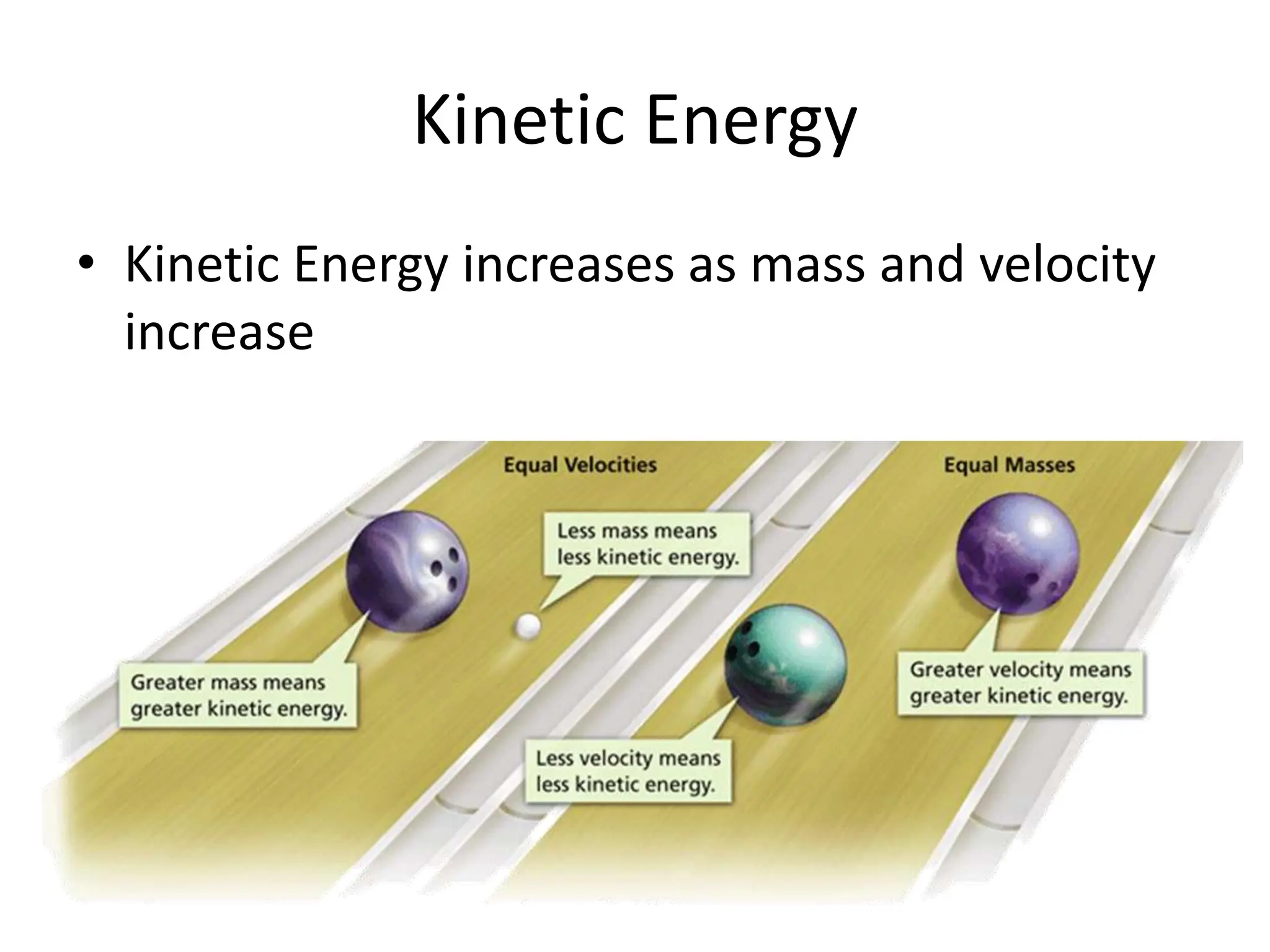
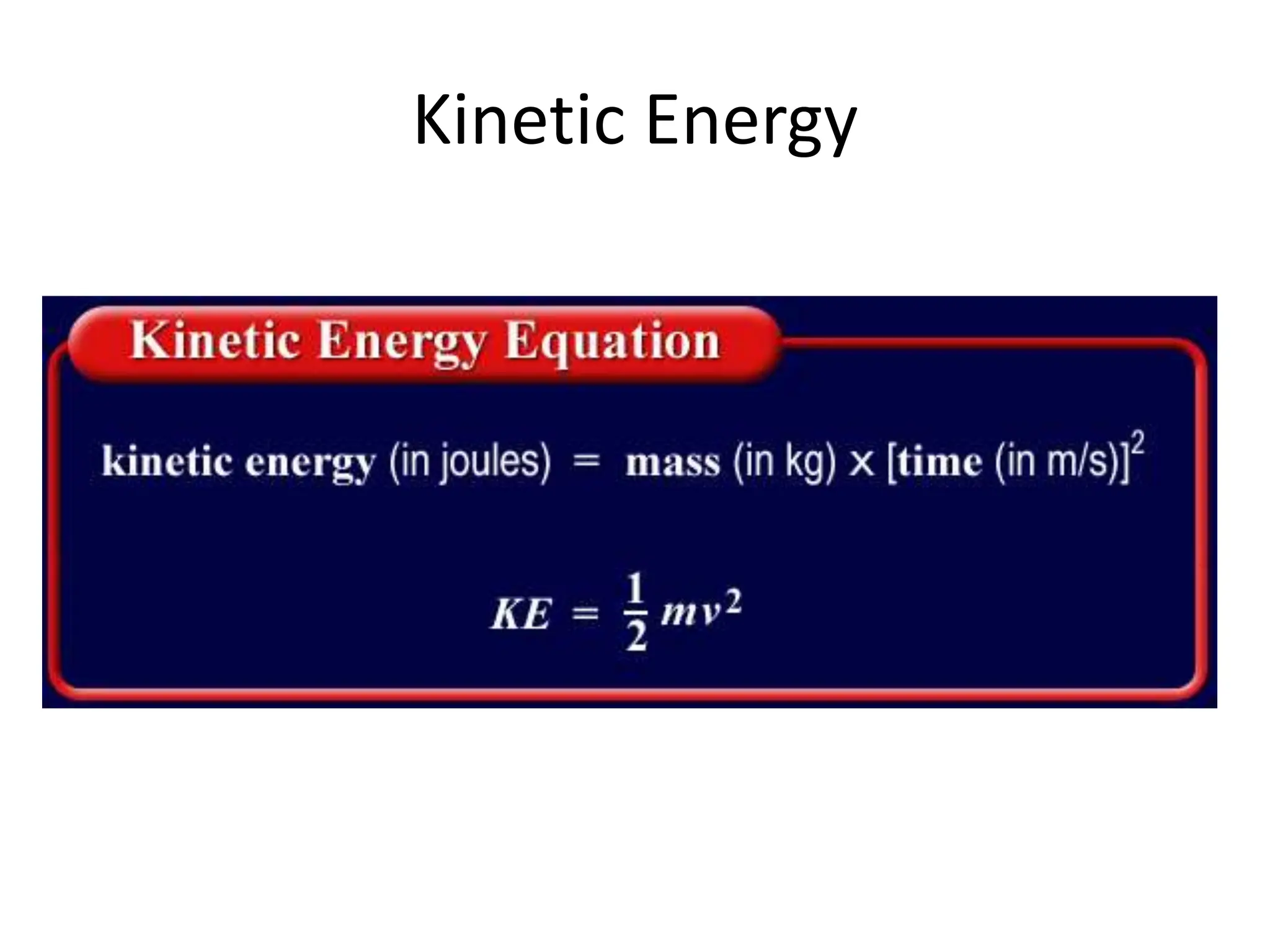
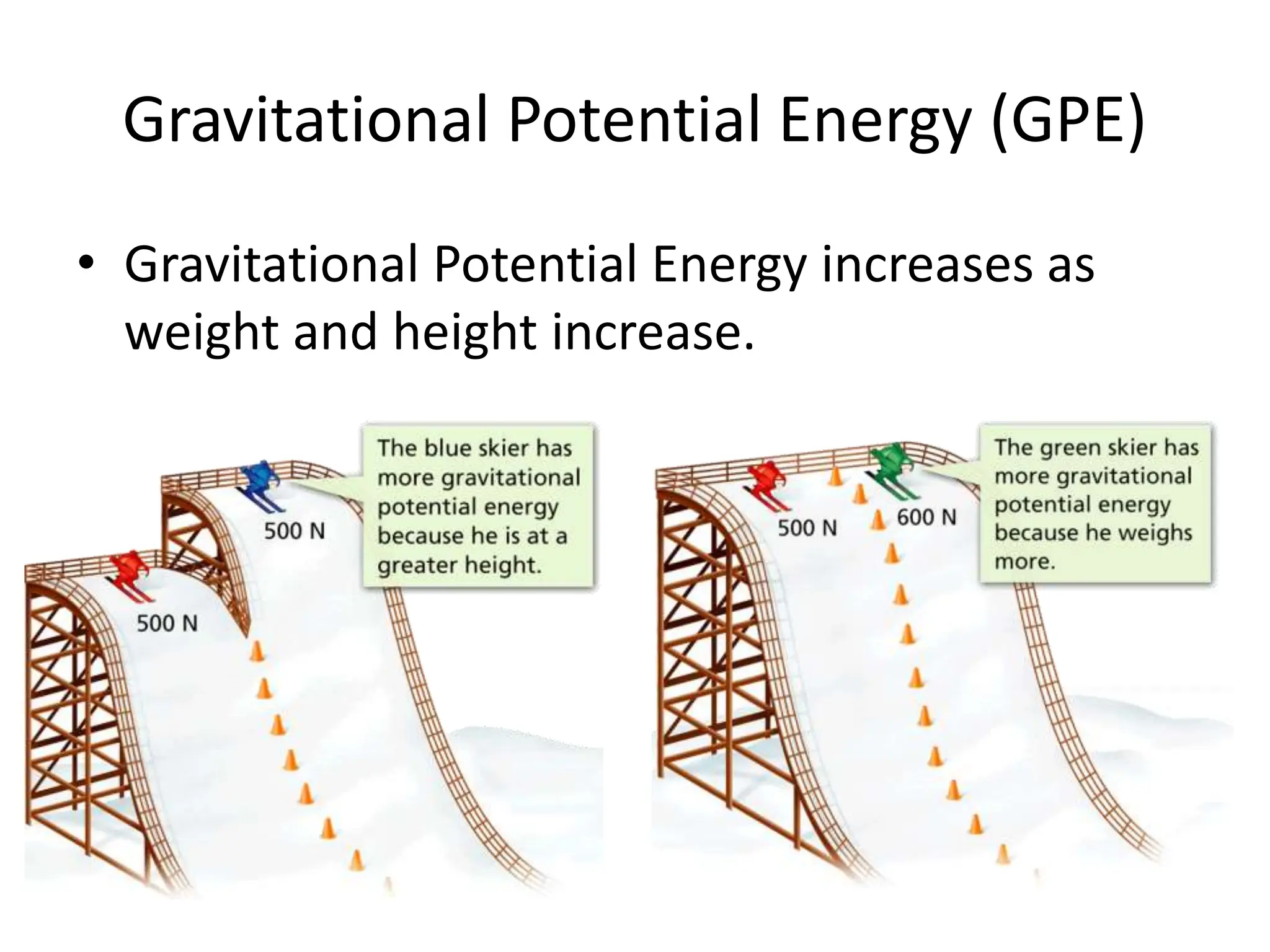
