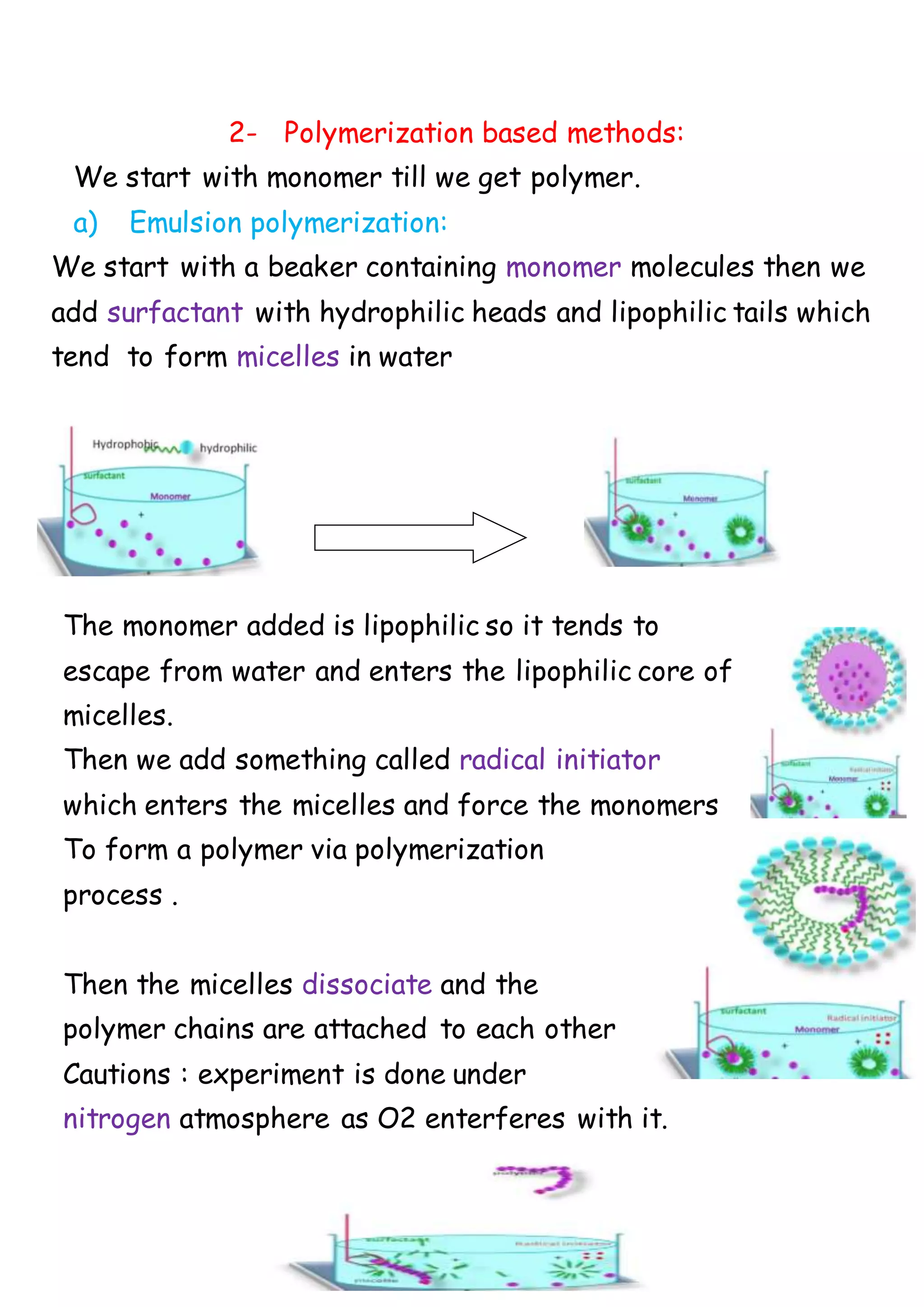
This document discusses methods for preparing polymeric nanoparticles. There are two main types of polymers used: natural hydrophilic polymers like proteins and polysaccharides, and synthetic lipophilic polymers that are either pre-polymerized or polymerized during preparation. The main preparation methods are amphiphilic macromolecule cross-linking using heat or chemical cross-linkers, polymerization-based methods involving emulsion, dispersion, or interfacial condensation polymerization, and polymer precipitation methods using solvent extraction/evaporation, solvent displacement, or salting out. Common techniques include single or double emulsion followed by solvent evaporation to create drug-loaded nanoparticles.