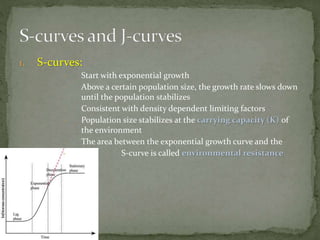
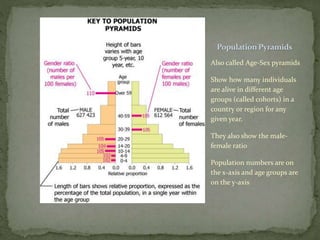
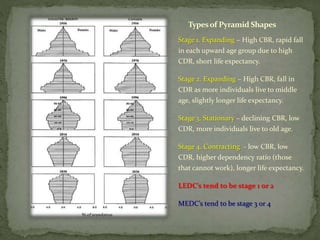
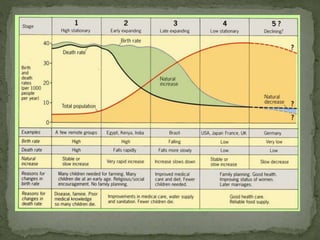
The document discusses factors that influence population growth, including density dependent and density independent factors. Density dependent factors, like limited resources, act as feedback mechanisms to regulate population size. Their effects increase with population size. Density independent factors, like weather, do not depend on population density. These two types of factors lead to different population growth patterns, including S-curves where growth slows and stabilizes, and J-curves with boom and bust cycles. The human population growth rate has declined as we approach the carrying capacity of Earth.