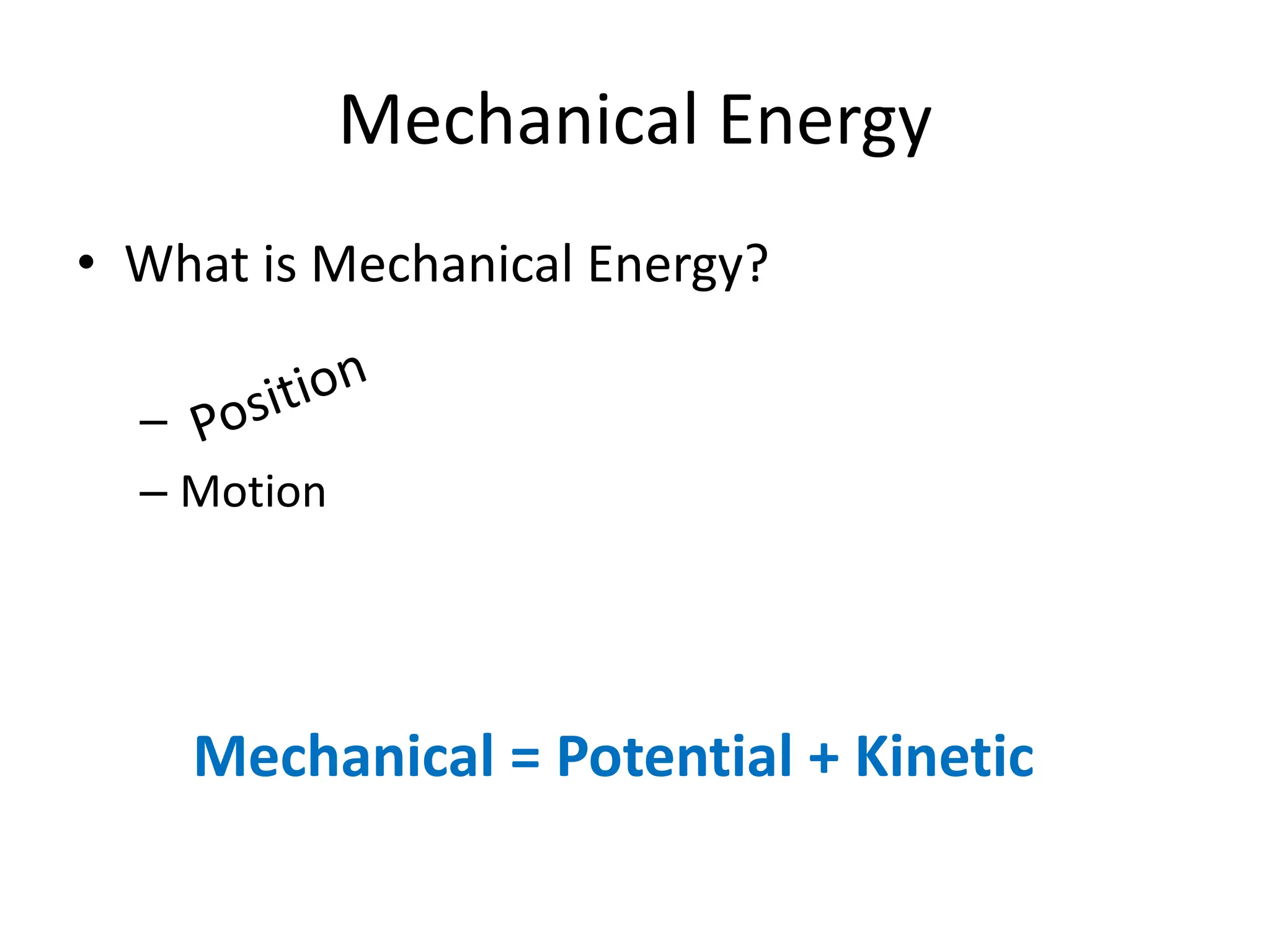
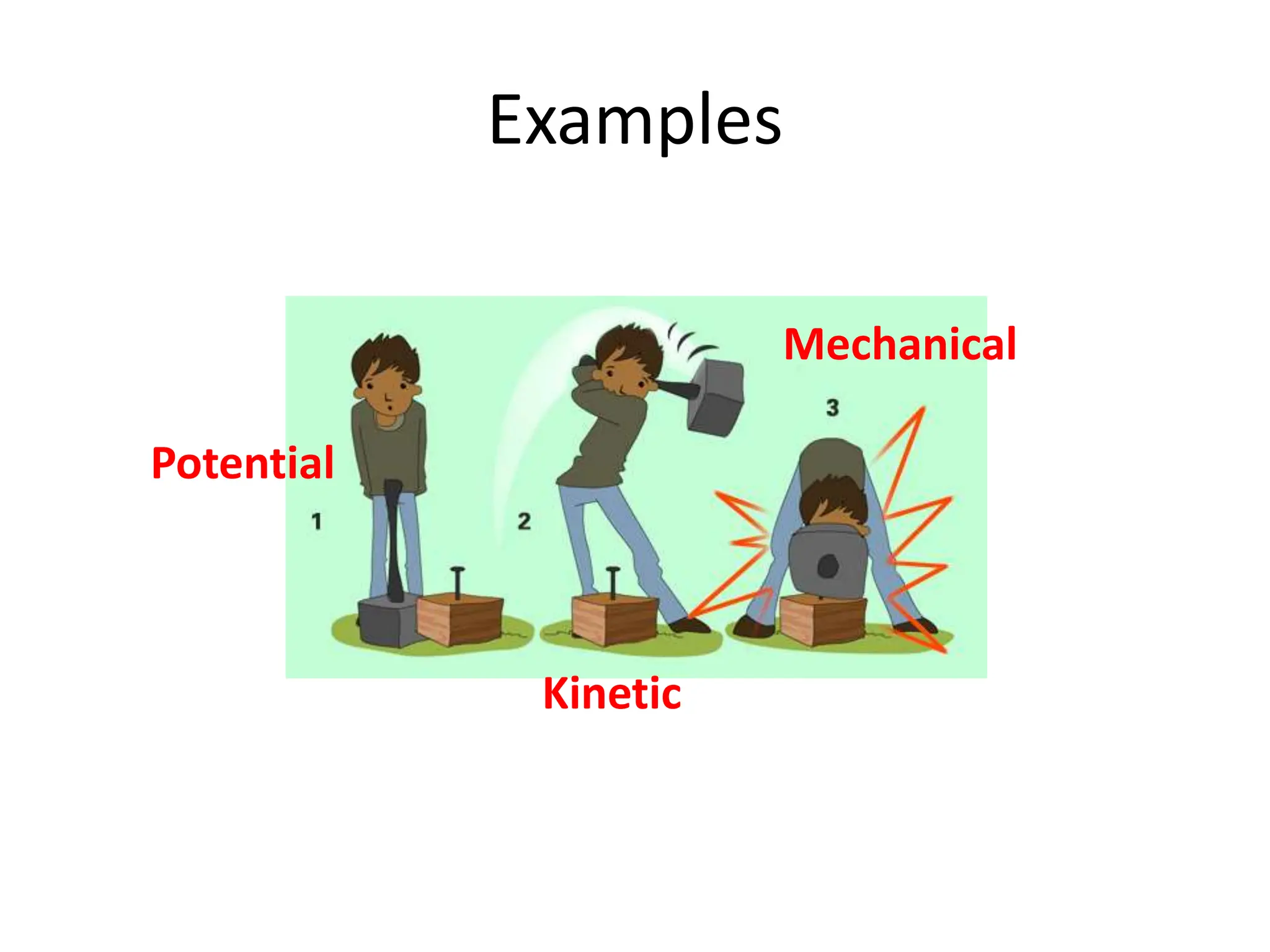
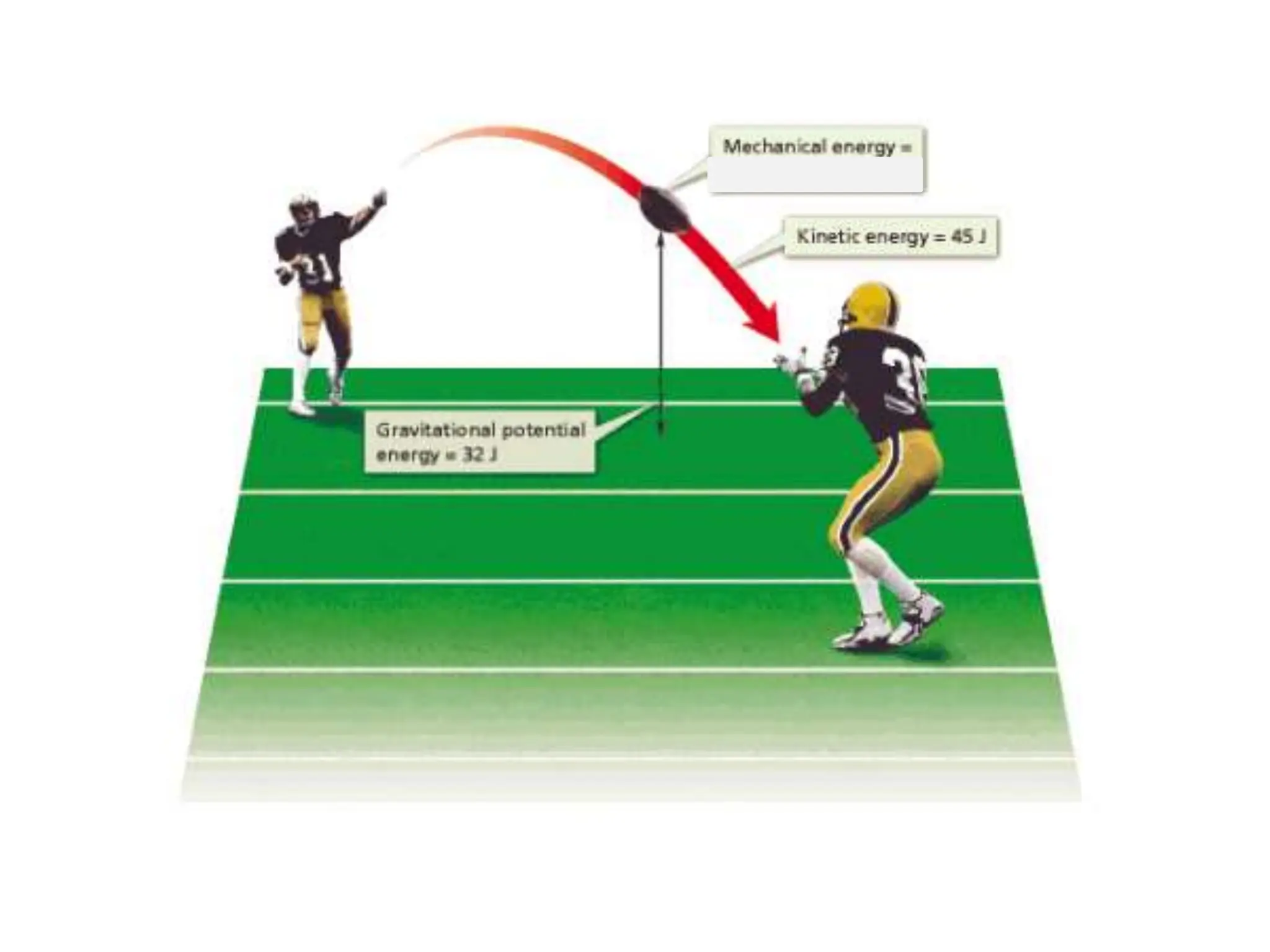
