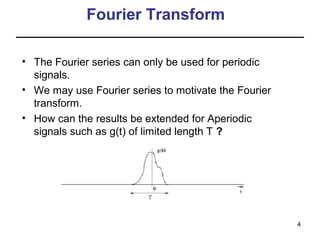
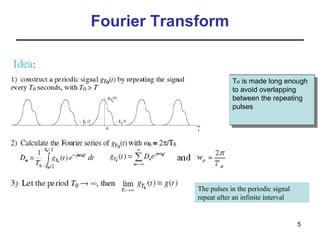
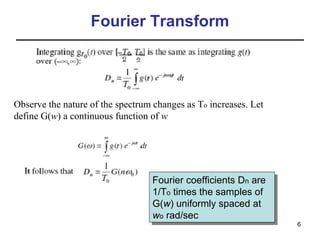
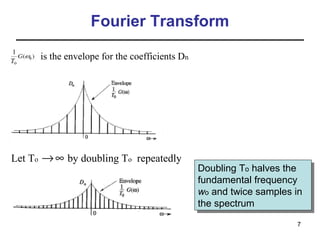
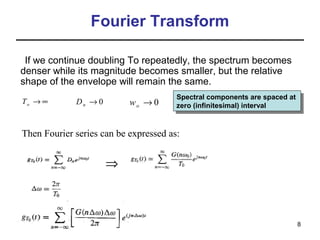
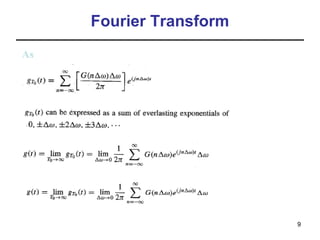
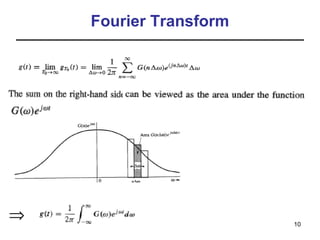
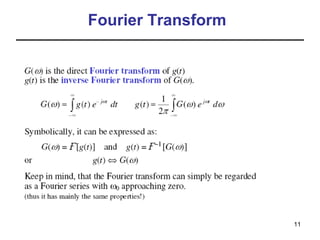
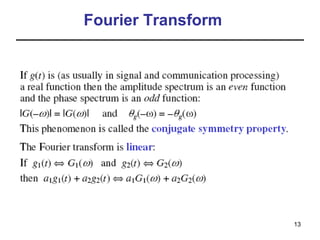
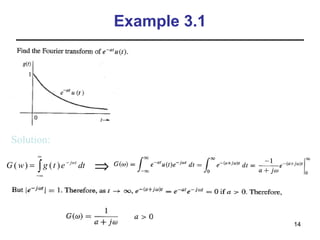
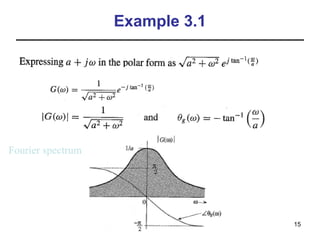
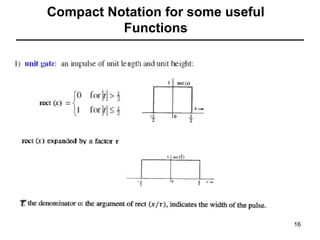
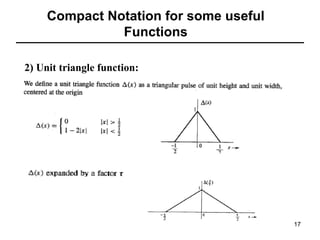
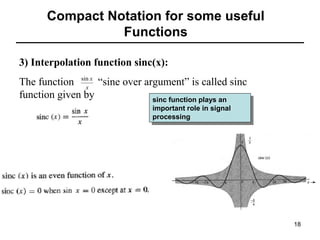
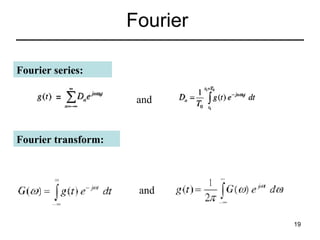
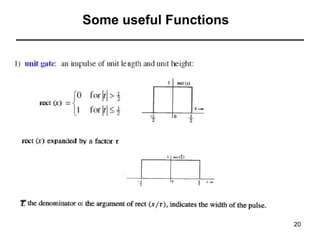
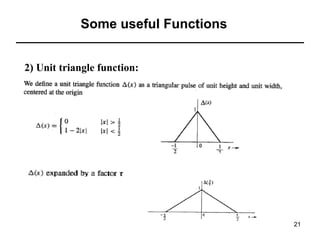
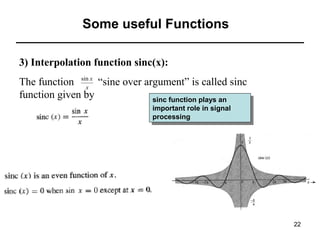
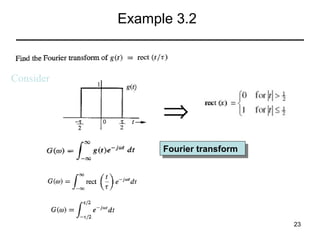
