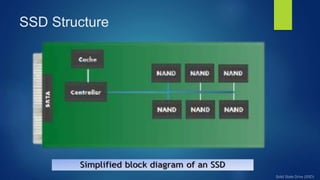
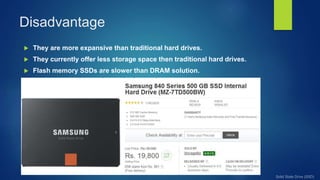
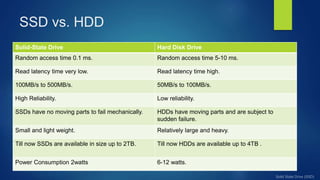
The document discusses solid state drives (SSDs) and how they differ from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs use solid state memory like NAND flash instead of spinning disks, so they have no moving parts. This makes SSDs faster, more durable, quieter, and more energy efficient than HDDs. However, SSDs currently have higher costs and lower storage capacities than HDDs. The document covers the history, components, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and performance comparisons of SSDs versus HDDs.