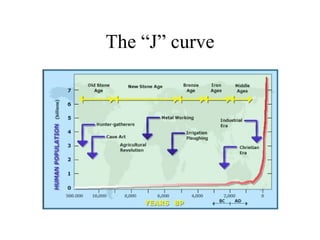
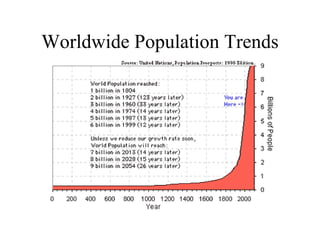
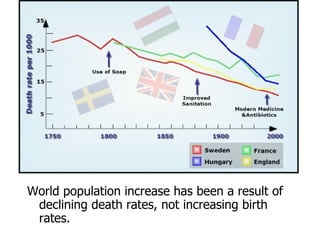
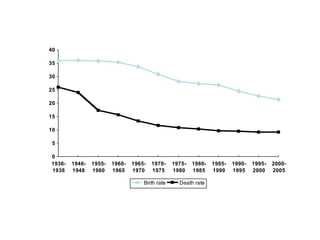
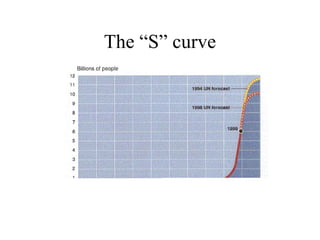
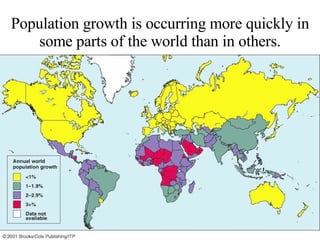
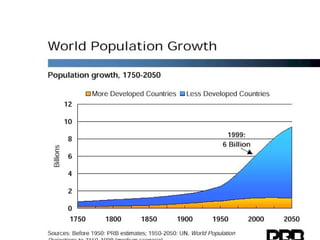
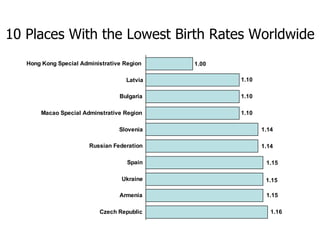
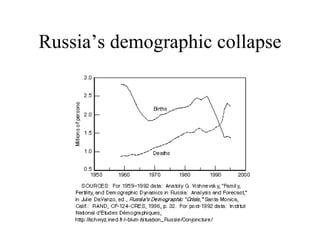
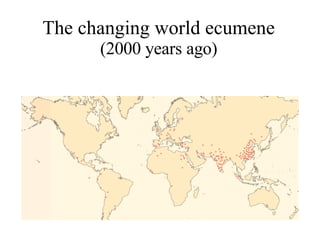
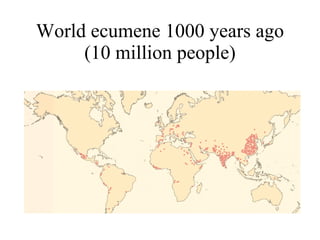
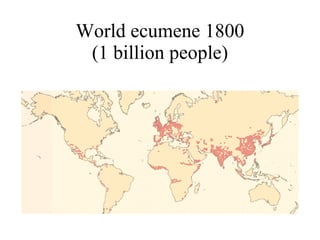
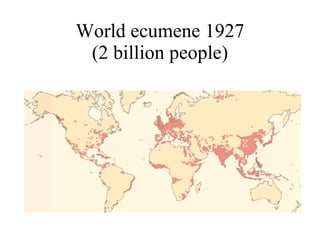
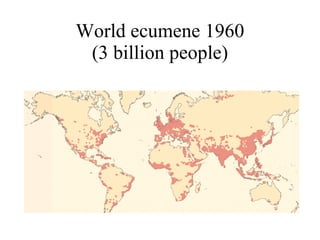
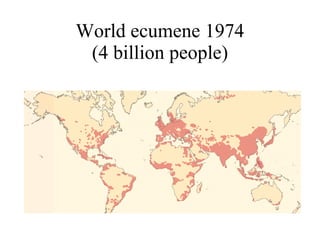
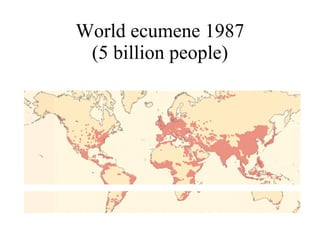
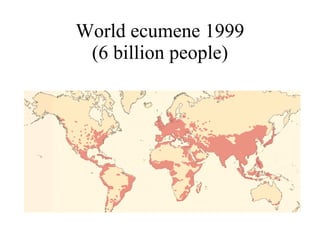
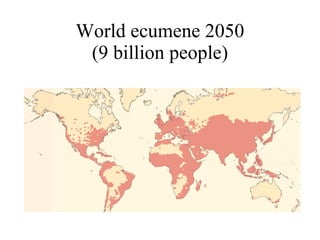
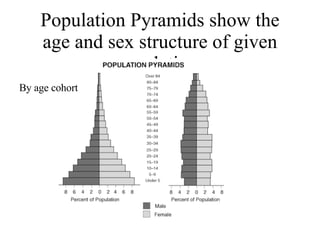
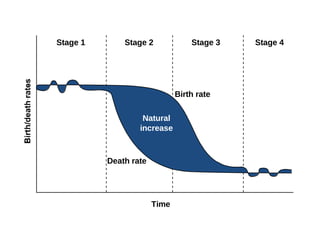
The document summarizes key topics relating to world population trends including the "J" and "S" curves of population growth. It discusses doubling times of populations around the world and factors influencing fertility rates such as economic development, social norms, and government policies. Examples of population growth patterns over time and debates around population issues are also outlined.