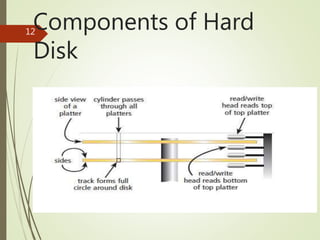
A hard disk is a storage device that uses magnetically coated platters to store data. It contains 1 or more disks with storage capacities ranging from 40GB to over 1TB. Hard disks can be either internal fixed disks inside a computer or portable removable disks that can be transferred. Data is stored using either longitudinal or perpendicular magnetic recording aligned on the disk surface. Key components include platters, read/write heads, and a spindle that rotates the platters to enable reading and writing of data in tracks and sectors. A head crash can occur if the read/write head touches the disk surface, potentially causing data loss.