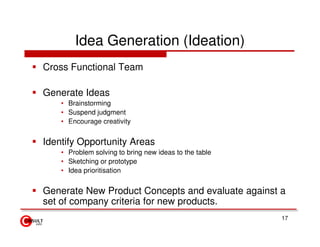
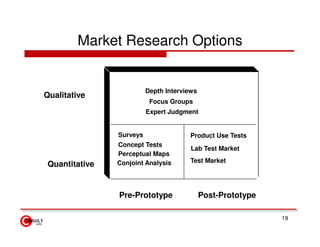
The document discusses new product development strategies and processes. It begins by outlining reasons for new product failures, such as overestimating market size. It then describes various NPD strategies including developing original products, acquisitions, and product improvements. The core of the document focuses on the multi-stage NPD process, from opportunity identification and concept development to testing, marketing planning, and commercialization. Cross-functional teams and market research methods like focus groups are also emphasized.