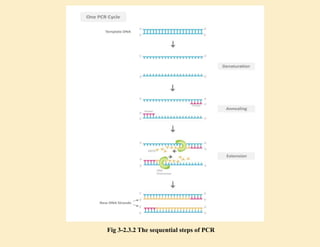
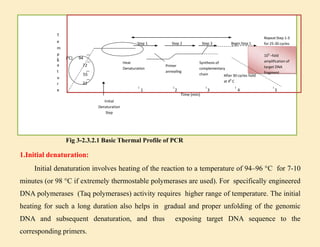
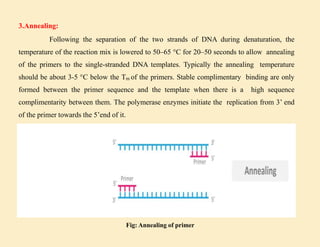
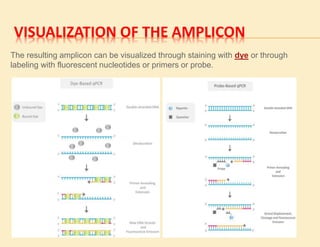
1. In 1971, scientists reported a process to copy DNA using primers, templates, and DNA polymerase. However, the polymerases could not withstand high temperatures. 2. In 1976, a heat-stable DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus was discovered that could function at high temperatures up to 95°C. 3. In 1985, Kary Mullis invented the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique using this thermostable Taq polymerase, for which he later won the Nobel Prize. PCR allows for exponential amplification of specific DNA regions.