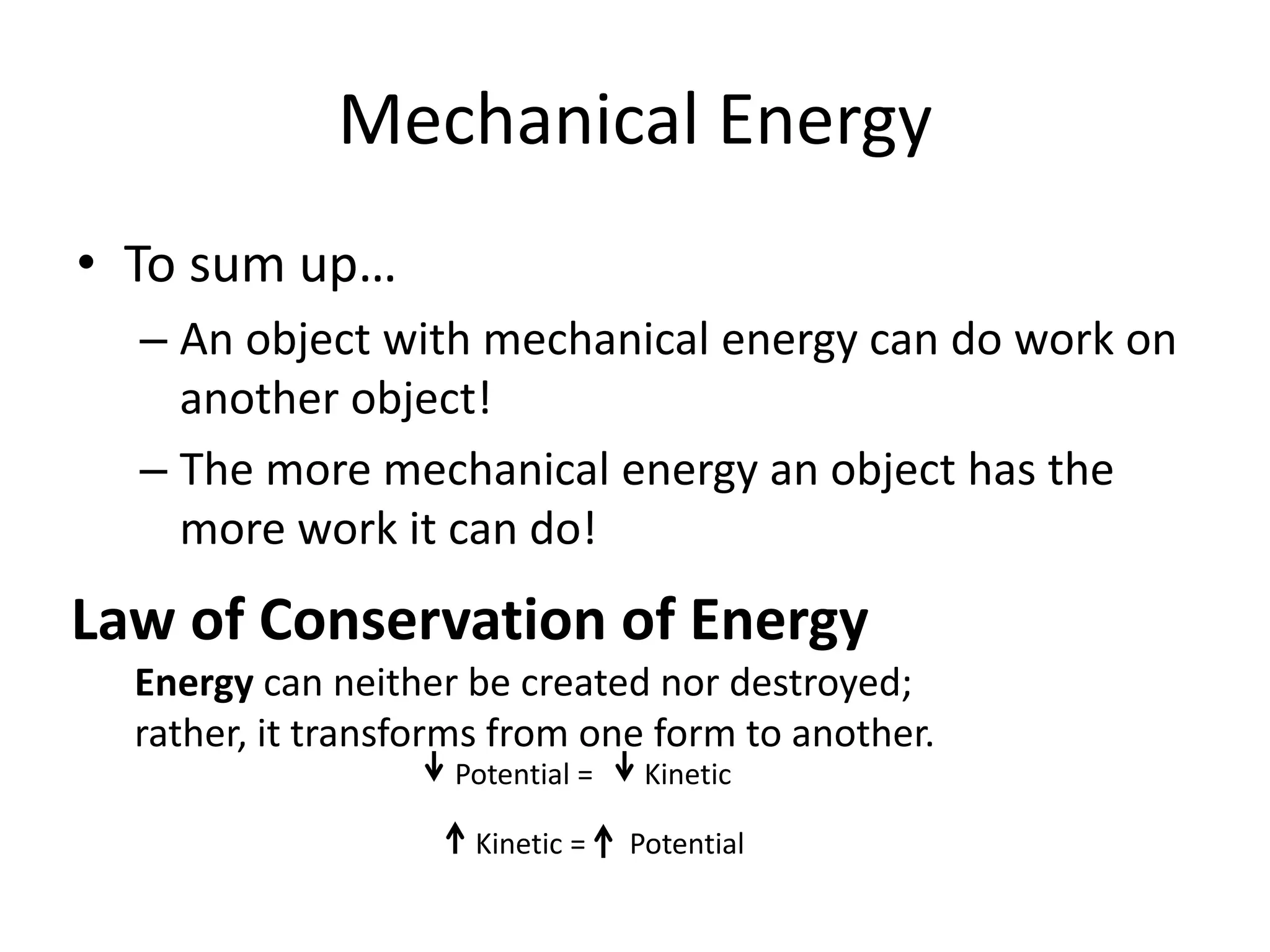
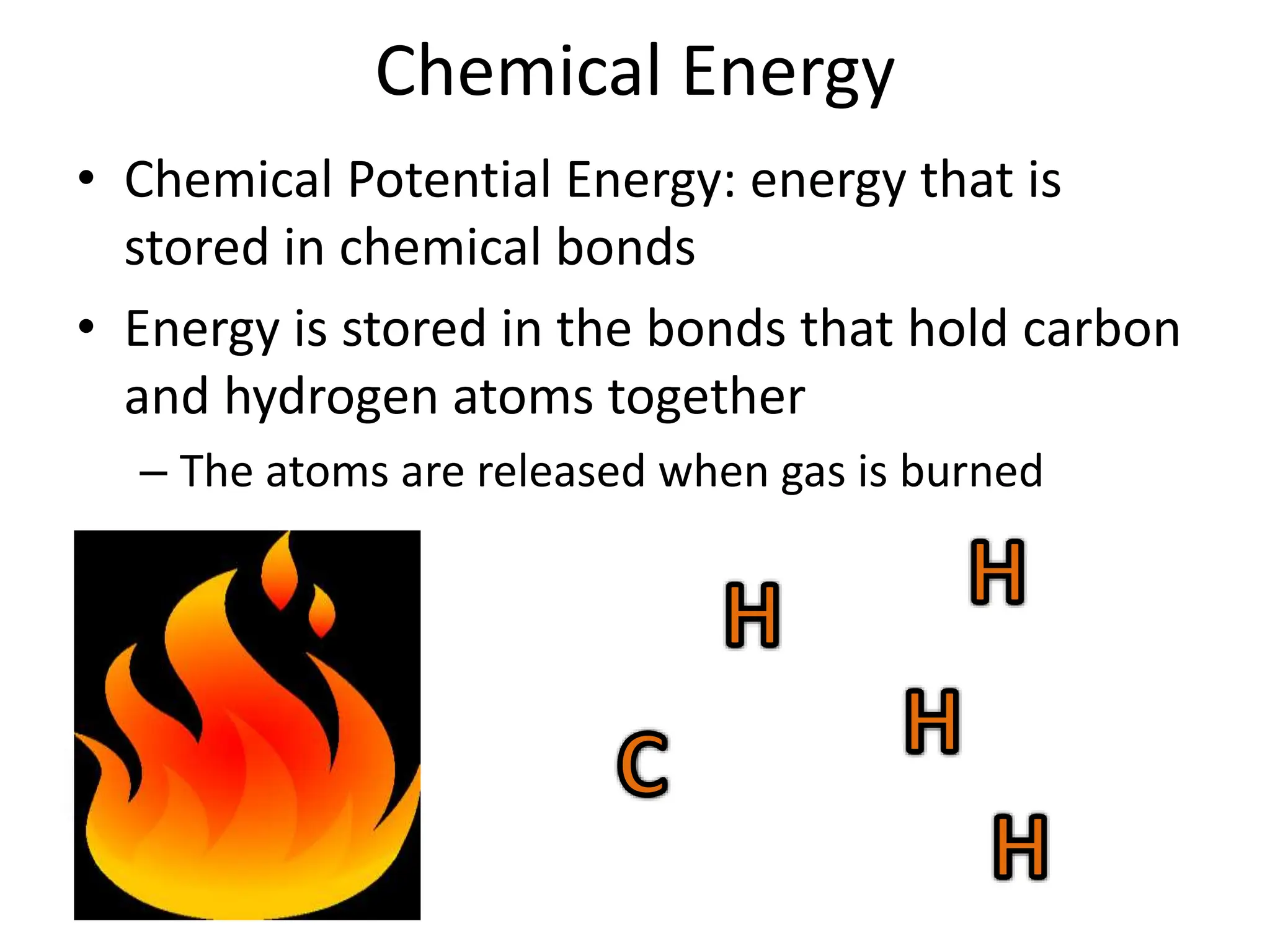
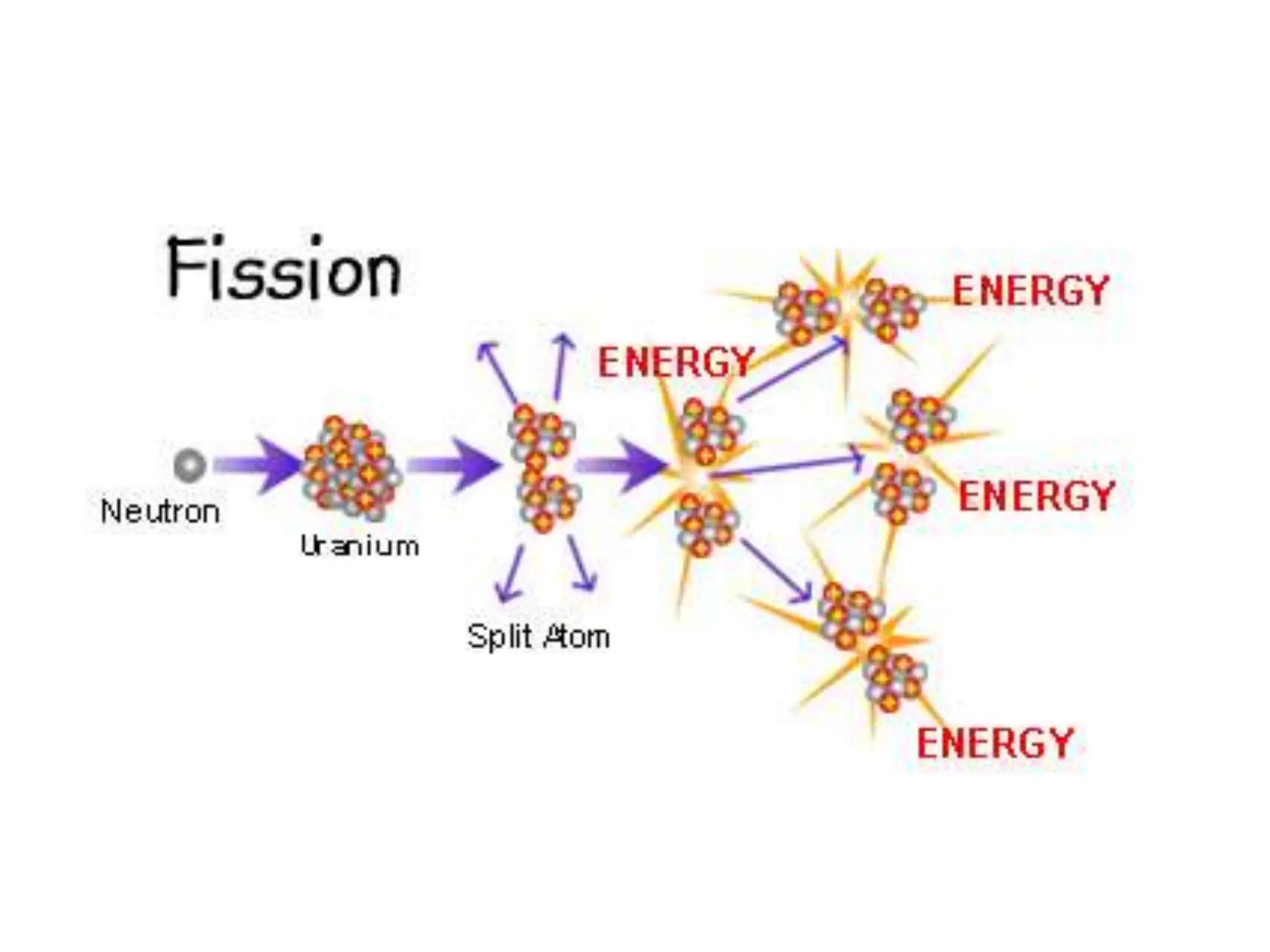
