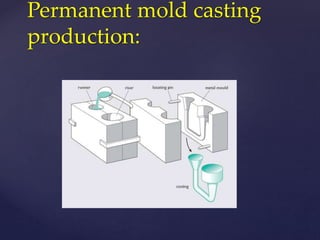
The document discusses gravity die casting or permanent mold casting, which uses permanent molds made of materials like cast iron or steel to pour molten metal into without external pressure. It describes the design of permanent molds including parting lines, risers, and cores. The summary also lists some applications of permanent mold casting such as carburetor bodies, brake cylinders, and aircraft/missile castings.