Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times




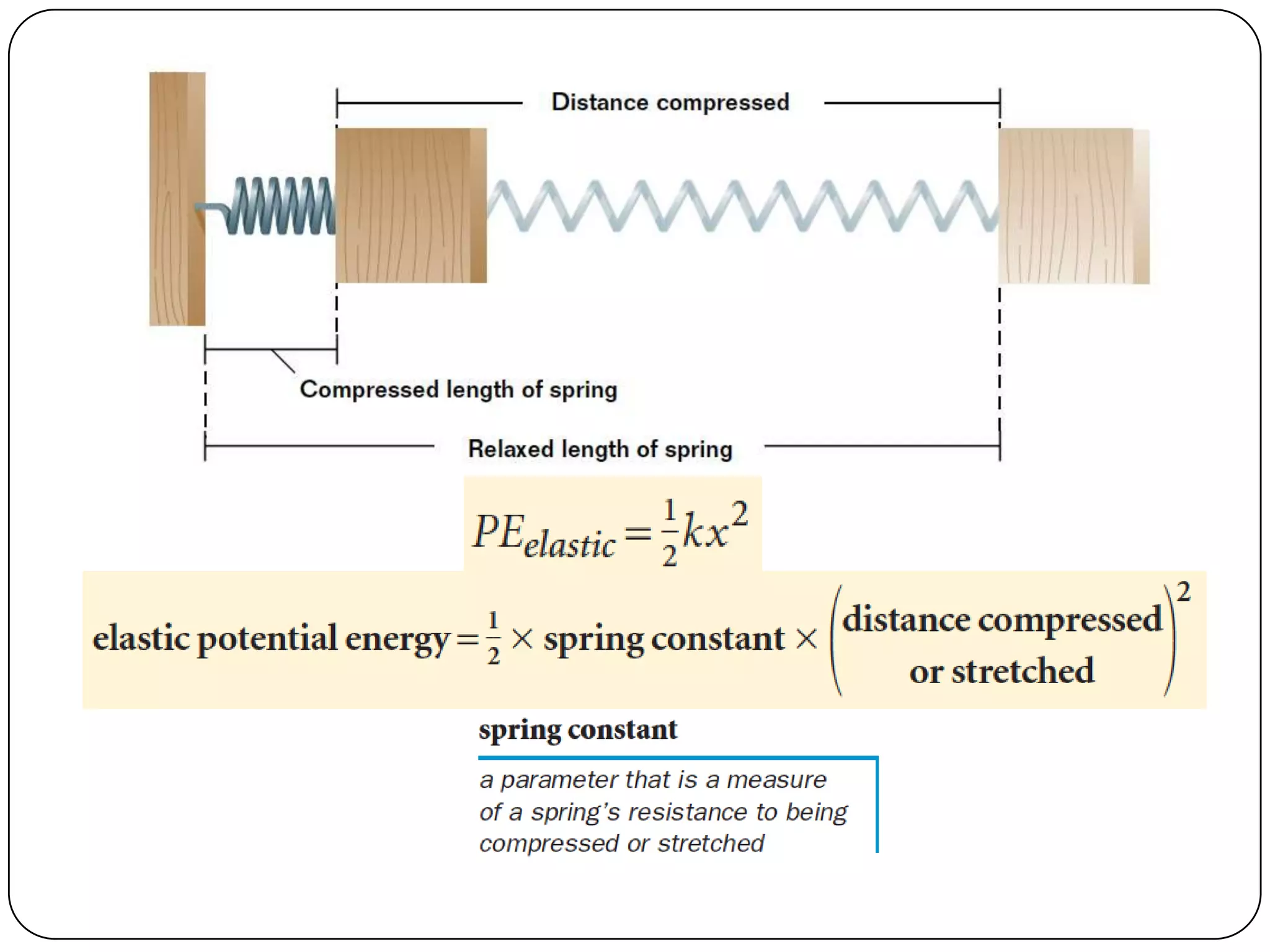


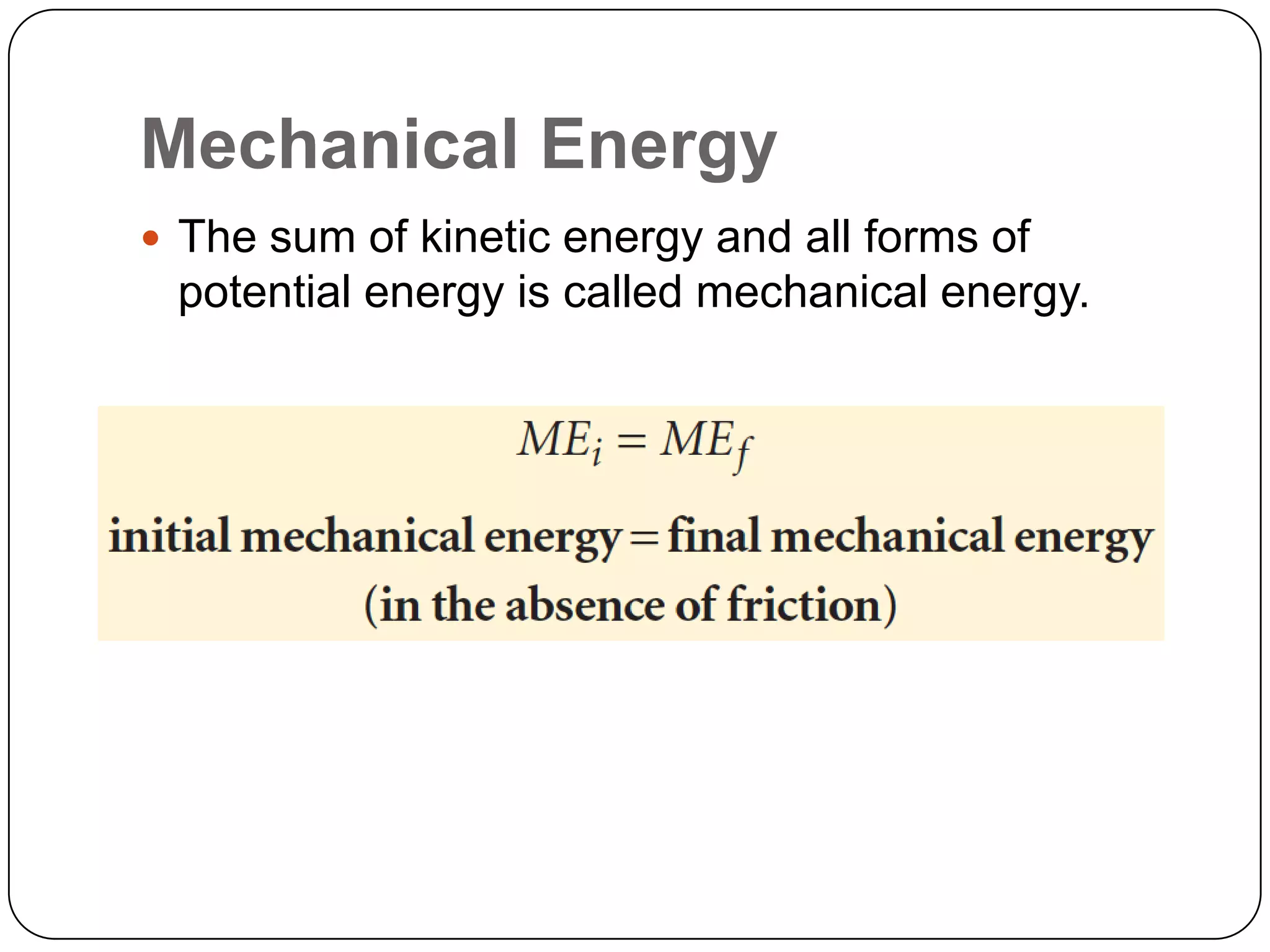


Potential energy is stored energy that depends on an object's position or state of deformation. There are different types of potential energy including gravitational potential energy due to height above a gravitational body, and elastic potential energy stored in deformed springs and elastic objects. An example problem calculates the elastic potential energy stored in a spring attached to a hanging mass that has stretched the spring from its relaxed length. The work-energy theorem states that changes in kinetic and potential energy are related, and mechanical energy is the total of an object's kinetic and potential energies. An example shows using this to calculate the speed of a child sliding from rest down a frictionless slide given her initial height and mass.