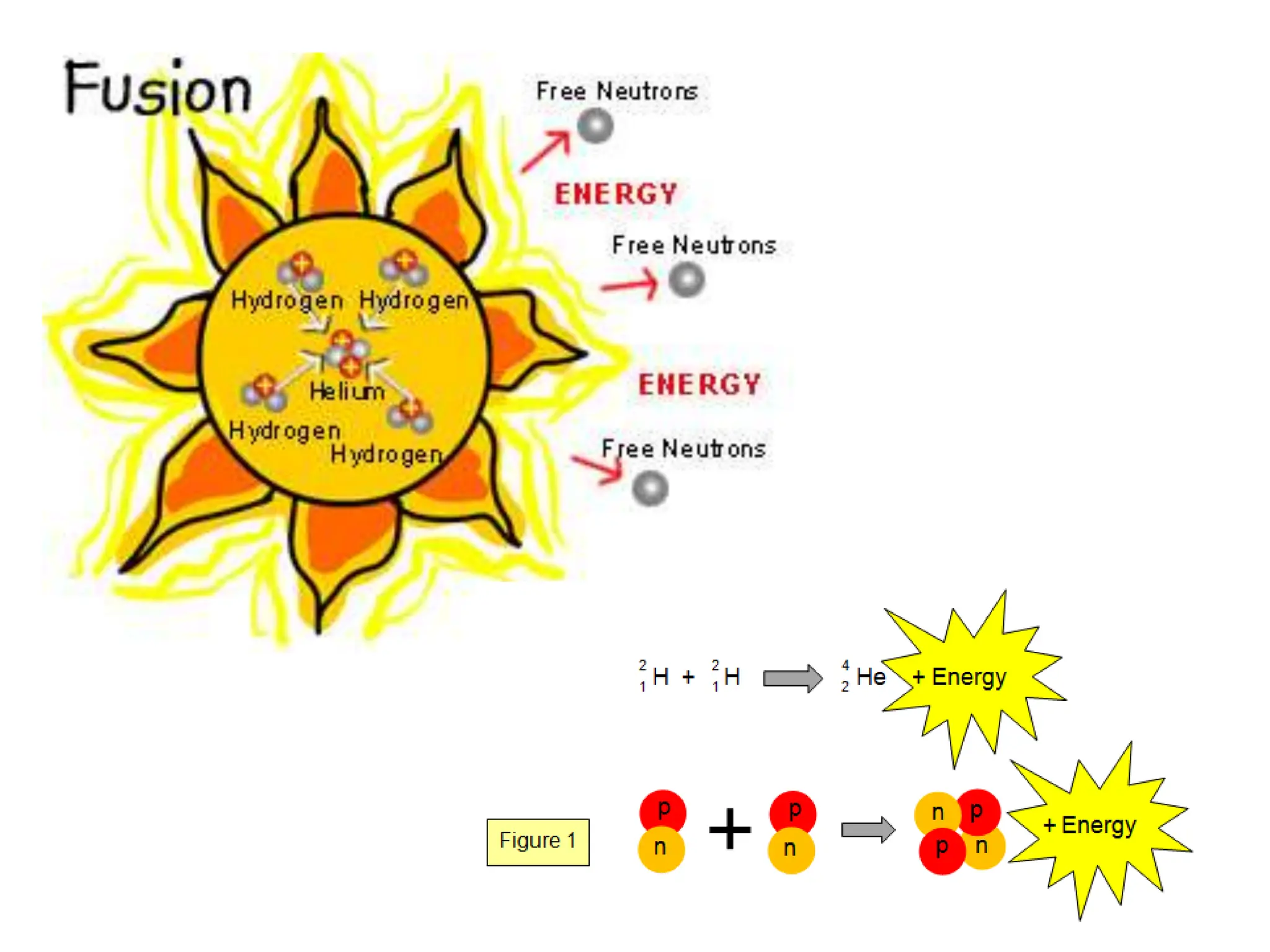
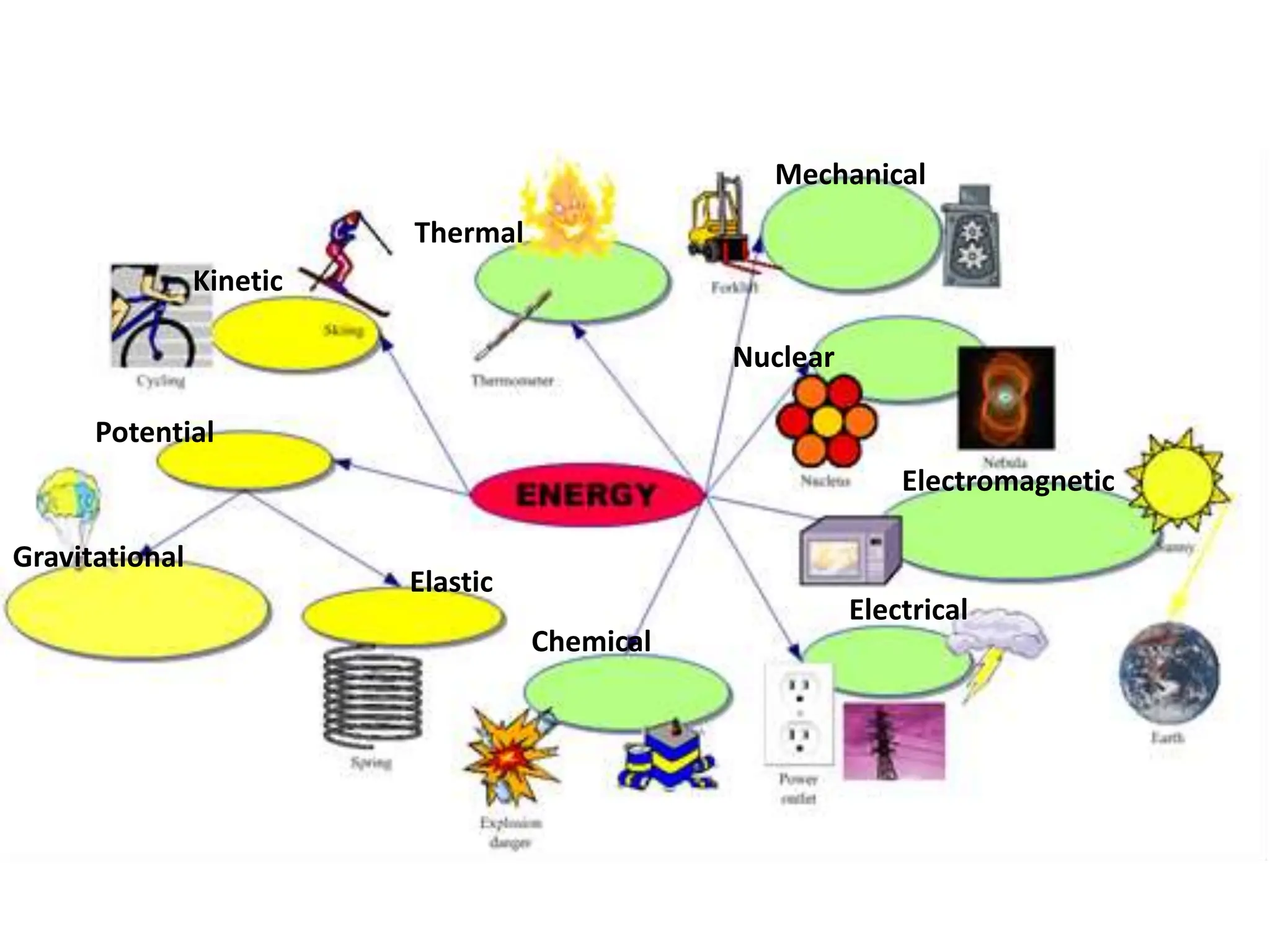
The document provides an overview of work, power, and energy, detailing their definitions and relationships, including types of energy such as kinetic, potential, mechanical, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and electromagnetic. It explains how energy can be defined, measured, and transformed, emphasizing concepts like gravitational and elastic potential energy, as well as the law of conservation of energy. The document illustrates these concepts through examples and calculations related to energy types and their applications.