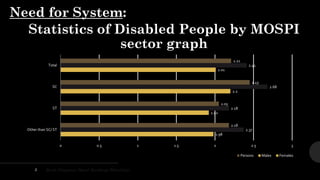
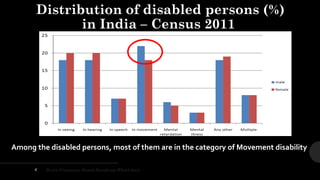
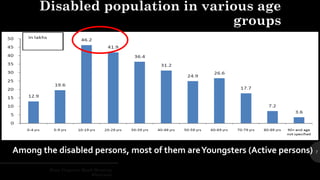
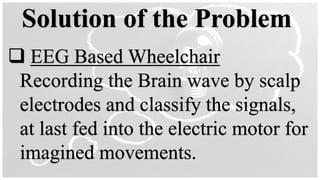
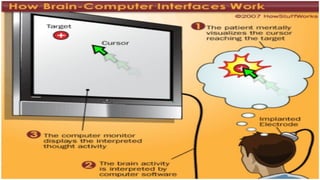
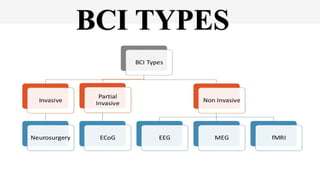
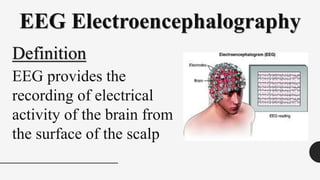
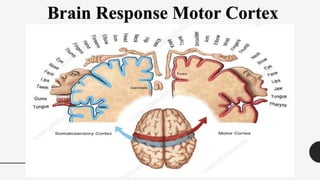
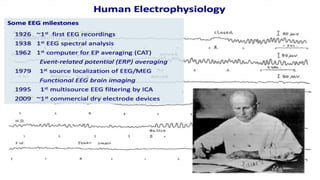
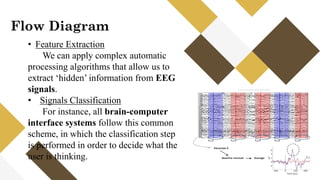
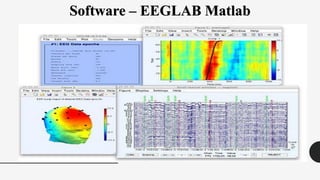
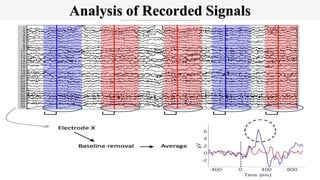
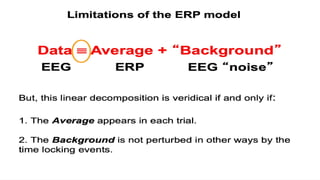
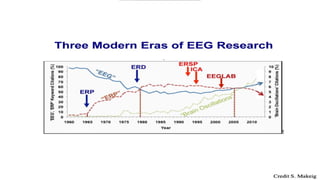
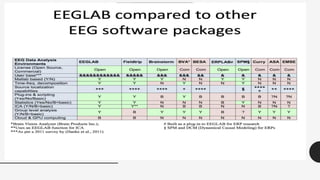
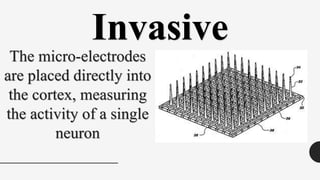
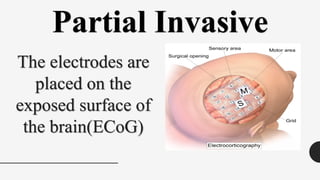
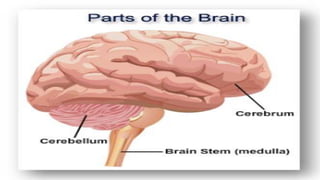
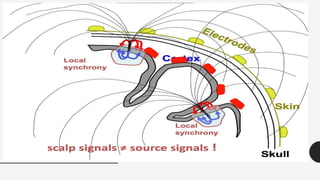
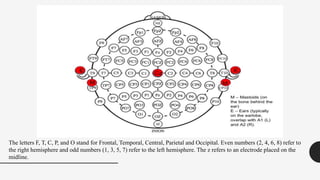
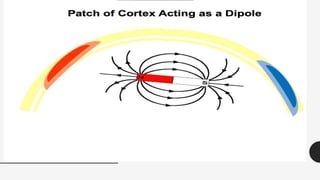
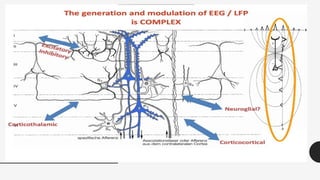
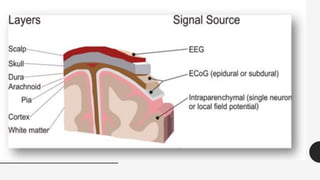
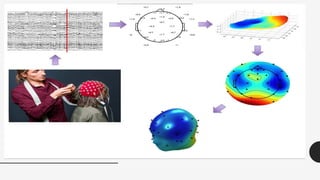
