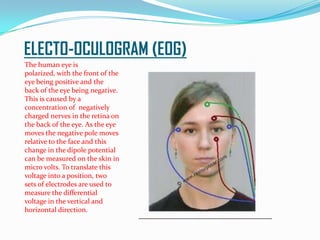
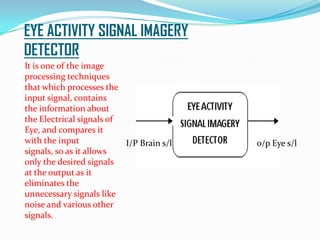
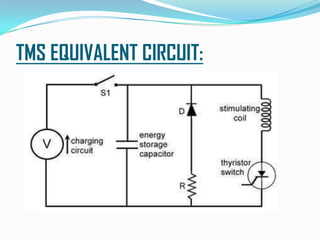
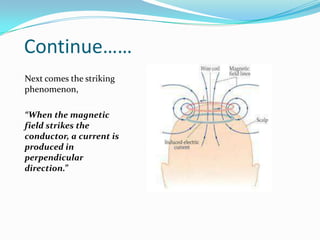
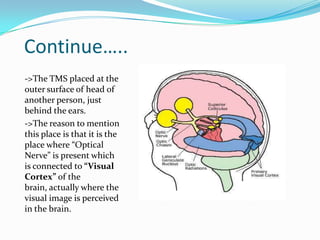
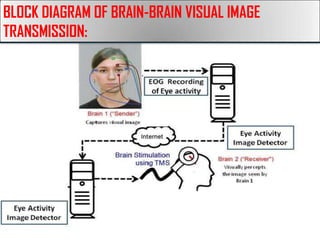
Giritharan Ravichandran proposes a system to provide artificial sight to visually impaired individuals through brain-to-brain visual transmission. The system uses electro-oculogram to record electrical signals from the eye, processes the signals to extract those corresponding to eye activity, and transmits the signals wirelessly to another brain. A transcranial magnetic stimulator induces equivalent electrical currents in the optic nerve of the recipient, allowing them to perceive the transmitted visual information. The proposed system aims to help those blinded due to eye or retinal defects by bypassing the eyes and providing artificial sight directly to the brain.