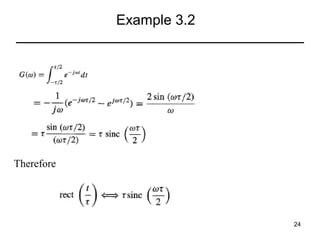
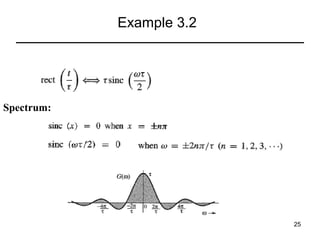
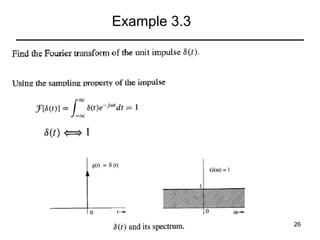
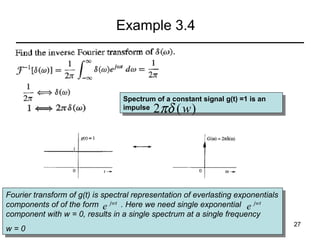
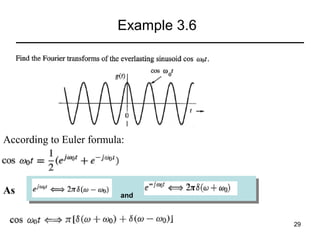
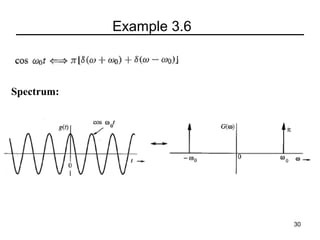
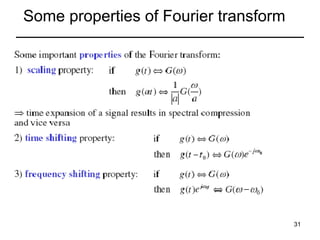
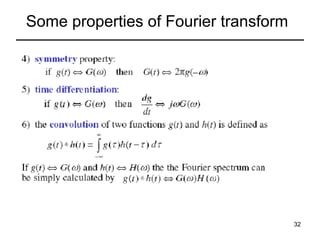
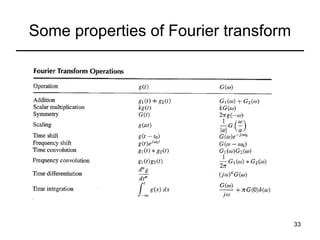
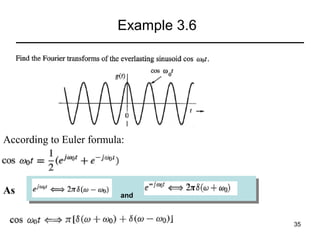
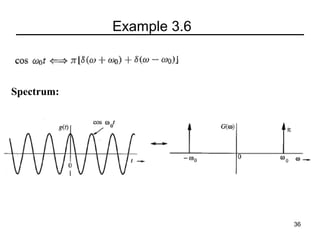
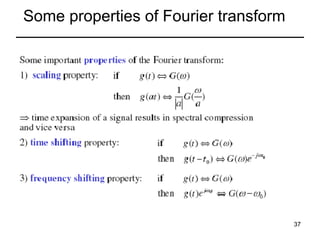
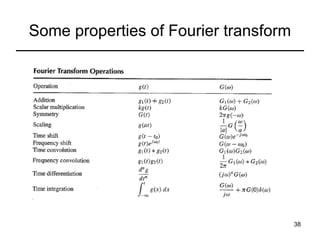
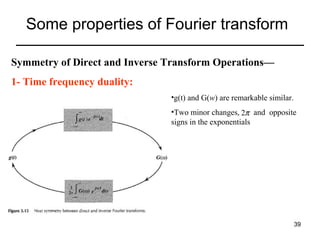
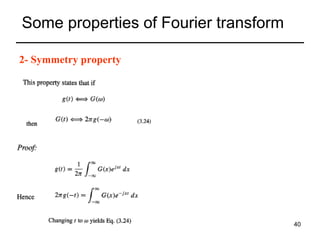
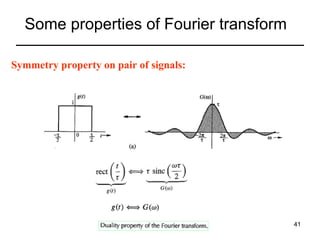
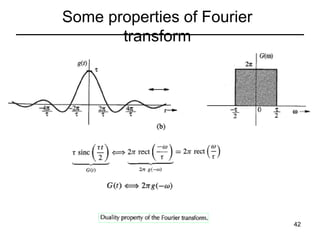
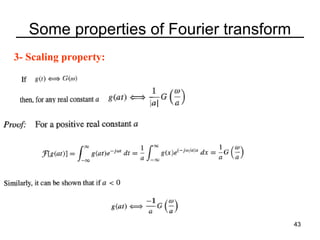
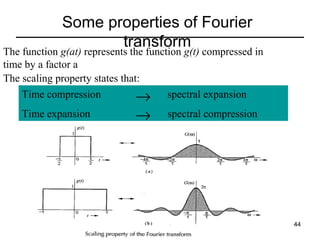
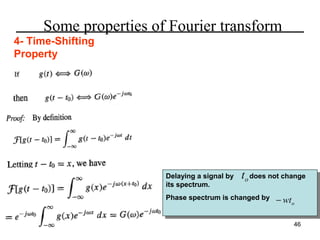
