Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times

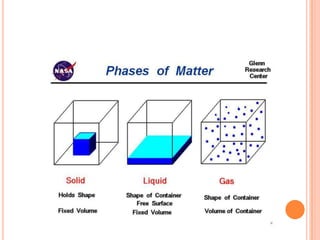



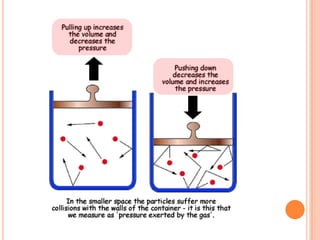



This document discusses the kinetic molecular theory and Boyle's law. It explains that gases are made of molecules that are far apart from each other and move randomly, colliding with the container walls. According to Boyle's law, if the volume of a container decreases, the pressure increases because the molecules collide with the walls more frequently. The document provides the formula for Boyle's law, P1V1 = P2V2, and gives examples of using it to calculate pressure and volume.









