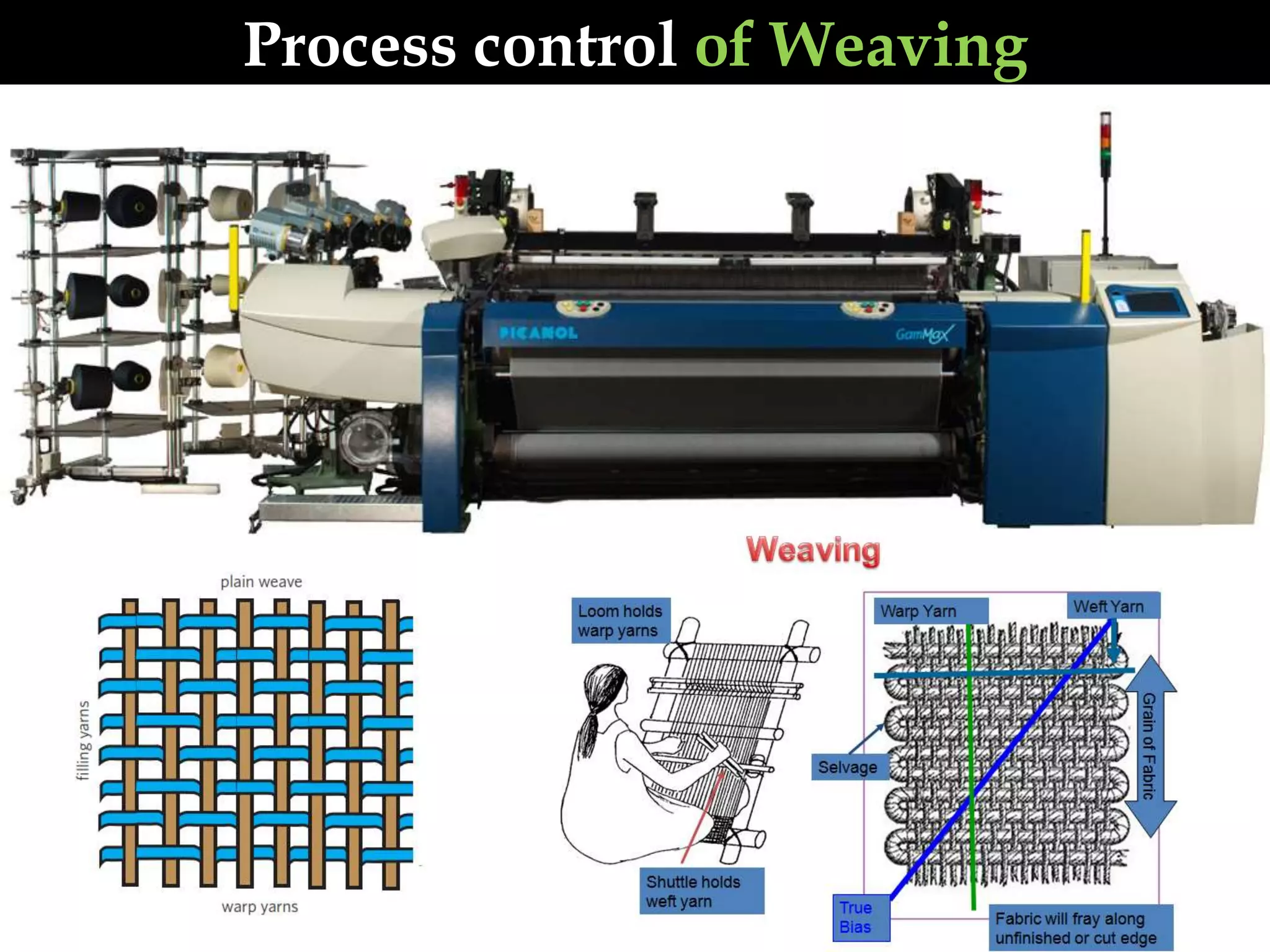
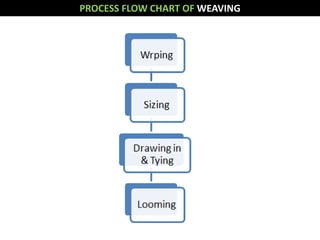
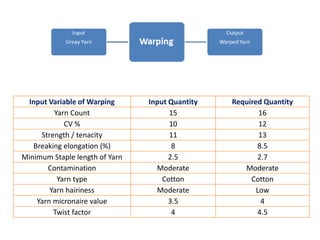
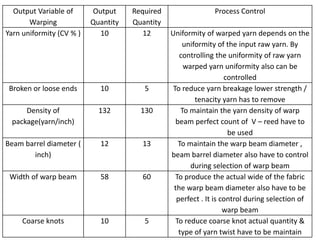
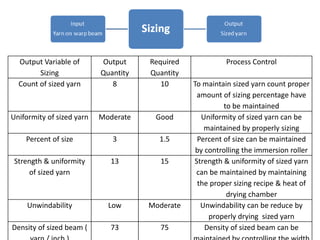
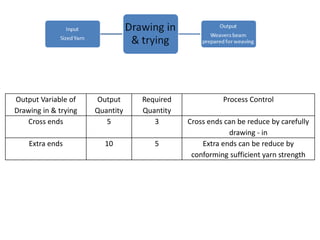
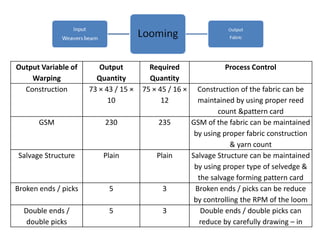
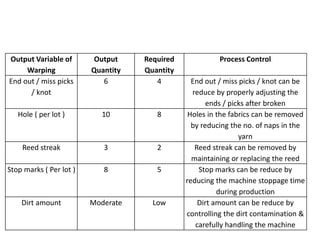
This document discusses process control in weaving. It begins by defining process control and explaining that quality is formed during production. It then outlines the 6 steps of process control: 1) draw a process flow chart, 2) segregate where changes occur, 3) find control points, 4) determine variables out of range, 5) identify causes, and 6) make recommendations. The document provides details on process control for the warping, sizing, drawing and trying, and looming sections of weaving. It concludes that this experiment increased knowledge of process quality control in weaving.