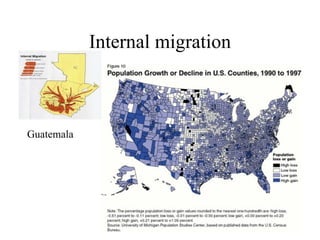
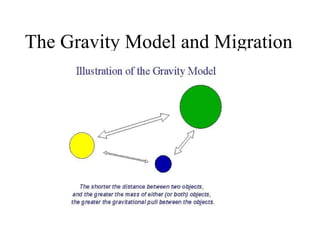
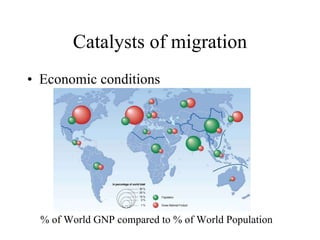
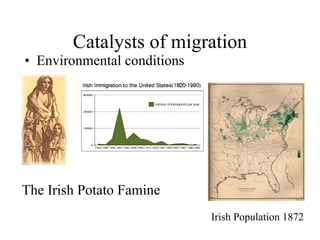
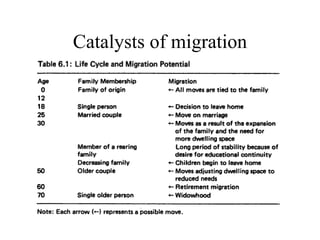
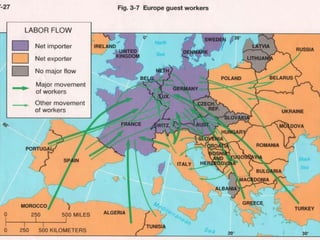
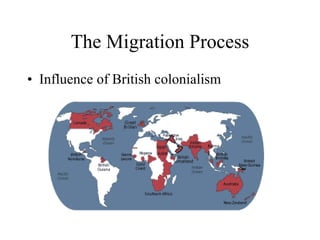
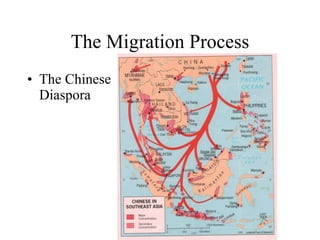
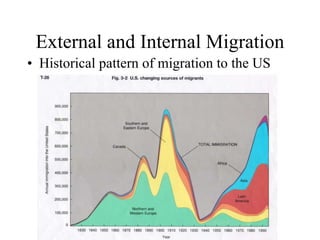
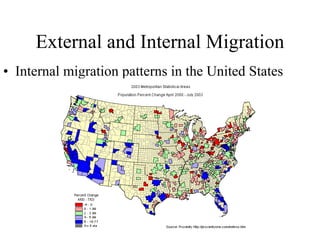
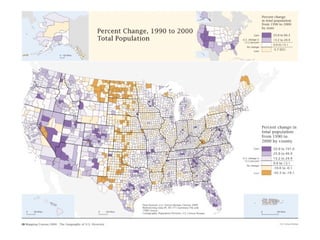
This document discusses various types and causes of human migration. It outlines Ravenstein's laws of migration from the 1870s, which found that most migrants travel short distances, migration is usually rural-to-urban, and each flow creates a counter-flow. The document also explores push and pull factors that influence migration decisions, such as economic conditions, political circumstances, armed conflicts, environmental issues, culture, technology, and information flows. Migration can be voluntary or forced, and includes temporary, seasonal, and return/counter flows.