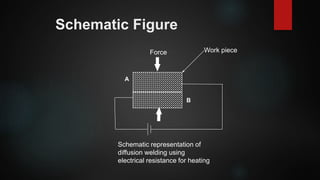
The document is a presentation on diffusion welding, detailing its definition as a solid-state welding process, schematic representation, and working principles involving deformation, grain boundary migration, and volume diffusion. It discusses specific applications in titanium and nickel welding, advantages like minimal deformation, and limitations such as costly equipment and preparation. Overall, diffusion welding allows for joining dissimilar materials while maintaining similar properties to base metals.