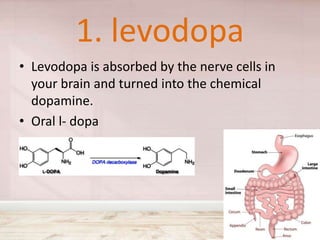
Parkinson's disease is caused by degeneration of nerve cells responsible for dopamine release in the brain. It causes difficulties with facial expressions, muscle stiffness, slowed movements, speech changes, and tremors. Parkinsonism is secondary to medications or head injuries. Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and tests like DaT-SPECT scans and MRIs. Treatment focuses on replacing dopamine through medications like levodopa, dopamine agonists like bromocryptine, and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors like selegiline.