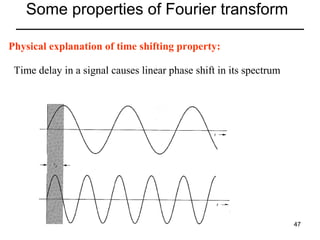
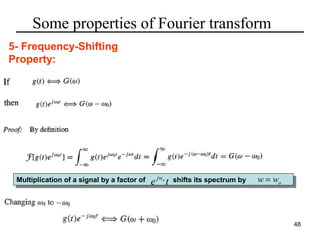
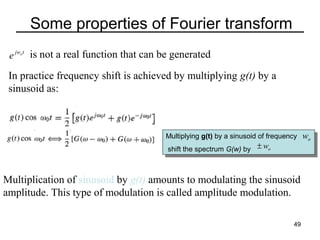
This document contains a summary of key concepts from a chapter on Fourier transforms and their properties. It begins with an overview of the motivation for Fourier transforms as an extension of Fourier series to allow representation of aperiodic signals. It then provides examples of Fourier transforms for common functions like a rectangular pulse and exponential. The remainder summarizes important properties of Fourier transforms including: time-frequency duality, symmetry of direct and inverse transforms, scaling which relates time/bandwidth compression, time-shifting which causes phase change, and frequency-shifting which translates the spectrum.