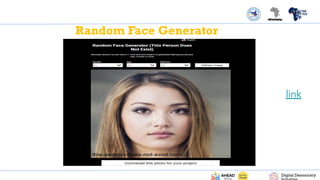
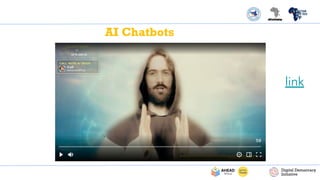
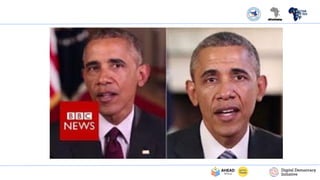
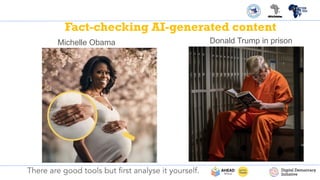
The PDF titled "Identifying AI Generated Misinformation & Deepfakes" focuses on understanding artificial intelligence (AI) and its implications in the realm of misinformation and deepfakes. It introduces concepts of AI, including machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI, while emphasizing the roles these technologies play in content creation and the dissemination of mis/disinformation. The document aims to educate readers on identifying fake versus real content, recognizing the risks associated with AI-generated misinformation, and verifying digital content through various fact-checking methods.