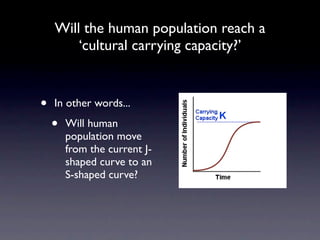
The document discusses human population dynamics and provides the following key points:
- The current global population is approximately 6.6 billion and is projected to grow to 9.2 billion by 2050, with much of this growth occurring in India and China.
- There are differing positions on population issues, ranging from concerns about overpopulation and environmental degradation to beliefs that human ingenuity can overcome resource constraints.
- Factors influencing population growth include birth rates, death rates, resource availability, education, urbanization, and government policies. Many countries are now experiencing aging populations with low birth rates.