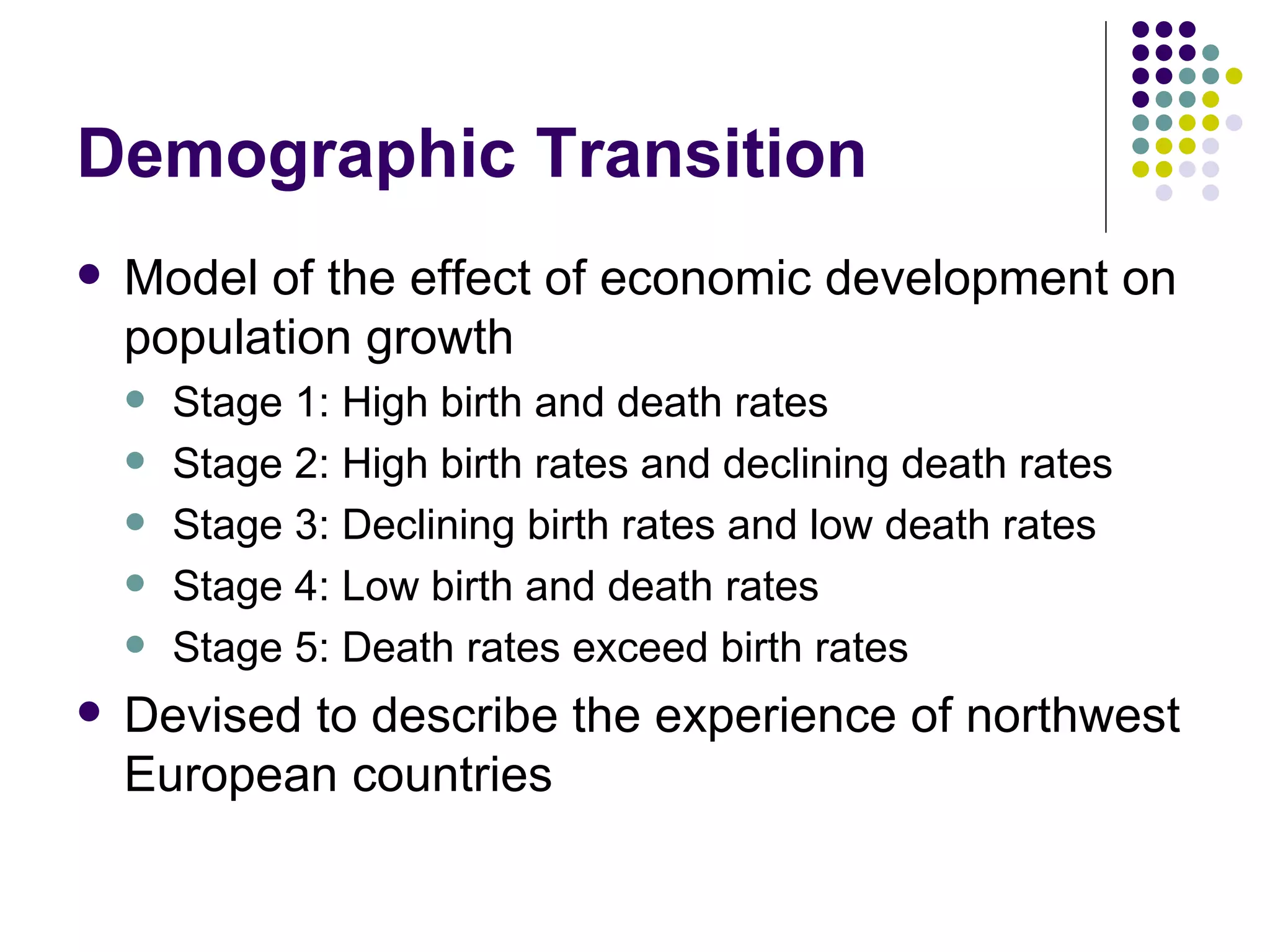
The document discusses key concepts related to population geography and demography. It covers topics like population growth rates, definitions of rates like birth and death rates, models of demographic transition, and population distributions and projections. It also discusses concepts like overpopulation, urbanization, and approaches to population control.