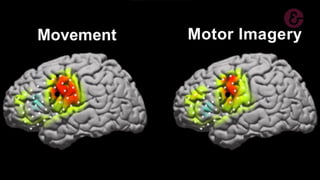
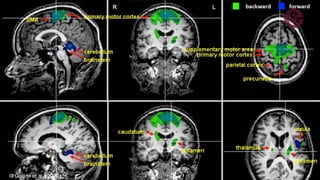
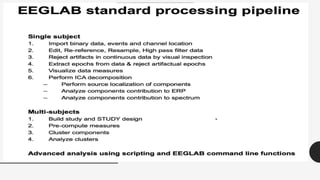
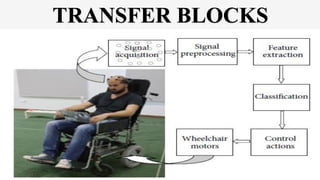
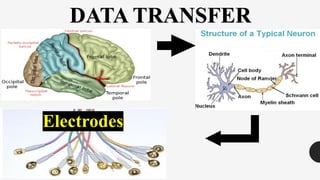
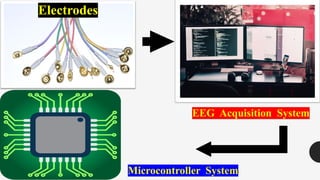
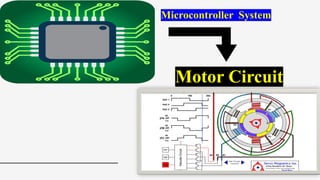
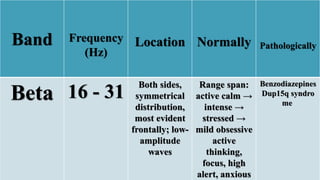
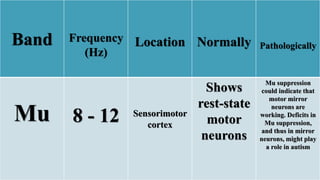
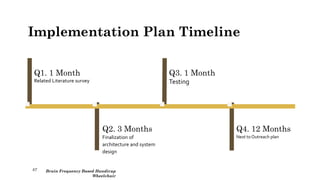
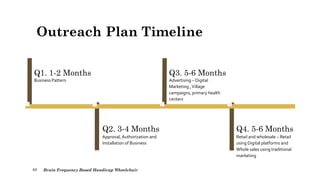
The document outlines a brain frequency-based wheelchair project aimed at assisting disabled individuals who require enhanced mobility solutions. It describes the technology behind the brain-computer interface (BCI) that allows users to control the wheelchair using EEG signals, addressing mobility challenges faced by disabled persons in India and around the world. Additionally, it includes implementation strategies, statistics on disability, and potential collaborations to optimize the device's effectiveness and accessibility.