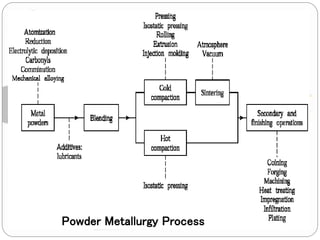
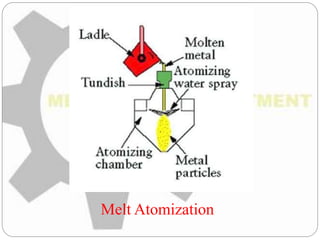
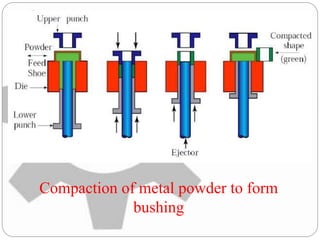
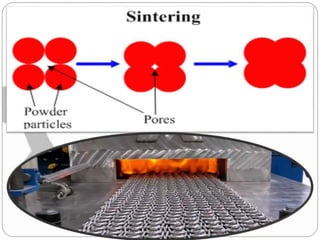
This document discusses the process of powder metallurgy. It begins by introducing powder metallurgy and some of its advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. The main steps of the powder metallurgy process are then outlined, including powder manufacture through various techniques like atomization, blending to ensure uniformity, compacting the powder under pressure, sintering the compacted powder by heating it below the melting point, and final finishing operations. A variety of end products that can be created using powder metallurgy are listed such as bearings, gears, and regulators.